Presentation
Longstanding gastro-esophageal reflux and dysphagia
Patient Data

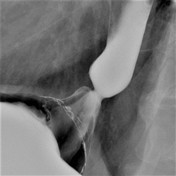
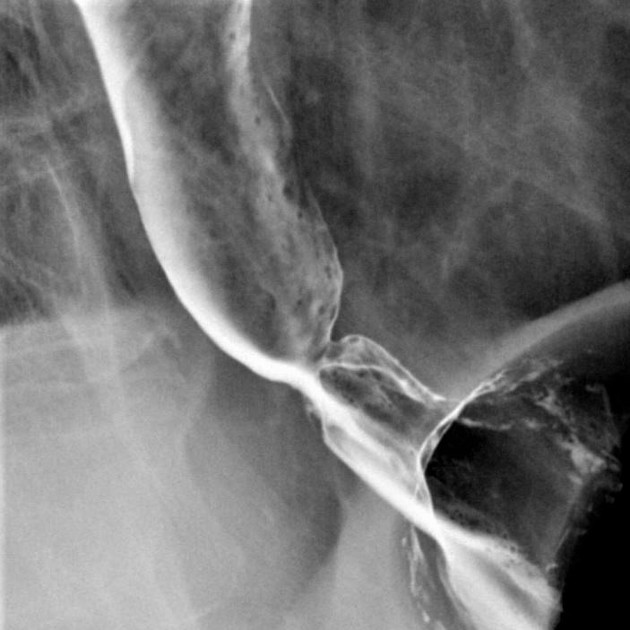
Asymmetric fixed short segment narrowing at the gastroesophageal junction, just above a small hiatal hernia.
Case Discussion
These images show a typical appearance for a ringlike peptic stricture, which can be confused with a mucosal B-ring (or "Schatzki ring" if symptomatic). Both are reactions from long-standing exposure to refluxed gastric acid, but the pathogenesis of the peptic stricture involves fibrosis of the submucosa and muscularis propria, whereas the mucosal ring is a ringed proliferation of mucosa. The B-ring is thin (3 mm or less) and circumferential. A mucosal web would not be circumferencial, but would still be thin. When the indentation is thicker and asymmetric, then this implies that there is underlying fibrosis, compatible with stricture formation.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.