From the case:
Progressive perilunate instability (diagram)



Download
Info
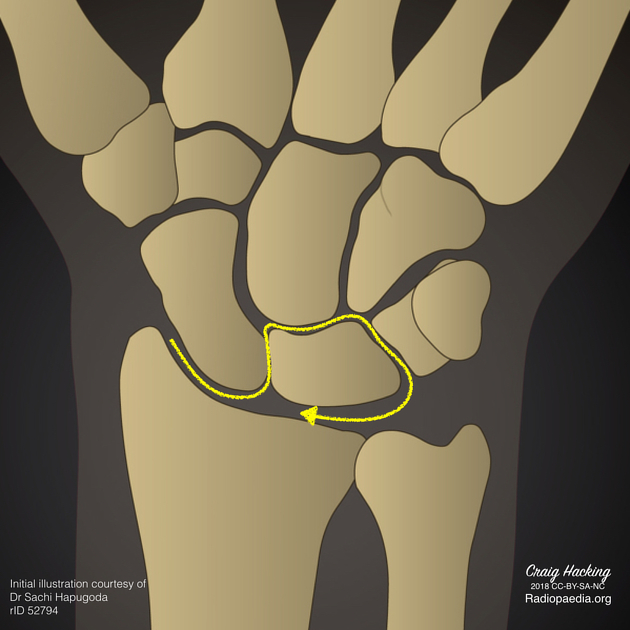
The arrow indicates the sequence of traumatic injury in progressive perilunate instability.
Original work of Sachi Hapugoda and Craig Hacking.
Case Discussion
Mayfield 1 described 4 stages of progressive injury to the ligaments surrounding the lunate leading to carpal instability:
- stage I: scapholunate dissociation
- stage II: perilunate dislocation
- stage III: midcarpal dislocation
- stage IV: lunate dislocation




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.