Thalamic radiations in vivo using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI)
Presentation
Thalamic radiations in vivo using diffusion tensor imaging (DTI).
Patient Data

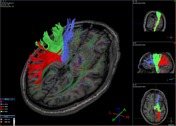
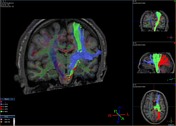
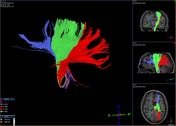

3D reconstruction result of thalamic radiations. Fiber-tracking technique.
Anterior thalamic radiation (blue); superior thalamic radiation (green); posterior thalamic radiation (red).
Case Discussion
The thalamus is known to have reciprocal connections (thalamic radiations) to large cortical regions, playing an important role in a diverse array of functions (for example, motor control, sensory relay, attention and awareness). Thalamic radiations (corticothalamic/thalamocortical fibers) are myelinated nerve fibers, arranged in a fanning pattern, grouped into four tracts or fasciculi:
- thalamo-frontal fibers (or anterior thalamic radiation), that penetrate the anterior limb of the internal capsule;
- thalamo-parietal fibers (or superior thalamic radiation), that penetrate the posterior limb of the internal capsule;
- thalamo-occipital fibers (or posterior thalamic radiation), that penetrate the retrolenticular part of the internal capsule, and ...
- ... thalamo-temporal fibers (or inferior thalamic radiation).
The thalamo-occipital fibers include the geniculocalcarine tract (or optic radiation).
Data acquisition
A 1.5 T Philips Achieva was used. DTI data were acquired using a single-shot echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequence with SENSE parallel imaging * (EPI factor = 59). Spin Echo technique (TR = 11090 ms; TE = 107 ms; Flip Angle = 90°; nex = 2). The imaging matrix was 112 x 112, with a field of view of 224 x 224 mm. The image orientation was axial, with a 2.0 mm slice thickness (slice gap = 0 mm), which was aligned parallel to the anterior-posterior commissure line. A total of 60 slices covered the entire cerebral hemispheres and the brainstem. The diffusion weighting was encoded along 32 independent orientations, with a maximum b-value = 800 s/mm2. The scanning time of one dataset was about 12 min. A co-registered T1-weighted 3D Gradient Echo was also recorded for anatomical guidance.
* SENSE parallel imaging was used to reduce the length of the EPI-train, thereby reducing susceptibility related distortions.
Reconstruction of tracts
The 3D tract reconstruction was performed using the FACT (Fiber Assignment by Continuous Tracking) method. Fractional Anisotropy (FA) threshold = 0.18.
Anterior thalamic radiation: first ROI was placed in axial slice (thalamus); the second ROI was placed in coronal slice (frontal lobe). Superior thalamic radiation: first ROI was placed in axial slice (thalamus); the second ROI was placed in axial slice (frontal and parietal lobes). Posterior thalamic radiation: first ROI was placed in axial slice (thalamus); the second ROI was placed in coronal slice (occipital lobe).
Acknowledgments
A. Politi, MD and G. M. Latagliata, MD.
Disclosure: I, Francesco Sciacca, have no actual or potential ethical or financial conflict of interest in relation to this device. This case is not intended to be a personal endorsement or recommendation of this product.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.