Presentation
Atraumatic back pain. Otherwise well.
Patient Data

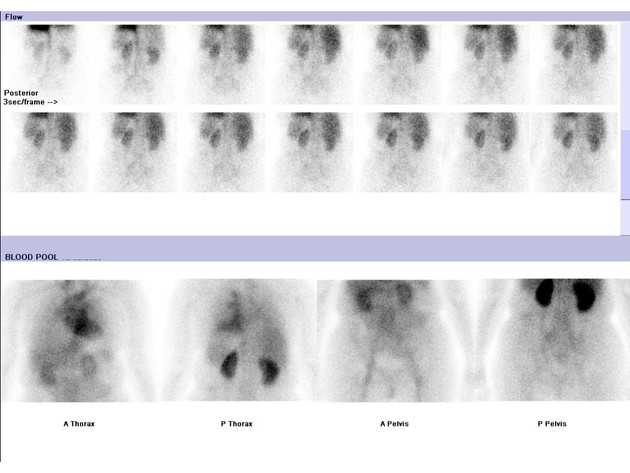
On the early phase blood pool image, there is minor focal hyperemia in the right lower thoracic spine, seen best on the posterior image.
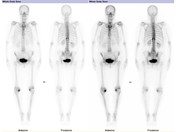
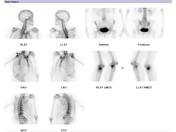
On planar delayed phase imaging, there is focally increased tracer accumulation in the lateral aspects of the T11 vertebral body. There is also incidental intense periarticular uptake in the medial compartments of both knees (right greater than left).
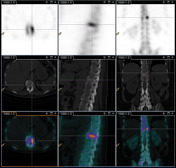
On SPECT/CT, there is linear uptake corresponding to the superior endplate of the T11 vertebral body, with mild endplate depression and sclerosis on low dose CT.
Case Discussion
On bone scan, acute or subacute endplate compression fractures demonstrate linear uptake on delayed phase imaging. There is variable hyperemia on early phase imaging, depending on the age of the fracture. Uptake does not cross the intervertebral junction as it would be expected to in a case of discitis.
SPECT/CT is useful to confirm the location of the uptake within the vertebral body.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.