Epibasal fracture of the thumb
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Epibasal thumb fracture
- Pseudo Bennett's fracture
- pseudo-Bennett fracture dislocation
- Pseudo-Bennett fracture
Epibasal fractures of the thumb (also called pseudo-Bennett fracture) are extra-articular two-piece fractures of the proximal first metacarpal bone. They are usually stable, depending on the degree of displacement, and often do not require surgery. It is important to distinguish them from intra-articular fractures (e.g. Bennett fracture-dislocation or Rolando fracture), which are usually unstable and require surgery.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Epibasal fracture of the thumb accounts for approximately 3% of all hand fractures and 16% of metacarpal fractures and is mostly (>80%) seen in young men 4.
Mechanism
These fractures usually result from longitudinal axial loading 5.
Radiographic features
Plain films are usually sufficient to diagnose and assess epibasal fractures; however, if adequate views cannot be obtained or there is suspicion of intra-articular involvement, further assessment with CT is prudent 3.
Plain radiograph
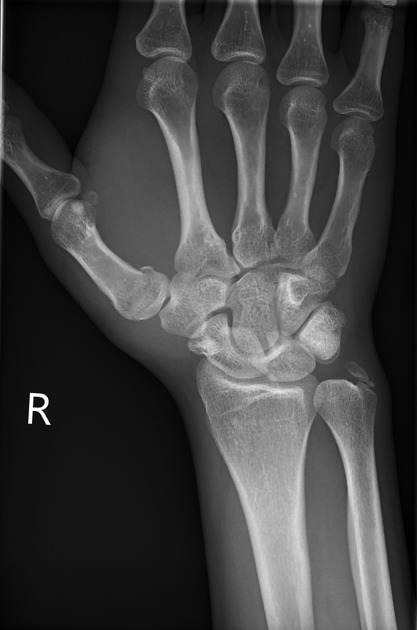
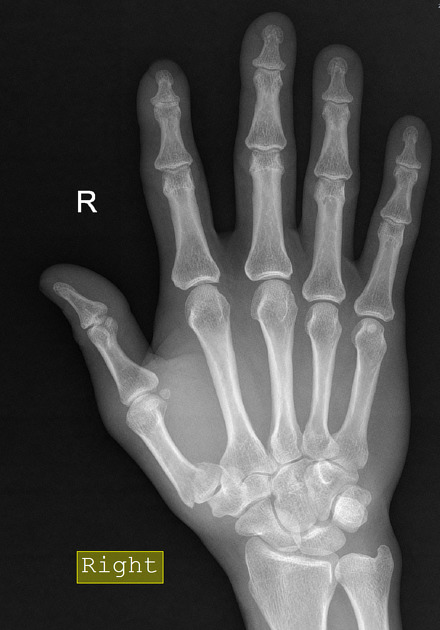
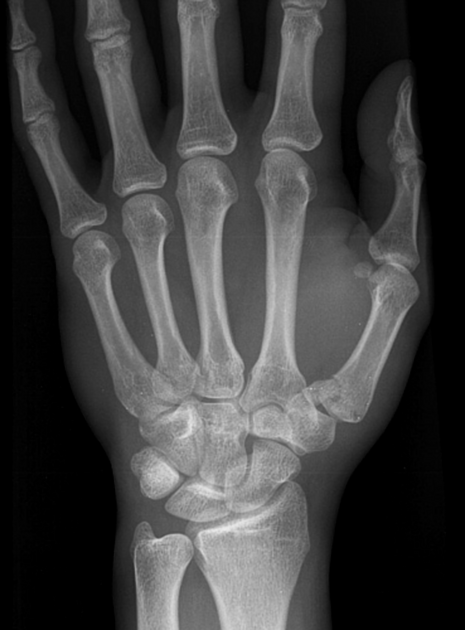
Epibasal fractures are divided according to the direction of fracture into transverse and oblique and can be variably angulated and displaced.
ADVERTISEMENT: Supporters see fewer/no ads
Treatment and prognosis
The vast majority of epibasal fractures are considered stable and can be treated conservatively with thumb spica immobilisation for 4-6 weeks 2,3. Both oblique fractures and transverse fractures with >30° of angulation usually require closed reduction and Kirschner wire fixation (CRIF) 2,3.
