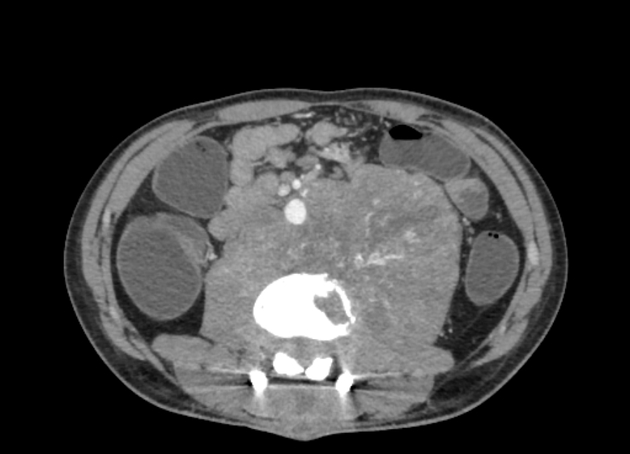
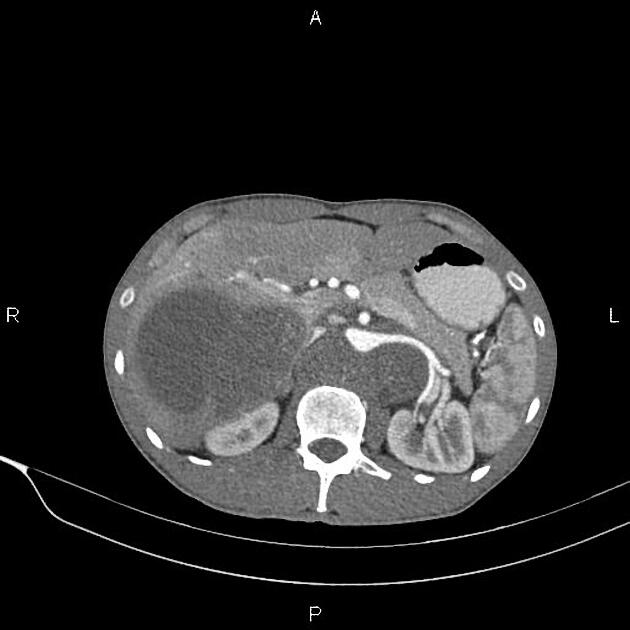
The floating aorta sign refers to displacing the abdominal aorta away from the vertebral column.
It is a radiographic sign of retroperitoneal masses and most commonly suggests a lymphoma diagnosis. Rarely, other diseases with diffuse retroperitoneal mass, such as Castleman's disease, primary retroperitoneal sarcomas, metastatic testicular cancer and tuberculous adenitis, may mimic a similar appearance.
Radiographic findings
On lateral lumbar spine radiographs, the expected location of the posterior aortic wall is expected to be ≤10 mm from the anterior margin of the spine in men and ≤7.3 mm in women.
Similarly, the anterior aortic wall is within 40 mm in men and 37.3 mm in women.
Any retroperitoneal masses arising posterior to the aorta can insinuate between the aorta and the vertebral column and displace the aorta anteriorly, hence the term floating aorta sign.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.