Drug-induced lung disease
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yuranga Weerakkody had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosures- Drug induced pneumonitis
- Drug induced interstitial lung disease
- Drug induced pulmonary disease
- Drug-induced lung injury
- Drug induced interstitial pulmonary disease
- Drug induced lung disease
- Toxic pneumonitis
- Drug induced pneumonitides
- Drug related pneumonitides
- Drug related pneumonitis
- Drug related pneumonitis (DRP)
- Drug-induced lung injury (DILI)
- Medication induced pulmonary injury
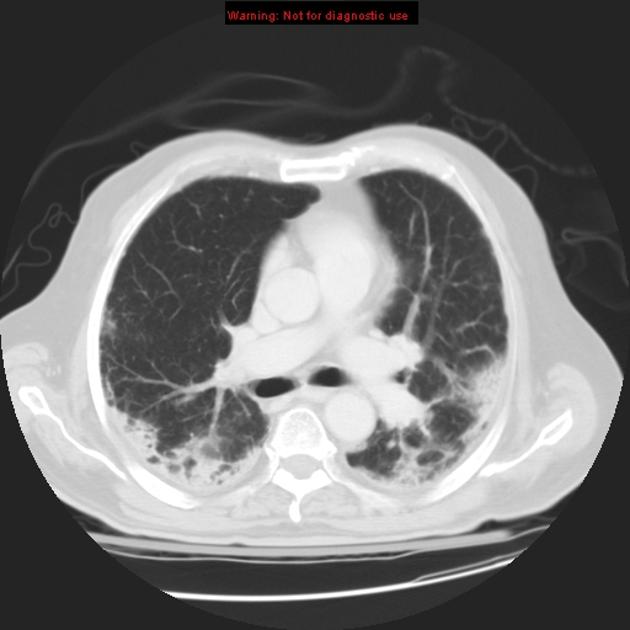
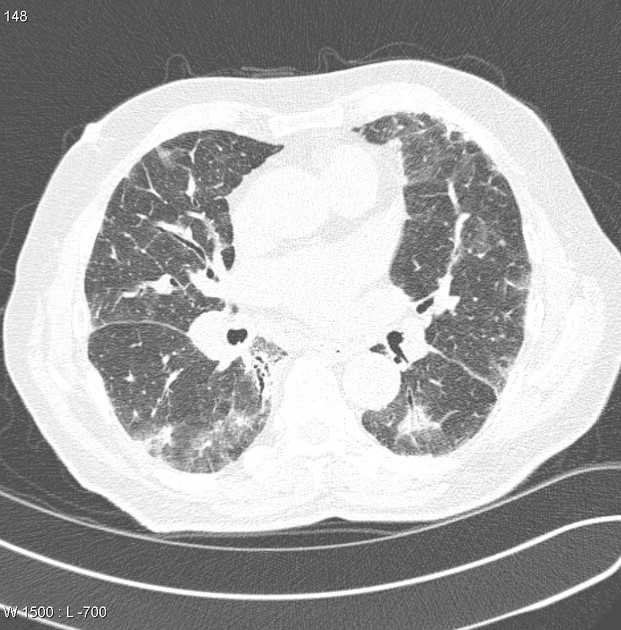
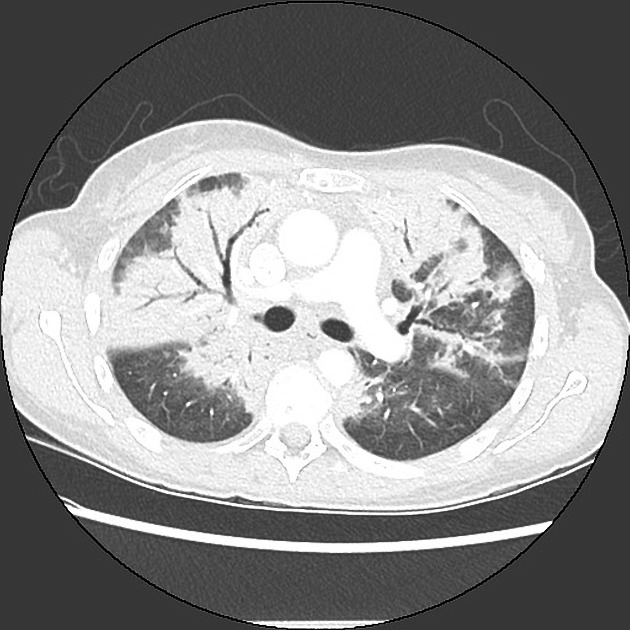
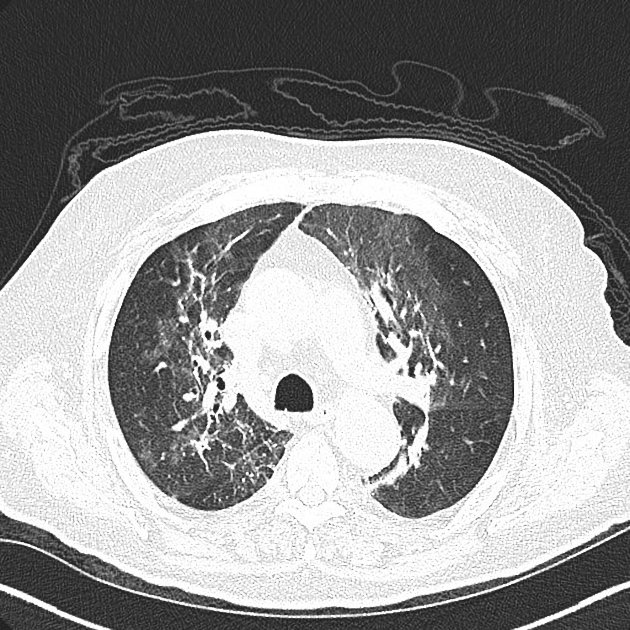
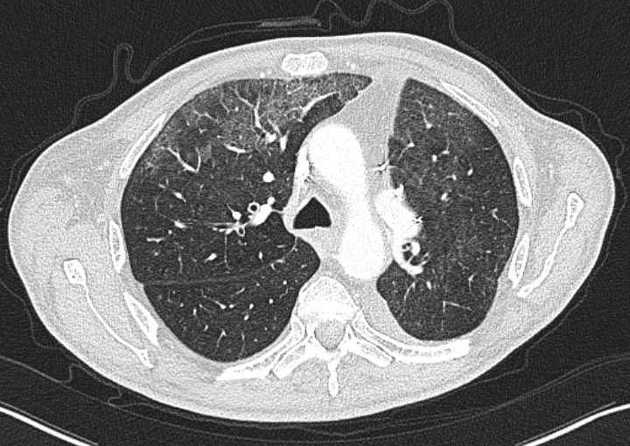
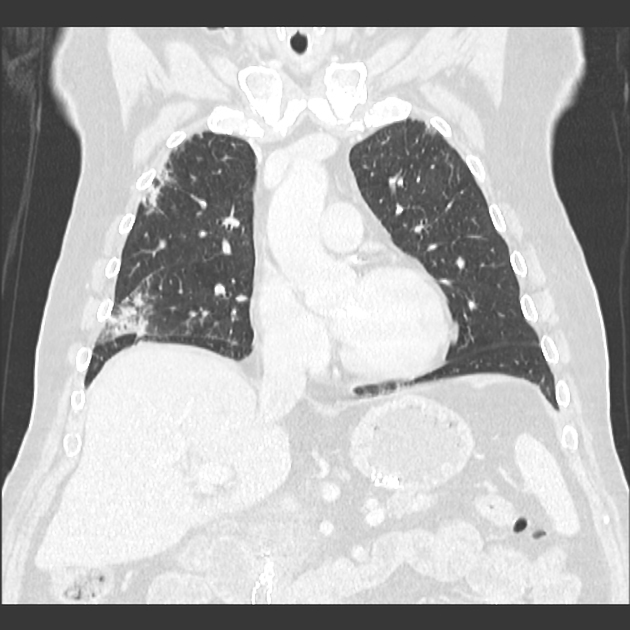
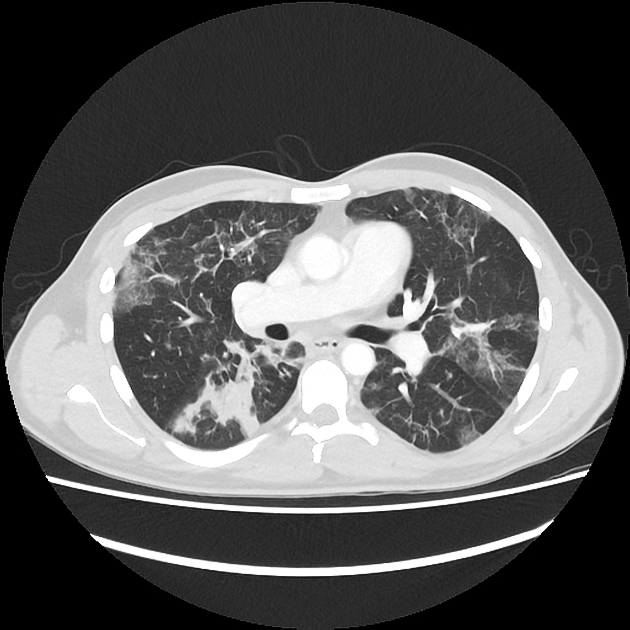
Drug-induced lung disease can result from a number of agents and may have a myriad of presentations, ranging from an adult respiratory distress syndrome type picture to established pulmonary fibrosis.