Practical points
In addition to stating that a fracture is present, one should assess and comment on:
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Burgener FA, Kormano M, Pudas T. Bone and Joint Disorders. Thieme Medical Pub. (2005) ISBN:1588904458. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 2. Brüser P, Gilbert A, Hand FO. Finger bone and joint injuries. Informa HealthCare. (1999) ISBN:1853176907. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 3. Browner BD, Levine AM, Jupiter JB et-al. Skeletal Trauma, Basic Science, Management, and Reconstruction. W B Saunders Company. (2009) ISBN:1416022201. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 4. Zhang Y. Clinical Epidemiology of Orthopedic Trauma. Thieme. ISBN:3131660414. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 5. Boer PD, Werken CV. Ao Handbook, Orthopedic Trauma Care. Tac. (2009) ISBN:3131470313. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
- 6. Brant WE, Helms C. Fundamentals of Diagnostic Radiology. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins. (2012) ISBN:1608319113. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Radial collateral ligament avulsion injury- thumb
- Epibasal thumb fracture
- Epibasal thumb fracture
- Green and O'Brien classification of thumb metacarpal fractures
- Thumb metacarpal fractures (illustration)
- Epibasal thumb fracture
- Bennet fracture
- Bennet fracture
- Pseudo-Bennett fracture
- Pseudo-Bennett fracture
- Bennett fracture
- Pseudo Bennett's fracture
- Rolando fracture
- Epibasal thumb fracture
- Pseudo Bennett's fracture
- Base of thumb metacarpal fracture
Related articles: Fractures
-
fracture
- terminology
- fracture location
- diaphyseal fracture
- metaphyseal fracture
- physeal fracture
- epiphyseal fracture
- fracture types
- avulsion fracture
- articular surface injuries
- complete fracture
- incomplete fracture
- infraction
- compound fracture
- pathological fracture
- stress fracture
- fracture displacement
- fracture location
- fracture healing
- skull fractures
-
facial fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
- alveolar process fractures
- frontal sinus fracture
- isolated zygomatic arch fractures
- mandibular fracture
- nasal bone fracture
- orbital blow-out fracture
- paranasal sinus fractures
- complex fractures
- dental fractures
- fractures involving a single facial buttress
-
spinal fractures
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- AO classification of upper cervical injuries
- AO classification of subaxial injuries
- Anderson and D'Alonzo classification (odontoid fracture)
- Roy-Camille classification (odontoid process fracture)
- Gehweiler classifcation (atlas fractures)
- Levine and Edwards classification (hangman fracture)
- Allen and Ferguson classification (subaxial spine injuries)
- subaxial cervical spine injury classification (SLIC)
- thoracolumbar spinal fracture classification systems
- three column concept of spinal fractures (Denis classification)
- classification of sacral fractures
-
cervical spine fracture classification systems
- spinal fractures by region
- spinal fracture types
- classification (AO Spine classification systems)
- rib fractures
- sternal fractures
-
upper limb fractures
- classification
- Rockwood classification (acromioclavicular joint injury)
- AO classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (clavicle fracture)
- Neer classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO classification (proximal humeral fracture)
- AO/OTA classification of distal humeral fractures
- Milch classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Weiss classification (lateral humeral condyle fracture)
- Bado classification of Monteggia fracture-dislocations (radius-ulna)
- Mason classification (radial head fracture)
- Frykman classification (distal radial fracture)
- Mayo classification (scaphoid fracture)
- Hintermann classification (gamekeeper's thumb)
- Eaton classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- Keifhaber-Stern classification (volar plate avulsion injury)
- upper limb fractures by region
- shoulder
- clavicular fracture
-
scapular fracture
- acromion fracture
- coracoid process fracture
- glenoid fracture
- humeral head fracture
- proximal humeral fracture
- humeral neck fracture
- arm
- elbow
- forearm
- wrist
-
carpal bones
- scaphoid fracture
- lunate fracture
- capitate fracture
- triquetral fracture
- pisiform fracture
- hamate fracture
- trapezoid fracture
- trapezium fracture
- hand
- shoulder
- classification
- lower limb fractures
- classification by region
- pelvic fractures
- hip fractures
- Pipkin classification (femoral head fracture)
- Garden classification (hip fracture)
- American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Cooke and Newman classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Johansson classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- Vancouver classification (periprosthetic hip fracture)
- femoral
- knee
- Schatzker classification (tibial plateau fracture)
- AO classification of distal femur fractures
- Meyers and McKeevers classification (anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture)
- tibia/fibula
- Watson-Jones classification (tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture)
- ankle
- foot
- Berndt and Harty classification (osteochondral lesions of the talus)
- Sanders CT classification (calcaneal fracture)
- Hawkins classification (talar neck fracture)
- Myerson classification (Lisfranc injury)
- Nunley-Vertullo classification (Lisfranc injury)
- pelvis and lower limb fractures by region
- pelvic fracture
- sacral fracture
- coccygeal fracture
-
hip
- acetabular fracture
- femoral head fracture
-
femoral neck fracture
- subcapital fracture
- transcervical fracture
- basicervical fracture
-
trochanteric fracture
- pertrochanteric fracture
- intertrochanteric fracture
- subtrochanteric fracture
- femur
- mid-shaft fracture
- bisphosphonate-related fracture
- distal femoral fracture
- knee
- avulsion fractures
- Segond fracture
- reverse Segond fracture
- anterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- posterior cruciate ligament avulsion fracture
- arcuate complex avulsion fracture (arcuate sign)
- biceps femoris avulsion fracture
- iliotibial band avulsion fracture
- semimembranosus tendon avulsion fracture
- Stieda fracture (MCL avulsion fracture)
- patellar fracture
- tibial plateau fracture
- avulsion fractures
- leg
- tibial tuberosity avulsion fracture
- tibial shaft fracture
- fibular shaft fracture
- Maisonneuve fracture
- ankle
- foot
- tarsal bones
- metatarsal bones
- phalanges
- classification by region
- terminology














 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.