Presentation
History of a surgery many years ago because of bronchiectasis, now referred with clinical suspicion of PTE
Patient Data
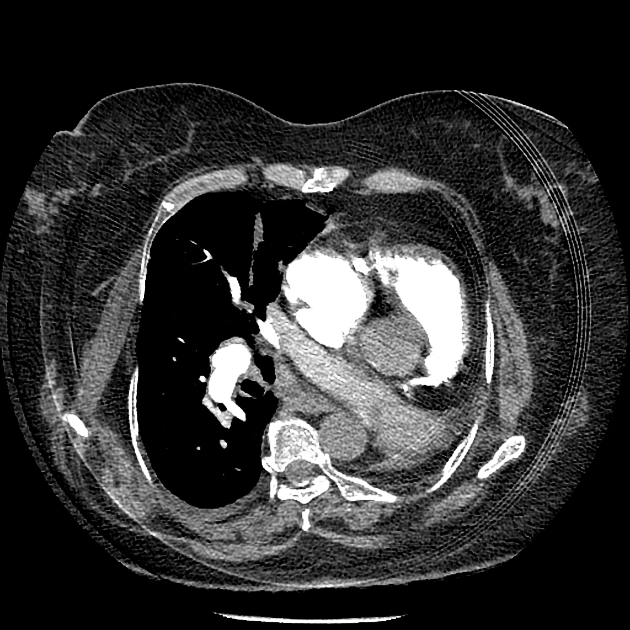
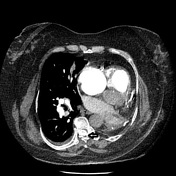
The left main bronchus and left main pulmonary artery are not visible more than a few millimeters after the carina and the pulmonary trunk bifurcation. There is no lung parenchyma on the left side, along with an ipsilateral mediastinal shift. Findings are compatible with a left pneumonectomy. No sign of pulmonary thromboembolism is evident. Minimal right-sided pleural effusion is visible. On scrutinizing, reviewing a calcified intradural mass is visible in the posterior part of the thoracic spinal canal, mostly suggestive of meningioma.
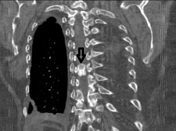

The black arrow shows the calcified mass within the thoracic spinal canal.
Case Discussion
The most common intradural extramedullary spinal masses are schwannoma and meningioma, calcification and dural base favors meningioma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.