Presentation
Right arm pain and numbness, exacerbated on abduction. Decreased right arm pulse on physical examination.
Patient Data
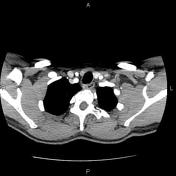

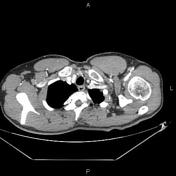


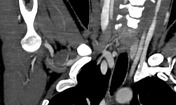
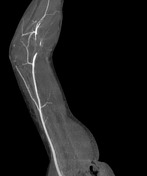
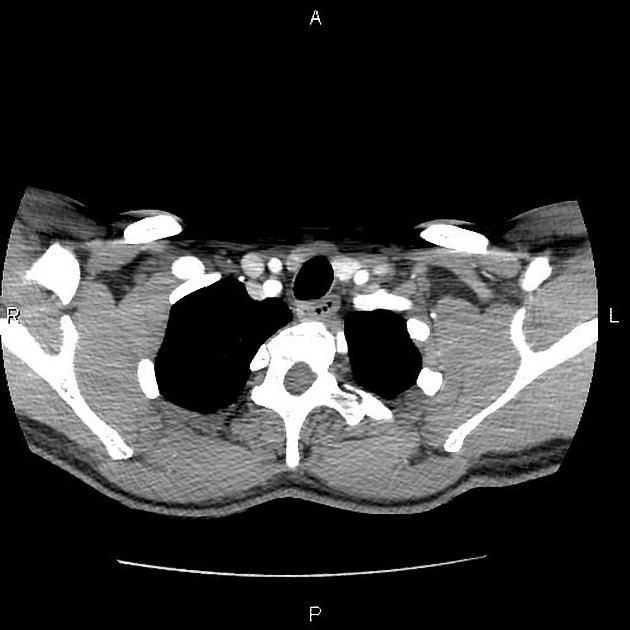
CT-angiography performed with arms in both neutral and raised positions clearly demonstrates dynamically induced compression of right subclavian artery in costoclavicular space. Compression is caused by abnormal fused cervical and first ribs. Findings are consistent with arterial thoracic outlet syndrome.
Condition is complicated by formation of saccular aneurysm of right subclavian artery at the site of damage (best seen when arms lowered) and brachial artery embolism.
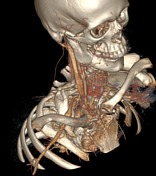
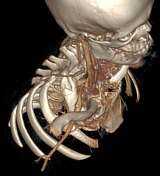
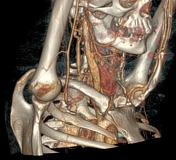
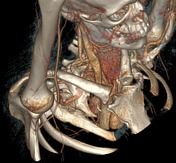
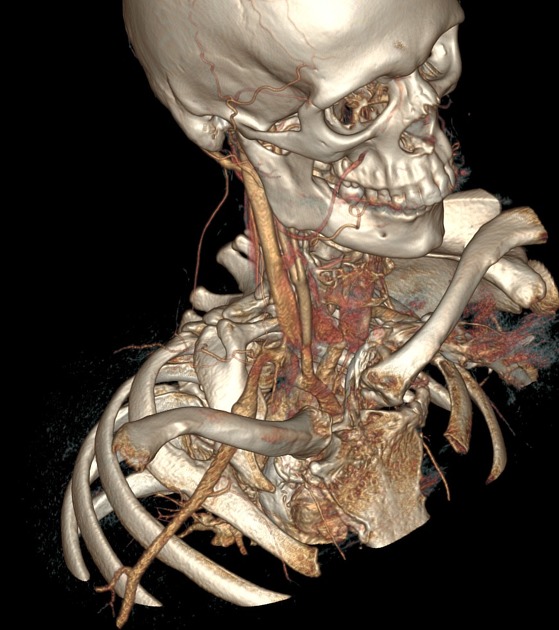
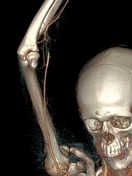
3D reconstructions demonstrating right subclavian artery occlusion with elevated arms, rib abnormality, and saccular aneurysm.
Case Discussion
Thoracic outlet syndrome (TOS) refers to a variety of conditions caused by compression of neurovascular structures as they traverse the thoracic outlet. Arterial TOS is considered the rarest form.
The diagnosis of TOS is usually made clinically. Imaging is helpful in identifying the exact location and cause of compression. CT-angiography is effective in demonstrating arterial compression if performed in neutral position and with raised arms. The contrast medium should be injected from the opposite side.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.