Extrarenal pelvis refers to the presence of the renal pelvis outside the confines of the renal hilum; it is a normal anatomic variant.
On this page:
Epidemiology
It is found in ~10% of the population 2.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
An extrarenal pelvis usually appears dilated, erroneously suggesting obstructive pathology. Subsequent investigation with CT usually clarifies a false interpretation on ultrasound.
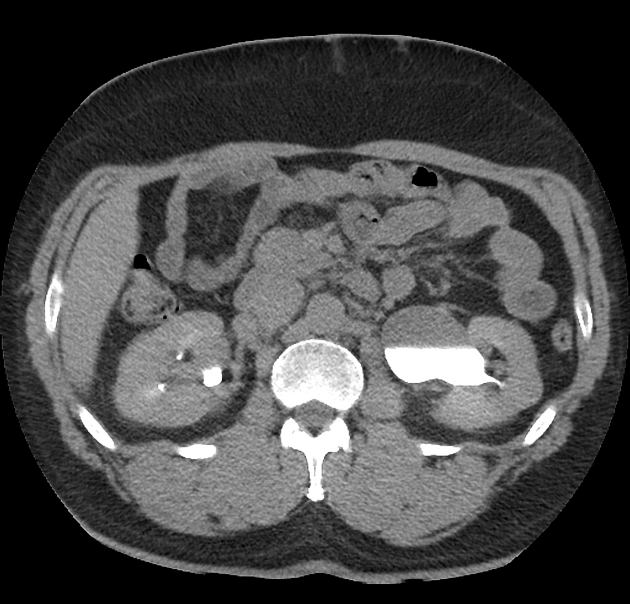
CT/MRI
a normal extrarenal pelvis will demonstrate normal renal cortical thickness, bilateral symmetrical contrast excretion, and normal-appearing calyces 3
Differential diagnosis
hydronephrosis, from whatever cause
Practical points
After evaluation with ultrasound and/or CT/MRI, if there is still confusion about whether a dilated renal pelvis is obstructed or not, renal scintigraphy can clarify.







 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.