Fissula ante fenestram
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Daniel J Bell had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosures- Fissula ante fenestram (FAF)
- Fissula ante fenestrum
- Fissulae ante fenestras
- Fissulae ante fenestram
- FAF
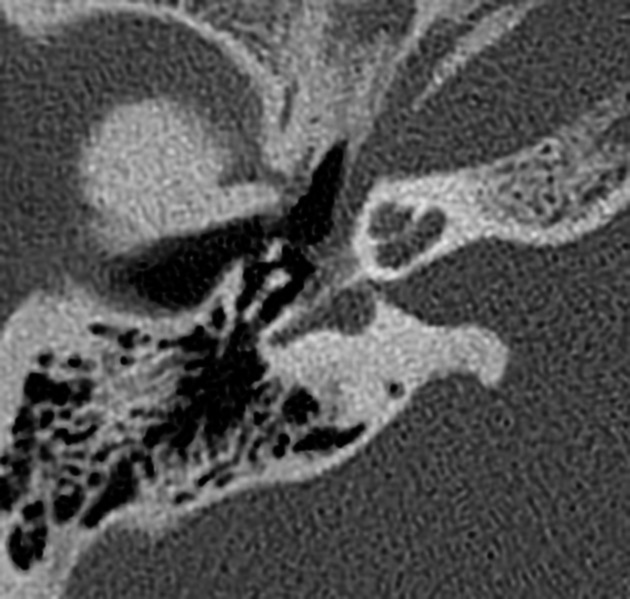
The fissula ante fenestram (plural: fissula ante fenestras) is a small connective tissue-filled cleft in the otic capsule of the temporal bone, not typically visible on CT. The area around the fissula ante fenestram is the usual origin of fenestral otosclerosis.
Gross anatomy
The fissula ante fenestram is situated in the region anterior to the oval window 1. The structure is an irregular projection from the junction of the vestibule and scala vestibuli that extends to the periosteum of the middle ear just beneath the cochleariform process, where the tendon of the tensor tympani muscle turns laterally toward the malleus 2.
The fissula ante fenestram was once thought to be related to the cochlear cleft 3, but studies have shown the latter to be a separate structure 4.
A structure called the fossula post fenestram is also described in histological studies and refers to a completely different but anatomically-proximate structure.
Anatomic trivia:
it is the only structure named fissula in the human body
it has not been found in any other animal
History and etymology
It is derived from the classical Latin:
fissula meaning a 'small cleft'
ante meaning 'forwards of'
fenestram (accusative form of fenestra) meaning 'window'.
Hence, it literally means 'the small cleft forwards of the window'.
The plural, although rarely seen, is fissula ante fenestras. It is not 'fissulae' as some might erroneously believe.
References
- 1. Lee TC, Aviv RI, Chen JM et-al. CT grading of otosclerosis. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2009;30 (7): 1435-9. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1558 [pubmed citation]
- 2. Bast TH. Development of the otic capsule: II. The origin, development and significant of the fissula ante fenestram and its relation to otosclerotic foci. (1933) Archives of Otolaryngology. 18 (1): 1. doi:10.1001/archotol.1933.03580060005001
- 3. Chadwell JB, Halsted MJ, Choo DI, Greinwald JH, Benton C. The cochlear cleft. (2004) AJNR. American journal of neuroradiology. 25 (1): 21-4. Pubmed
- 4. Pucetaite M, Quesnel AM, Juliano AF, Curtin HD, Reinshagen KL. The Cochlear Cleft: CT Correlation With Histopathology. (2020) Otology & neurotology : official publication of the American Otological Society, American Neurotology Society [and] European Academy of Otology and Neurotology. doi:10.1097/MAO.0000000000002637 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.