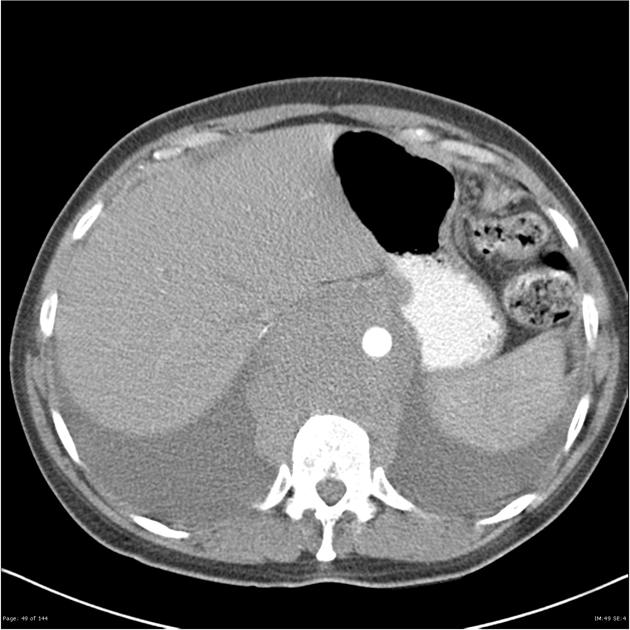
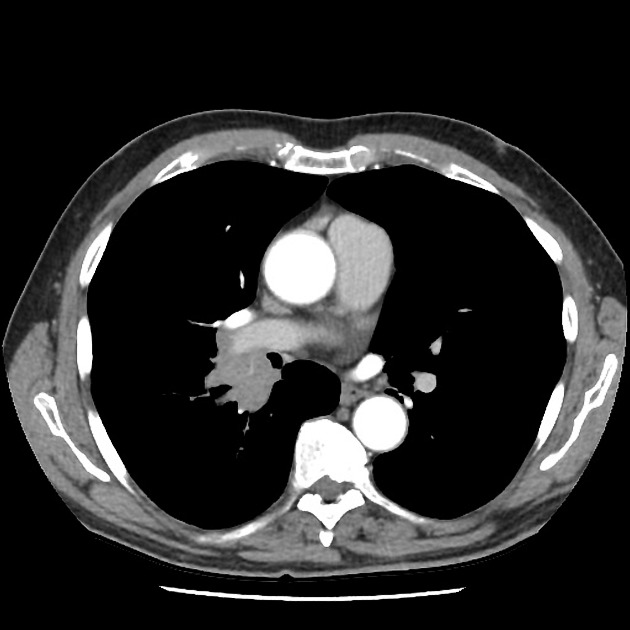
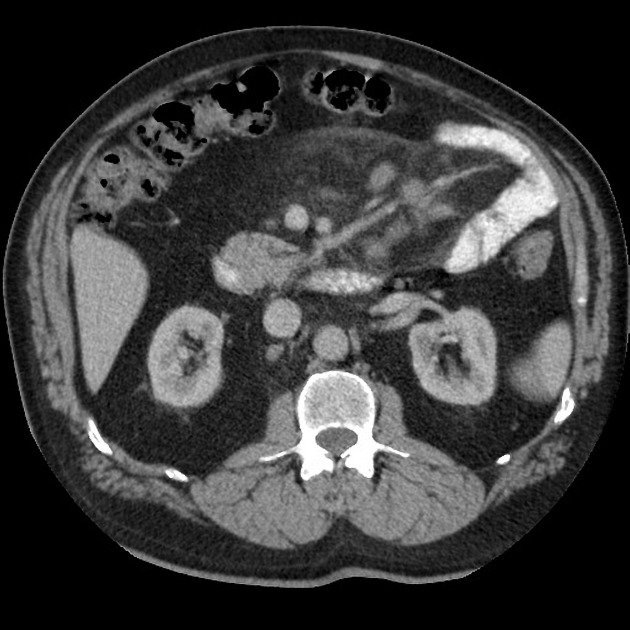
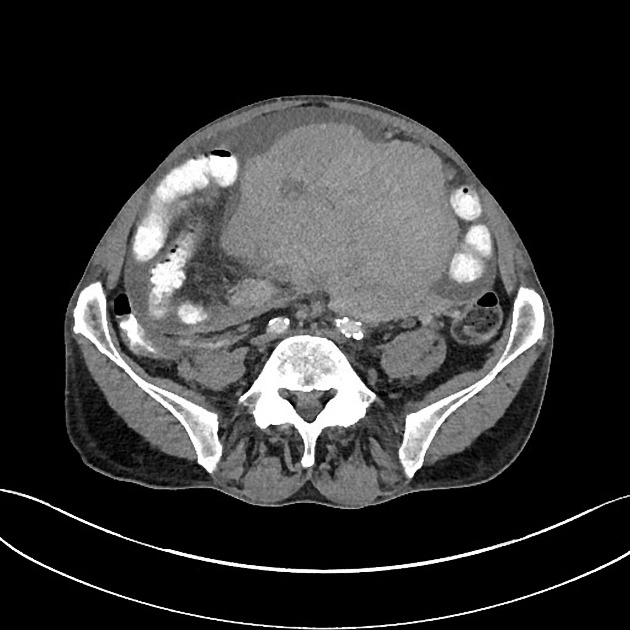
Follicular lymphoma is the most common subtype of indolent non-Hodgkin lymphoma (NHL), second most common overall, behind diffuse large B-cell lymphoma 6.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Estimated to account for ~45% of all NHL cases 1. Higher rates in North America and Europe 4.
Pathology
Nodal effacement by closely packed follicles containing small cleaved cells without nucleoli (centrocytes) and larger non-cleaved cells with moderate cytoplasm, open chromatin and multiple nucleoli (centroblasts).
Follicular lymphoma is categorized into grades according to the number of centroblasts per high-power fields (HPF) as follows5:
- grade 1: 0-5 centroblasts per HPF
- grade 2: 6-15 centroblasts per HPF
- grade 3: >15 centroblasts per HPF
Markers
- CD10: positive
- CD5: negative
- CD20: positive
Genetics
Translocation t(14;18) is found in the majority of patients with follicular lymphoma.
Treatment and prognosis
It is often indolent yet incurable with a high prevalence of residual mass post-treatment 2.
Complications
Transformation to a more aggressive type of NHL.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.