Presentation
Pelvic pain for 24 hours, right lateral uterine mass with large amounts of ascites observed on ultrasound (not shown here).
Patient Data
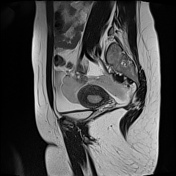

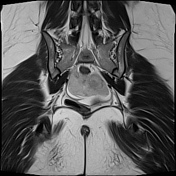

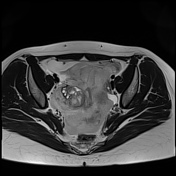

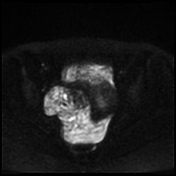

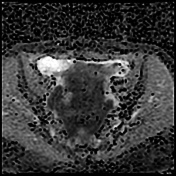

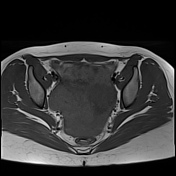

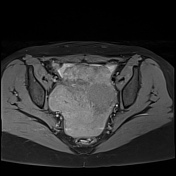

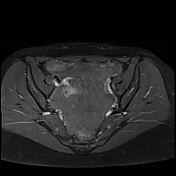

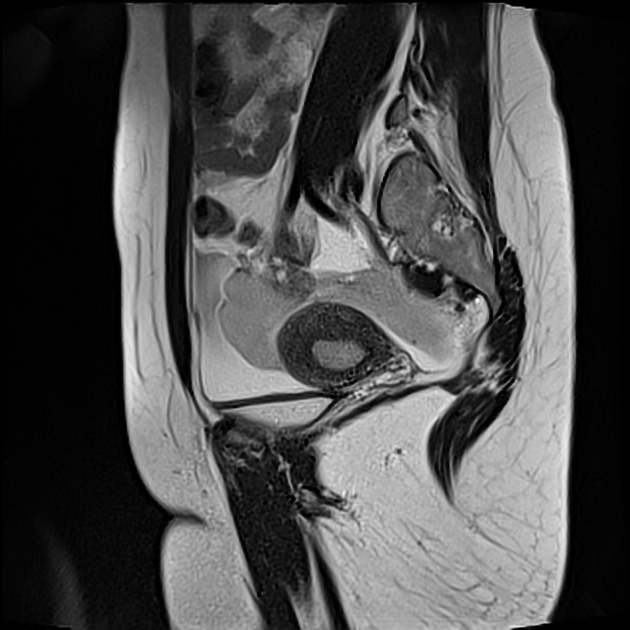
Important hemoperitoneum with significant pelvic clotting occupying peritoneal spaces around the uterus and the right ovary.
There is a right para-ovarian formation measuring 25 x 21 mm, round shaped, well-defined by a thick incomplete crown, hypointense on T2 slightly hyperintense on T1 with perilesional contrast enhancement in a blush pattern that may correspond to an active bleeding, These findings are most likely corresponding to an extrauterine gestational sac.
Globular uterus with a thick regular endometrium, without visualization of an intrauterine gestational sac.
The patient reports a menstrual delay of approximately 6 weeks. A blood test was promptly performed, confirming elevated beta-HCG levels and leading to the diagnosis of an ectopic pregnancy (EP).
Case Discussion
An ectopic pregnancy is a life-threatening condition where the fertilized egg implants outside the uterine cavity, most commonly in the fallopian tubes. It requires urgent medical attention, as a ruptured ectopic pregnancy can lead to severe internal bleeding and hemorrhagic shock, endangering the patient's life.
Early diagnosis is crucial and is primarily based on clinical findings, such as abdominal pain and bleeding, coupled with ultrasound imaging to confirm the diagnosis. MRI is rarely used in these cases, as ultrasound is typically sufficient to detect a ruptured ectopic pregnancy and guide immediate intervention.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.