Presentation
Incidental finding on previous imaging. Follow-up.
Patient Data


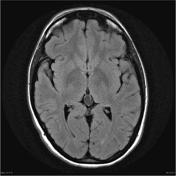

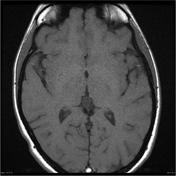

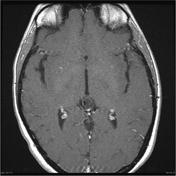

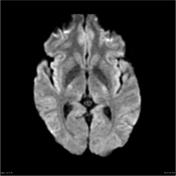

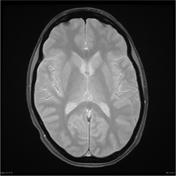

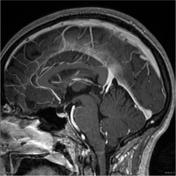

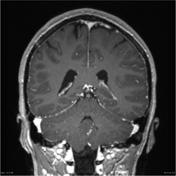

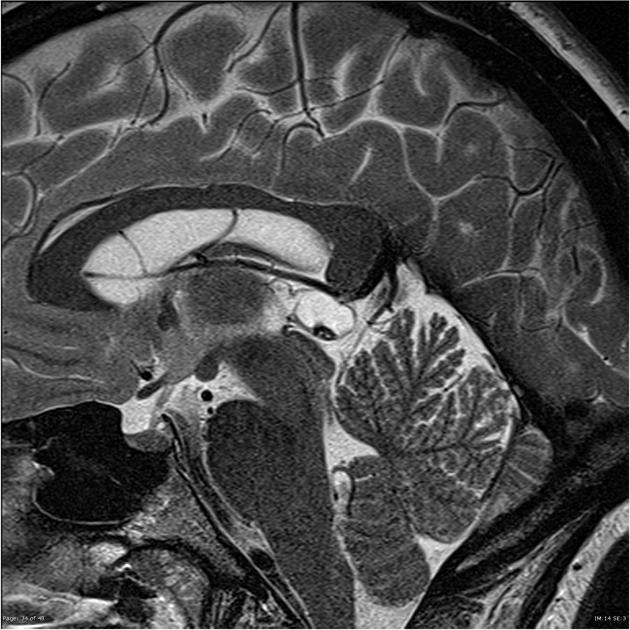
A cystic pineal gland lesion measuring 8 x 13 x 7 millimeters is demonstrated, which is located above the pineal calcifications, and below the internal cerebral veins. There is no convincing mass effect upon the tectal plate, and no evidence of hydrocephalus. Following the administration of contrast no solid enhancement can be identified.
The remainder of the brain is within normal limits, with no intra or extraaxial collection masses or focal regions of abnormal contrast enhancement noted. Incidental note is made of mucosal thickening in the the paranasal sinuses without evidence of acute sinusitis.
Conclusion:
Cystic pineal gland lesion as described most likely represents a benign pineal cyst. Given its size, follow-up is recommended, as a cystic pineocytoma could have similar appearances.
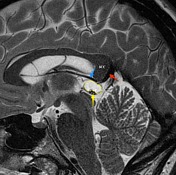
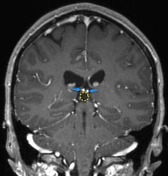
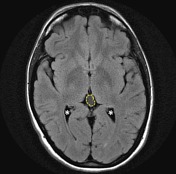
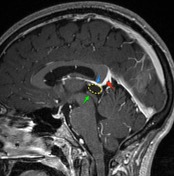
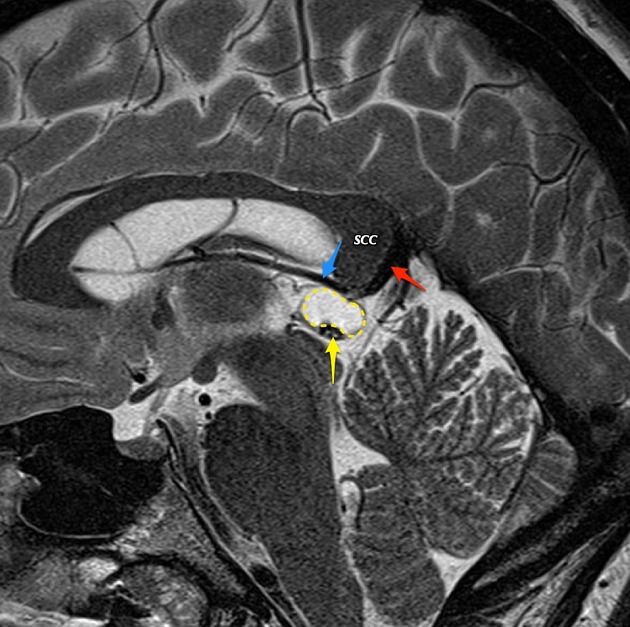
The pineal cyst (yellow dotted line) displaces pineal calcification (yellow arrow) inferiorly. The internal cerebral veins (blue) are located above the cyst easily seen on sagittal and coronal images. They drain into the vein of Galen (red) just below the splenium of the corpus callosum (SCC).
Although the cyst is of near-CSF intensity on T1 and T2 images, on FLAIR it does not fully attenuate - the difference is easily seen when comparing the cyst to the CSF in the lateral ventricles ( * ).
Case Discussion
Typical appearances of a large pineal cyst displacing pineal calcifications. This patient has been followed up for a number of years since this scan with no change evident.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.