Presentation
Left knee pain and swelling after external rotation with fixed foot. Joint effusion and pain present on examination.
Patient Data
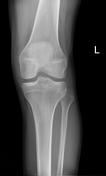
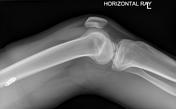


Displayed image shows a displaced fracture of the anterior intercondylar region with avulsed fracture fragment along the lateral tibial condyle corresponding with Segond fracture.
Associated knee lipohemarthrosis.
Avulsion fracture of the anterior aspect of the tibial spine indicating anterior cruciate ligament avulsion. The lateral tibial plateau fracture line has the typical appearance of a Segond fracture which (controversially) indicates anterolateral ligament avulsion.
Case Discussion
Lipohemarthrosis is an important sign of underlying fracture, in this case an ACL avulsion from the tibial eminence.
The Segond fracture is a subtle but important finding and in some cases this may be the only indication of significant internal derangement. The magnified X-ray image demonstrates the importance of a careful search and the utility of a sharp algorithm for bone detail. There is a strong association with ACL injury and both are caused by internal rotation with varus stress.
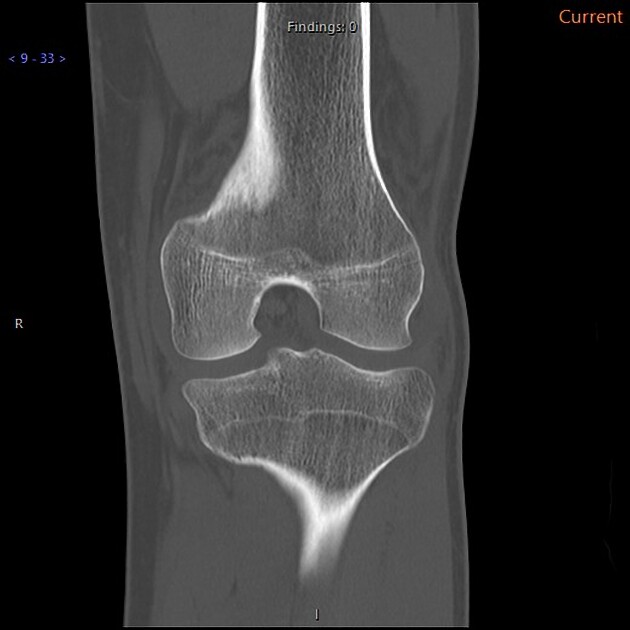
CT demonstrates the fractures well but does not change management. The patient proceeded to ACL reconstruction.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.