Due to this, it can be extremely difficult to pinpoint the offending agent on imaging appearances alone and correlation with the medical history is mandatory.
Pathology
Aetiology
Chemotherapy agents
These can give several patterns of disease which include 1,5:
interstitial fibrosis: typically NSIP 5 pattern
hypersensitivity pneumonitis pattern
adult respiratory distress syndrome / diffuse alveolar damage pattern
bronchiolitis obliterans organising pneumonia type pattern
Example agents include:
-
crizotinib: crizotinib associated intersitial pneumonitis
tyrosine kinase inhibitors: alectinib 18
-
epidermal growth factor receptor inhibitors tyrosine kinae inhibitors:
osimertinib 19
Immunosuppressive agents
sirolimus: sirolimus-associated pulmonary toxicity 9
leflunomide (arava): leflunomide-induced acute interstitial pneumonia 10
Immunotherapy agents
Immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy-related pneumonitis / immune-mediated pneumonitis usually happens between 8 to 14 weeks after the start of treatment 13. Examples of agents include:
nivolumab
-
pembrolizumab
ipilimumab
Monoclonal antibody
trastuzumab-deruxtecan (T-Dxd) - trastuzumab deruxtecan-related interstitial lung disease
Disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs)
TNF-alpha blockers: adalimumab-induced interstitial lung disease 16
Cardiovascular agents
amiodarone lung toxicity
Antibiotic agents
Can also give similar patterns to that of chemotherapeutic agents:
Anti-inflammatory agents
Non-medical drug use
IV methylphenidate: Ritalin lung, panacinar emphysema
IV heroin: pulmonary oedema, pulmonary haemorrhage, eosinophilic pneumonia 6
IV cocaine: pulmonary oedema
Antiseizure medications
phenytoin: eosinophilic pneumonia 4
Others
-
herbicides
paraquat (N,N′-dimethyl-4,4′-bipyridinium dichloride): paraquat-induced lung disease
References
- 1. Ellis S, Cleverley J, Müller N. Drug-Induced Lung Disease: High-Resolution CT Findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175(4):1019-24. doi:10.2214/ajr.175.4.1751019 - Pubmed
- 2. Aronchick J & Gefter W. Drug-Induced Pulmonary Disorders. Semin Roentgenol. 1995;30(1):18-34. doi:10.1016/s0037-198x(05)80004-5 - Pubmed
- 3. Rosenow E, Myers J, Swensen S, Pisani R. Drug-Induced Pulmonary Disease. An Update. Chest. 1992;102(1):239-50. doi:10.1378/chest.102.1.239 - Pubmed
- 4. Cleverley J, Screaton N, Hiorns M, Flint J, Müller N. Drug-Induced Lung Disease: High-Resolution CT and Histological Findings. Clin Radiol. 2002;57(4):292-9. doi:10.1053/crad.2001.0792 - Pubmed
- 5. Rossi S, Erasmus J, McAdams H, Sporn T, Goodman P. Pulmonary Drug Toxicity: Radiologic and Pathologic Manifestations. Radiographics. 2000;20(5):1245-59. doi:10.1148/radiographics.20.5.g00se081245 - Pubmed
- 6. Restrepo C, Carrillo J, Martínez S, Ojeda P, Rivera A, Hatta A. Pulmonary Complications from Cocaine and Cocaine-Based Substances: Imaging Manifestations. Radiographics. 2007;27(4):941-56. doi:10.1148/rg.274065144 - Pubmed
- 7. Souza C, Müller N, Johkoh T, Akira M. Drug-Induced Eosinophilic Pneumonia: High-Resolution CT Findings in 14 Patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2006;186(2):368-73. doi:10.2214/AJR.04.1847 - Pubmed
- 8. Schwaiblmair M, Behr W, Haeckel T, Märkl B, Foerg W, Berghaus T. Drug Induced Interstitial Lung Disease. Open Respir Med J. 2012;6(1):63-74. doi:10.2174/1874306401206010063 - Pubmed
- 9. Pham P, Pham P, Danovitch G et al. Sirolimus-Associated Pulmonary Toxicity. Transplantation. 2004;77(8):1215-20. doi:10.1097/01.tp.0000118413.92211.b6 - Pubmed
- 10. Takeishi M, Akiyama Y, Akiba H, Adachi D, Hirano M, Mimura T. Leflunomide Induced Acute Interstitial Pneumonia. J Rheumatol. 2005;32(6):1160-3. - Pubmed
