Presentation
Acute knee pain with effusion.
Patient Data

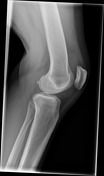
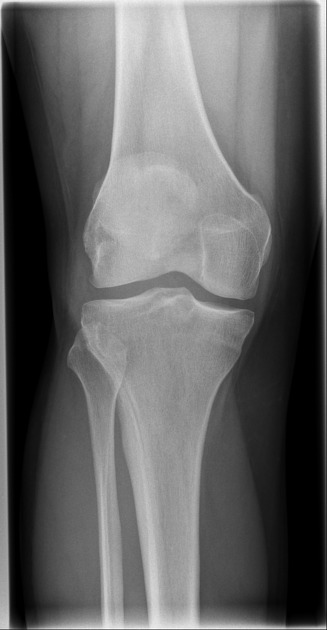
Moderate suprapatellar effusion but no acute fracture or malalignment is identified.
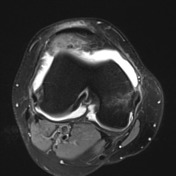

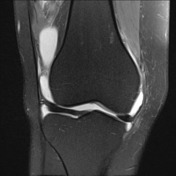

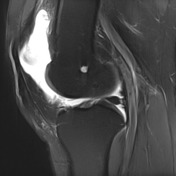

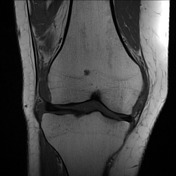

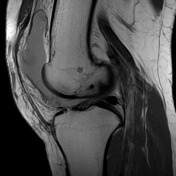

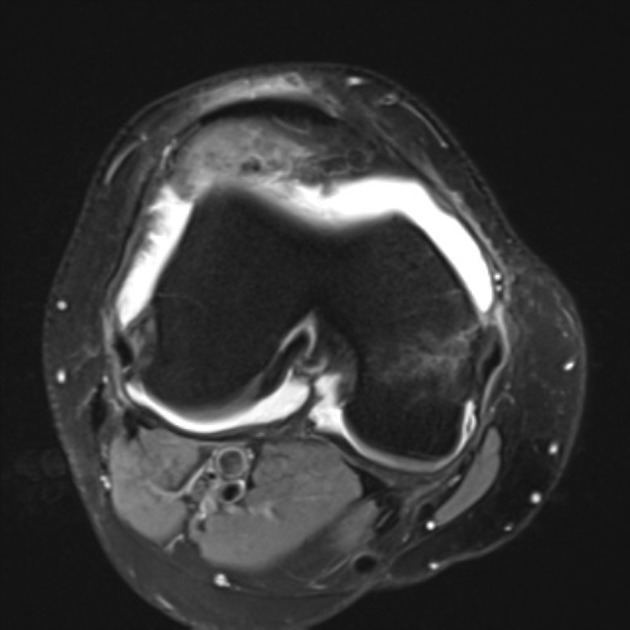
Large joint effusion with evidence of chronic synovitis.
Heterogeneous mass within the anterolateral aspect of the knee joint.
No Baker's cyst. Menisci are intact. No parameniscal cyst. Cruciate and collateral ligaments are intact. Posterolateral corner structures are normal.
Lateral patellar subluxation. Marked hyperintensity of the superolateral aspect of Hoffa's fat pad. Partial and full thickness medial and lateral patellar facet chondral fissuring with subchondral edema.

Pathology report.
Case Discussion
In retrospect, there was an opacity on the lateral knee x-ray overlying Hoffa's fat pad. Non-traumatic causes of acute knee pain are uncommon but should always be kept in the back of one's mind. Pigmented nodular synovitis (PVNS) is now termed tenosynovial giant cell tumor - this is a localized intra-articular subtype.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.