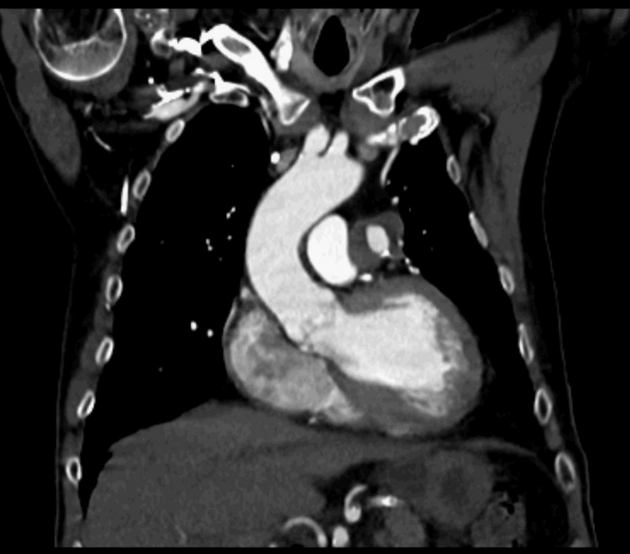
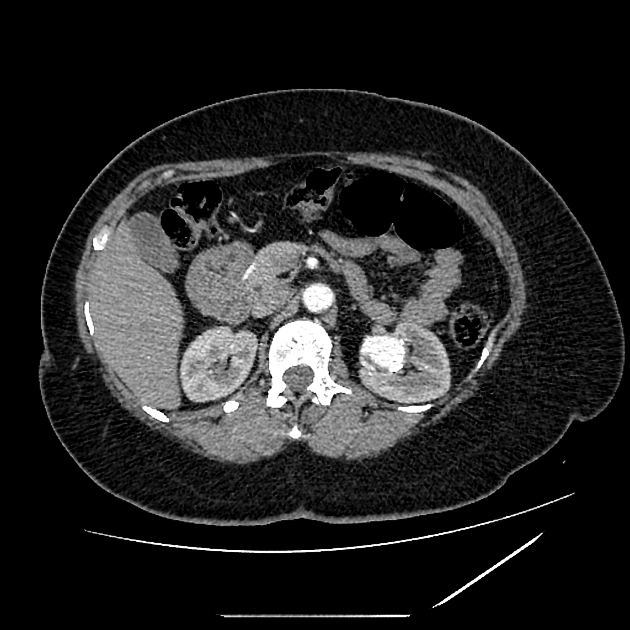
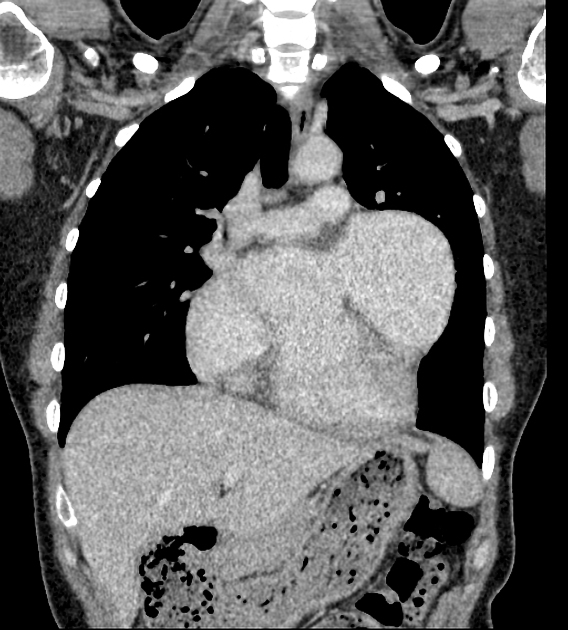
Aneurysms are focal abnormal dilatation of a blood vessel. They typically occur in arteries; venous aneurysms are rare. Aneurysms may also occur in the heart.
