Cricopharyngeal bar refers to the radiographic appearance of a prominent cricopharyngeus muscle contour on barium swallow.
On this page:
Terminology
The terms cricopharyngeal bar and cricopharyngeal muscle spasm/achalasia are often used synonymously but this is incorrect because studies have demonstrated that presence of a cricopharyngeal bar is not always related to cricopharyngeus spasm but can be due to other pathologies 4.
Epidemiology
Present in up to 20% of barium studies 1.
Clinical presentation
Mostly asymptomatic and found as an incidental finding on barium swallow. One-third of patients may complain of dysphagia but a cricopharyngeal bar is rarely a cause 1,5.
Pathology
Causes include 1,2:
idiopathic (i.e. normal variant)
cricopharyngeal muscle spasm/achalasia (i.e. failed relaxation)
cricopharyngeus muscle hypertrophy and/or fibrosis
Associations
seen in up to 50% of patients with gastro-esophageal reflux disease 6
Radiographic features
Fluoroscopy
On barium swallow lateral projection:
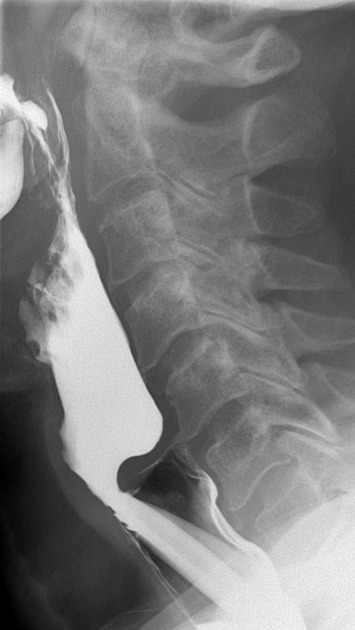
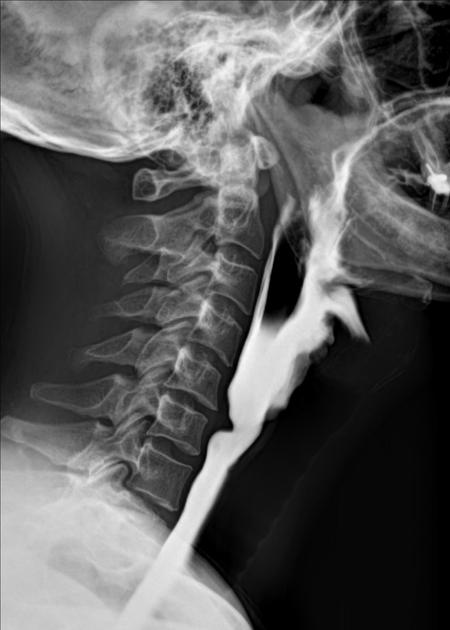
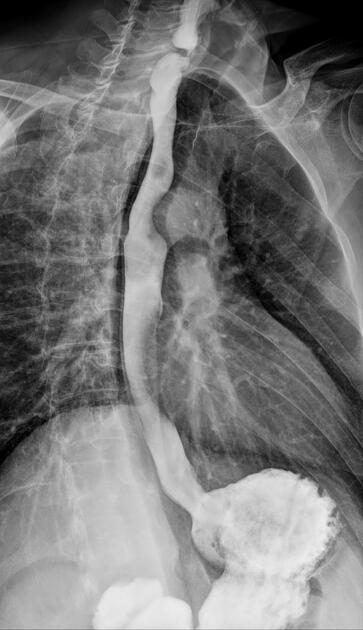
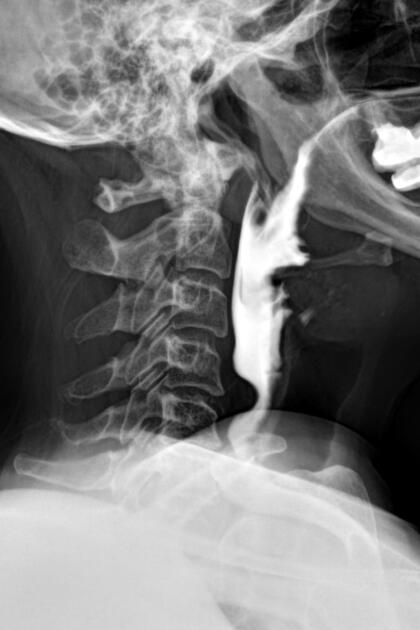
a smooth posterior shelf-like filling defect (indentation) of the esophagus at the level of C5-C6
Treatment and prognosis
In selected patients with no other cause for dysphagia demonstrated, cricopharyngeal bars can be treated with a myotomy, esophageal dilatation and/or botulinum toxin injection 5,6.
Complications
due to increased upper esophageal pressure may result in a Zenker diverticulum 2




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.