Distinguishing between an empyema and a peripherally located pulmonary abscess is essential.
A pulmonary abscess is usually managed with prolonged antibiotics and physiotherapy with postural drainage, whereas an empyema usually requires percutaneous or surgical drainage.
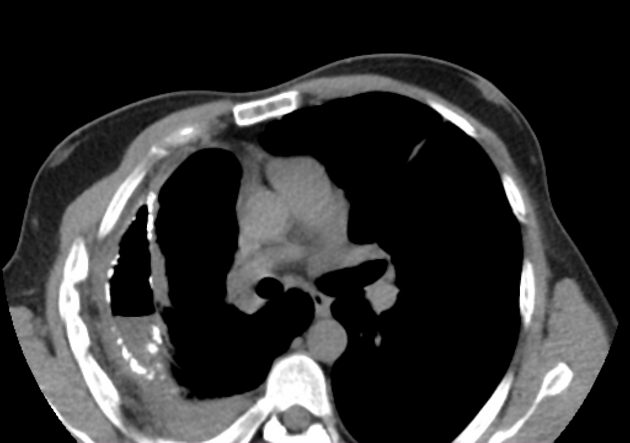
Radiographic features
Plain radiograph
-
shape
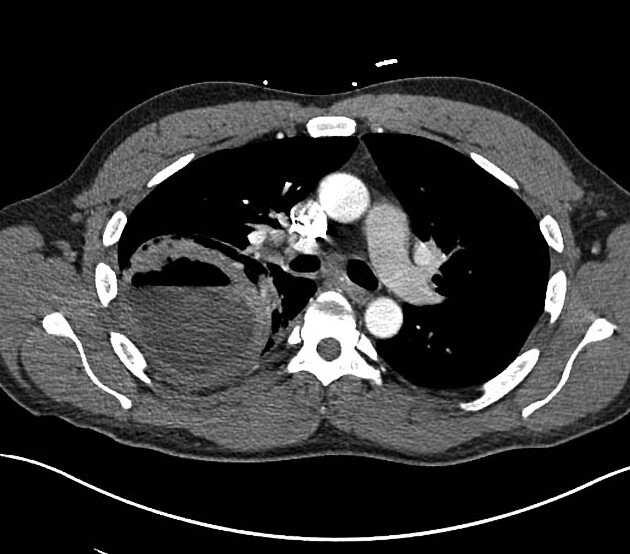
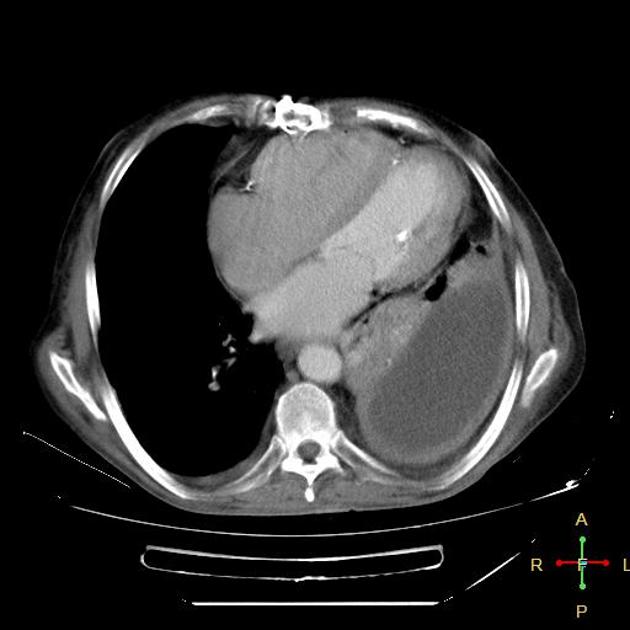
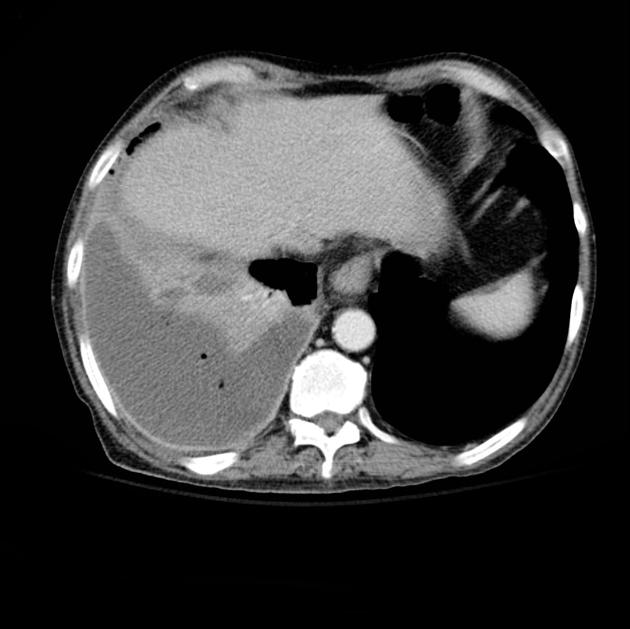
an abscess is usually (but not always) round in all projections
an abscess may form acute angles with the costal surface / chest wall
an empyema is usually (but not always) lentiform
CT
-
relationship to adjacent bronchi/vessels
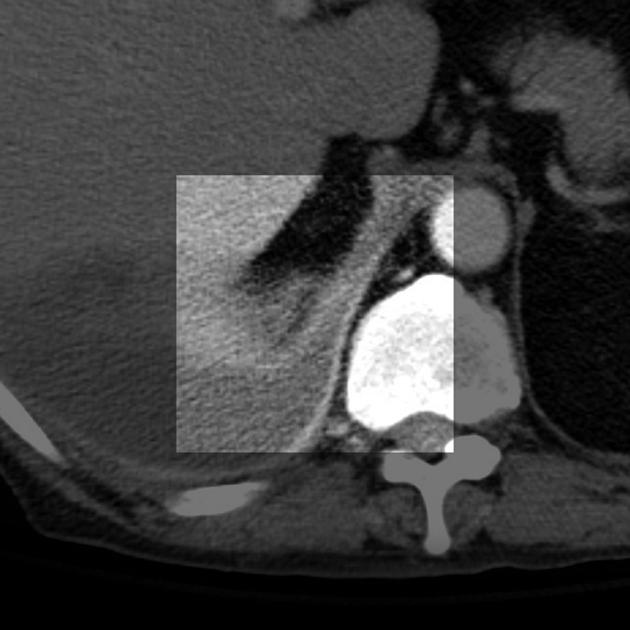
an abscess will abruptly interrupt the bronchovascular structures
an empyema will usually distort and compress adjacent lung
-
an empyema causes thickening and separation of the visceral and parietal pleura
-
wall
an abscess has thick irregular walls
an empyema usually has smoother walls
-
angle with pleura
an abscess usually has acute angles (claw sign)
an empyema tends to have obtuse angles
-
pleural enhancement
an empyema tends to show more pleural enhancement
-
extrapleural fat
an empyema tends to show edema/haziness of the extrapleural fat




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.