On this page:
Pathology
Pathological types
Etiology
Atherosclerotic
Non-atherosclerotic
-
infection: mycotic aneurysm, syphilis (luetic aneurysm)
iatrogenic
myocardial infarction: may cause left a ventricular aneurysm
flow-related (in cerebral AVM, contralateral ICA occlusion, etc.)
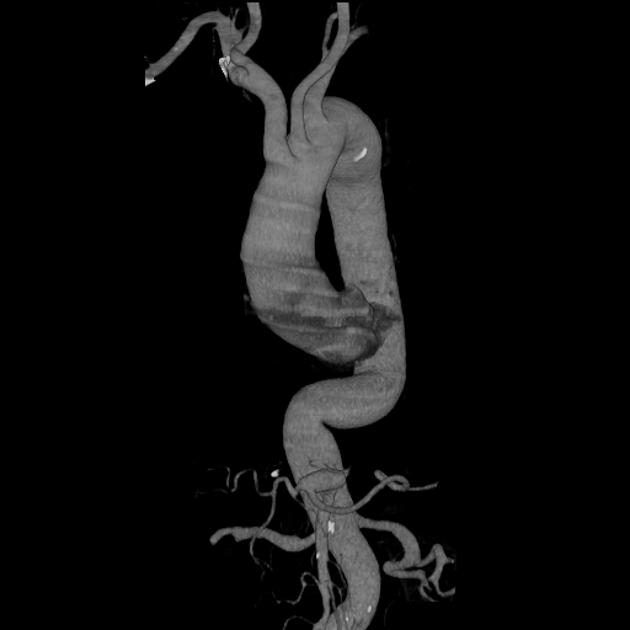
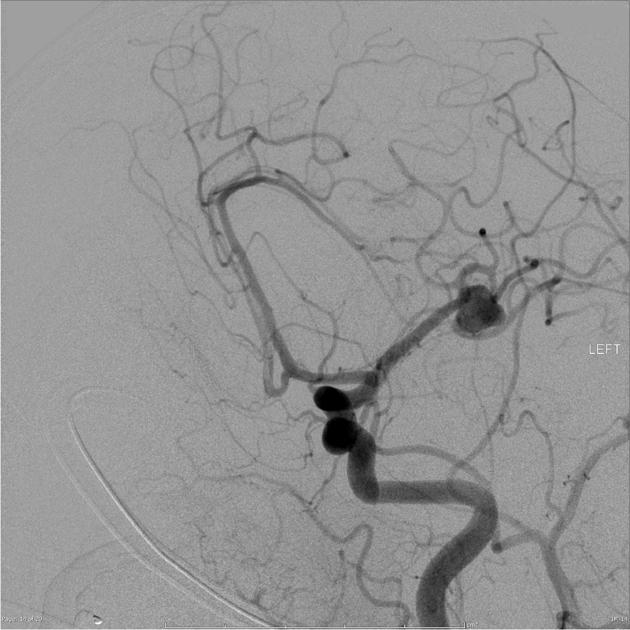
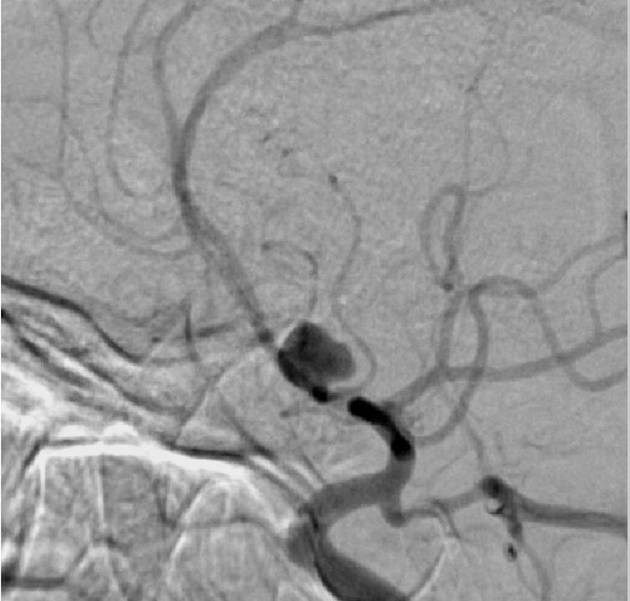
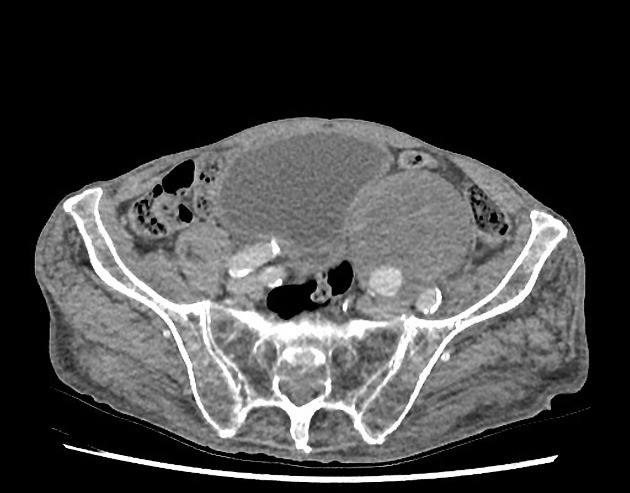
Morphology
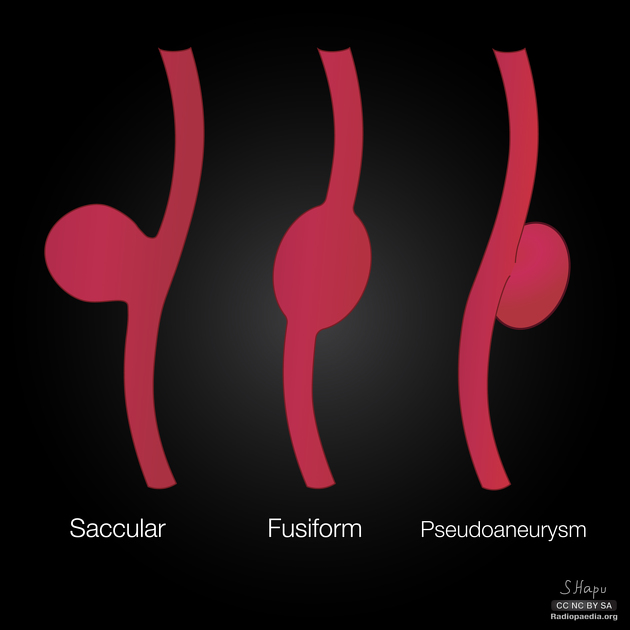