- 11. Wang C, Chang H, Chang C. Docetaxel-Related Interstitial Pneumonitis. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2015;11:1813-6. doi:10.2147/TCRM.S90488 - Pubmed
- 12. Read W, Mortimer J, Picus J. Severe Interstitial Pneumonitis Associated with Docetaxel Administration. Cancer. 2002;94(3):847-53. doi:10.1002/cncr.10263 - Pubmed
- 13. Kumar V, Chaudhary N, Garg M, Floudas C, Soni P, Chandra A. Current Diagnosis and Management of Immune Related Adverse Events (IrAEs) Induced by Immune Checkpoint Inhibitor Therapy. Front Pharmacol. 2017;8:49. doi:10.3389/fphar.2017.00049 - Pubmed
- 14. Chi D, Brogan F, Turenne I, Zelonis S, Schwartz L, Saif M. Gemcitabine-Induced Pulmonary Toxicity. Anticancer Res. 2012;32(9):4147-9. - Pubmed
- 14. Kang M, Ju J, Kim H et al. Thalidomide Induced Nonspecific Interstitial Pneumonia in Patient with Relapsed Multiple Myeloma. Korean J Intern Med. 2010;25(4):447-9. doi:10.3904/kjim.2010.25.4.447 - Pubmed
- 15. Dhakal B, Singh V, Shrestha A, Rao A, Choong N. Pemetrexed Induced Pneumonitis. Clin Pract. 2011;1(4):e106. doi:10.4081/cp.2011.e106 - Pubmed
- 16. Aqsa A, Sharma D, Chalhoub M. Adalimumab Induced Interstitial Lung Disease. Respir Med Case Rep. 2020;29:101012. doi:10.1016/j.rmcr.2020.101012 - Pubmed
- 17. Johkoh T, Lee K, Nishino M et al. Chest CT Diagnosis and Clinical Management of Drug-Related Pneumonitis in Patients Receiving Molecular Targeting Agents and Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Position Paper from the Fleischner Society. Radiology. 2021;298(3):550-66. doi:10.1148/radiol.2021203427
- 18. Ikeda S, Yoshioka H, Arita M et al. Interstitial Lung Disease Induced by Alectinib (CH5424802/RO5424802). Jpn J Clin Oncol. 2015;45(2):221-4. doi:10.1093/jjco/hyu183 - Pubmed
- 19. Lu H & Dowell J. Osimertinib in Pulmonary Manifestations: Two Case Reports and Review of the Literature. In Vivo. 2020;34(1):315-9. doi:10.21873/invivo.11776 - Pubmed
- 20. Sridhar S, Kanne J, Henry T, Revels J, Gotway M, Ketai L. Medication-Induced Pulmonary Injury: A Scenario- and Pattern-Based Approach to a Perplexing Problem. Radiographics. 2022;42(1):38-55. doi:10.1148/rg.210146 - Pubmed
- 21. Portalatin G, Chin J, Foster B, Perry K, McWilliams C. Daptomycin-Induced Acute Eosinophilic Pneumonia. Cureus. 2021;13(2):e13509. doi:10.7759/cureus.13509 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Rituximab-induced interstitial lung disease
- Upper lobe pulmonary fibrosis
- Diffuse alveolar damage
- Daptomycin induced lung toxicity
- Paclitaxel lung toxicity
- COVID-19
- Leflunomide induced acute interstitial pneumonia
- Melphalan associated pulmonary toxicity
- Nitrofurantoin related lung changes
- Non-specific interstitial pneumonia
- Perilobular fibrosis
- Methotrexate lung disease
- Adalimumab-induced interstitial lung disease
- Thalidomide induced interstitial pneumonitis
- Pembrolizumab induced pneumonitis
- Crizotinib associated interstitial pneumonitis
- Pemtrexed induced pneumonitis
- Pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- Trastuzumab deruxtecan related interstitial lung disease
- Pneumonitis
Related articles: Chest
- imaging techniques
-
chest radiograph
- radiography
-
approach
- ABCDE
- ABCDEFGHI
- congenital heart disease
- medical devices in the thorax
- common lines and tubes
- nasogastric tubes
- endotracheal tubes
- central venous catheters
- oesophageal temperature probe
- tracheostomy tube
- pleural catheters
- cardiac conduction devices
- prosthetic heart valve
- review areas
-
airspace opacification
- differential diagnoses of airspace opacification
- lobar consolidation
-
atelectasis
- mechanism-based
- morphology-based
- lobar lung collapse
- chest x-ray in the exam setting
- cardiomediastinal contour
- chest radiograph zones
- tracheal air column
- fissures
