Presentation
Pregnant woman with previous cesarean delivery presented for follow up.
Patient Data

The placenta is completely covering the cervical internal os consistent with placenta previa centralis.
Protrusion of placental tissues beyond the outer confines of the uterine myometrium with indistinct uterine serosa-bladder wall complex.
Color Doppler ultrasound shows increased vascularity between serosa and bladder.
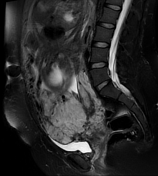





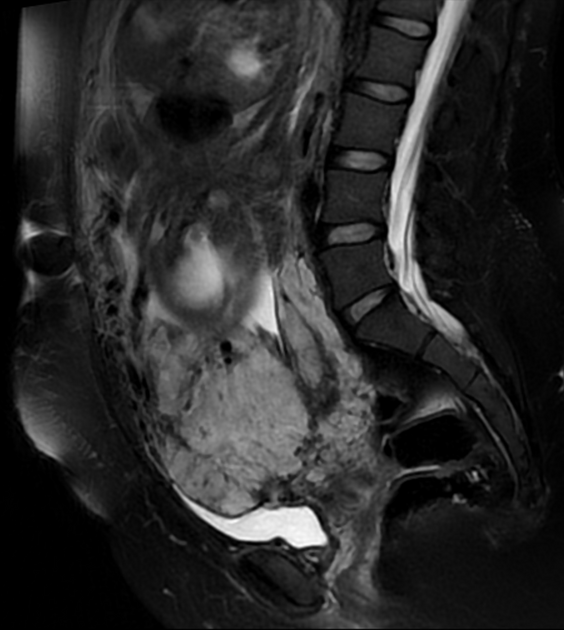
The placental is completely covering uterine cervix consistent with placenta previa centralis.
Uterine bulging with heterogenous signal of the placenta, lumpy contour, rounded edges, intraplacental hypointense bands, and disruption of the hypointense line at myometrial interface by placenta that appears to be contiguous with urinary bladder suggesting bladder invasion.
Features indicate placenta previa centralis, placenta accreta with suspicion of placenta percreta.
Case Discussion
Placenta percreta is the most severe and least common form of placental insertion abnormalities. The increasing frequency of cesarean section deliveries has led to more of these abnormalities. Ultrasound and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) have a key role in diagnosing these abnormal adherences since it shows best transmural extension of the placental tissue 1.
Our case of a woman with a previous cesarean delivery who had been diagnosed with a placenta previa centralis on ultrasound and a suspicion of transmural extension. The MRI features also, highly suggest placenta percreta.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.