Morphologically there are two main types of aneurysms. The morphology is not specific for any cause:
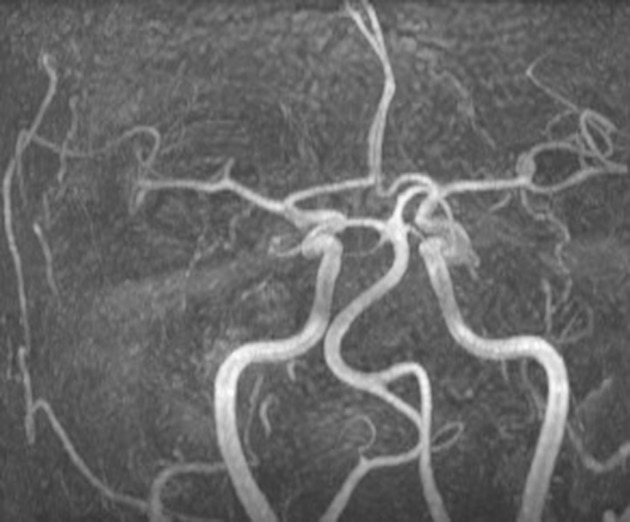
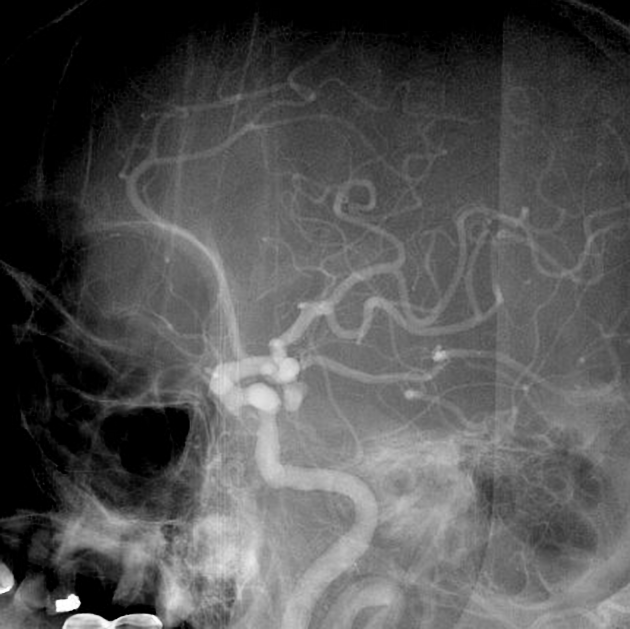
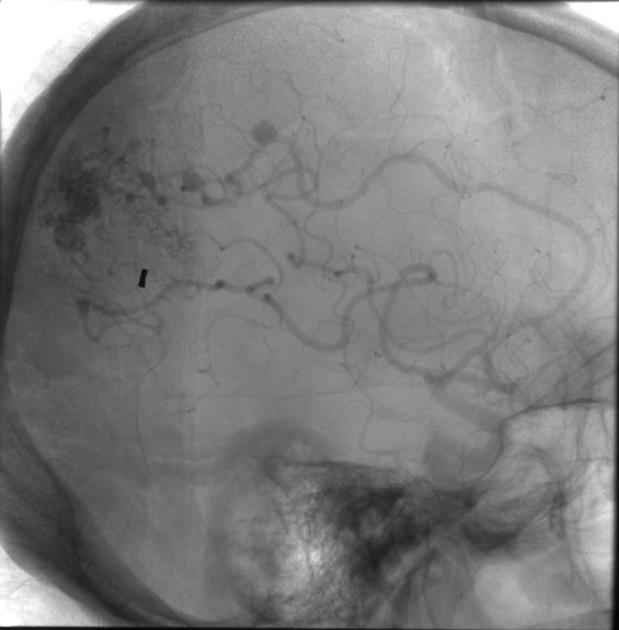
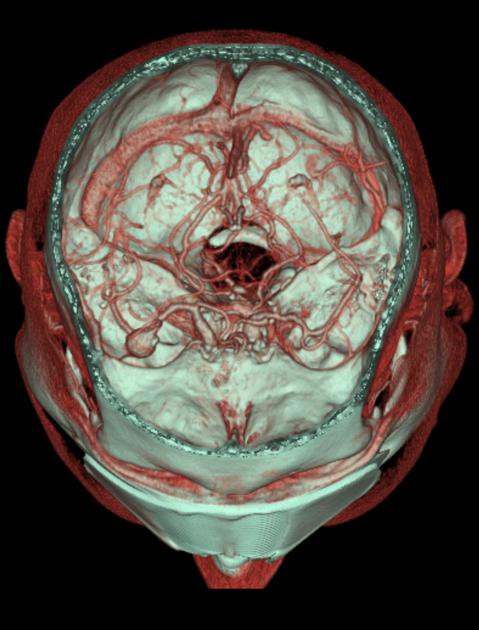
saccular aneurysm: eccentric, involving only a portion of the circumference of the vessel wall (e.g. cerebral berry aneurysm)
fusiform aneurysm: concentric, involving the full circumference of the vessel wall
Occasionally a 3rd type, serpentine aneurysm has been classified as a separate entity 3.
Treatment and prognosis
Complications
rupture
distal thromboembolism
pressure effects
History and etymology
The word aneurysm traces its roots back to ancient Greek, specifically the word ἀνεύρυσμα (aneurysma), literally translating as an 'aperture'. It is itself a compound construction, derived from two roots, 'ἄνω-' (ano) meaning 'up' and 'εὐρύς-' (eurys), meaning 'wide' 4,5.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.