- normal chest x-ray appearance of the diaphragm
- nipple shadow
-
lines and stripes
- anterior junction line
- posterior junction line
- right paratracheal stripe
- left paratracheal stripe
- posterior tracheal stripe/tracheo-oesophageal stripe
- posterior wall of bronchus intermedius
- right paraspinal line
- left paraspinal line
- aortic-pulmonary stripe
- aortopulmonary window
- azygo-oesophageal recess
- spaces
- signs
- air bronchogram
- big rib sign
- Chang sign
- Chen sign
- coin lesion
- continuous diaphragm sign
- dense hilum sign
- double contour sign
- egg-on-a-string sign
- extrapleural sign
- finger in glove sign
- flat waist sign
- Fleischner sign
- ginkgo leaf sign
- Golden S sign
- Hampton hump
- haystack sign
- hilum convergence sign
- hilum overlay sign
- Hoffman-Rigler sign
- holly leaf sign
- incomplete border sign
- juxtaphrenic peak sign
- Kirklin sign
- medial stripe sign
- melting ice cube sign
- more black sign
- Naclerio V sign
- Palla sign
- pericardial fat tag sign
- Shmoo sign
- silhouette sign
- snowman sign
- spinnaker sign
- steeple sign
- straight left heart border sign
- third mogul sign
- tram-track sign
- walking man sign
- water bottle sign
- wave sign
- Westermark sign
- HRCT
-
chest radiograph
- airways
- bronchitis
- small airways disease
-
bronchiectasis
- broncho-arterial ratio
- related conditions
- differentials by distribution
- narrowing
-
tracheal stenosis
- diffuse tracheal narrowing (differential)
-
bronchial stenosis
- diffuse airway narrowing (differential)
-
tracheal stenosis
- diverticula
- pulmonary oedema
-
interstitial lung disease (ILD)
- Anti-Jo-1 antibody-positive interstitial lung disease
- drug-induced interstitial lung disease
-
hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- acute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- subacute hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis
- aetiology
- bird fancier's lung: pigeon fancier's lung
- farmer's lung
- cheese workers' lung
- bagassosis
- mushroom worker’s lung
- malt worker’s lung
- maple bark disease
- hot tub lung
- wine maker’s lung
- woodsman’s disease
- thatched roof lung
- tobacco grower’s lung
- potato riddler’s lung
- summer-type pneumonitis
- dry rot lung
- machine operator’s lung
- humidifier lung
- shower curtain disease
- furrier’s lung
- miller’s lung
- lycoperdonosis
- saxophone lung
-
idiopathic interstitial pneumonia (mnemonic)
- acute interstitial pneumonia (AIP)
- cryptogenic organising pneumonia (COP)
- desquamative interstitial pneumonia (DIP)
- non-specific interstitial pneumonia (NSIP)
- idiopathic pleuroparenchymal fibroelastosis
- lymphoid interstitial pneumonia (LIP)
- respiratory bronchiolitis–associated interstitial lung disease (RB-ILD)
- usual interstitial pneumonia / idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (UIP/IPF)
-
pneumoconioses
- fibrotic
- non-fibrotic
-
lung cancer
-
non-small-cell lung cancer
-
adenocarcinoma
- pre-invasive tumours
- minimally invasive tumours
- invasive tumours
- variants of invasive carcinoma
- described imaging features
- adenosquamous carcinoma
- large cell carcinoma
- primary sarcomatoid carcinoma of the lung
- squamous cell carcinoma
- salivary gland-type tumours
-
adenocarcinoma
- pulmonary neuroendocrine tumours
- preinvasive lesions
-
lung cancer invasion patterns
- tumour spread through air spaces (STAS)
- presence of non-lepidic patterns such as acinar, papillary, solid, or micropapillary
- myofibroblastic stroma associated with invasive tumour cells
- pleural invasion
- vascular invasion
- tumours by location
- benign neoplasms
- pulmonary metastases
- lung cancer screening
- lung cancer staging
-
non-small-cell lung cancer




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.