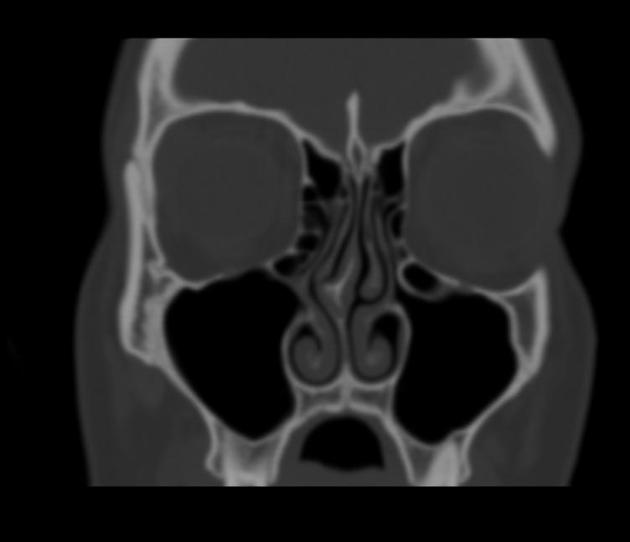
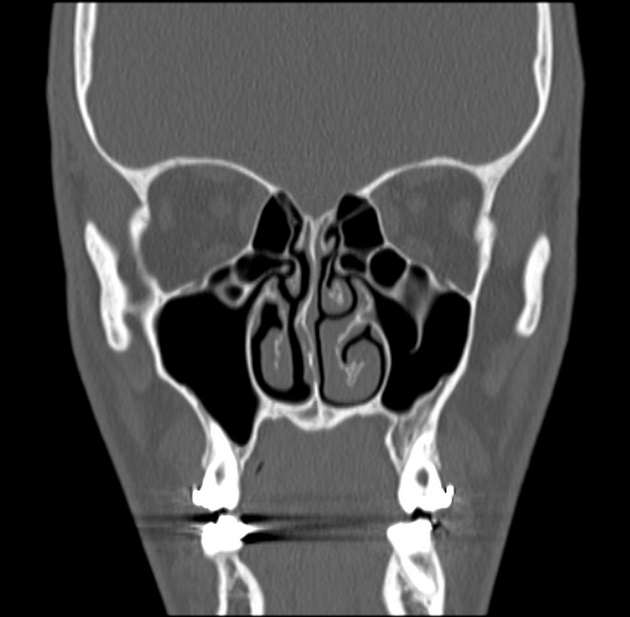
Haller cells
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Daniel J Bell had no recorded disclosures.
View Daniel J Bell's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Yuranga Weerakkody had no recorded disclosures.
View Yuranga Weerakkody's current disclosures- Infraorbital ethmoidal air cells
- Maxilloethmoidal cells
- Maxillo-ethmoidal cells
- Maxillo-ethmoidal cell
- Infraorbital ethmoidal air cell
- Haller's cell
- Haller's cells
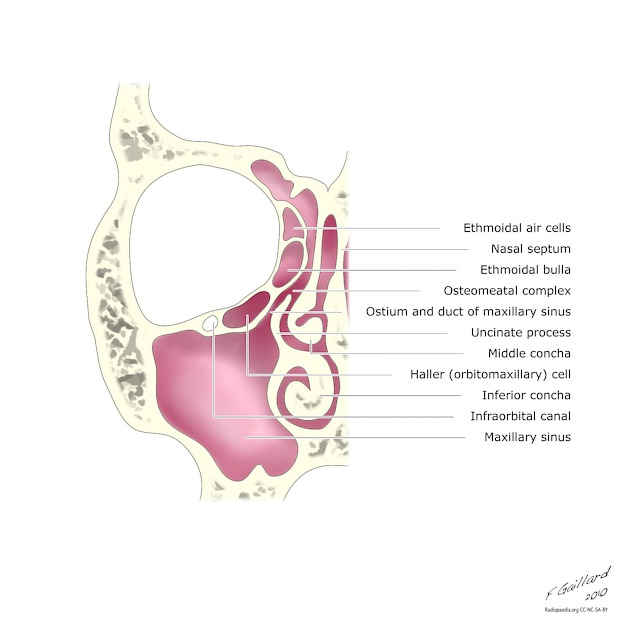
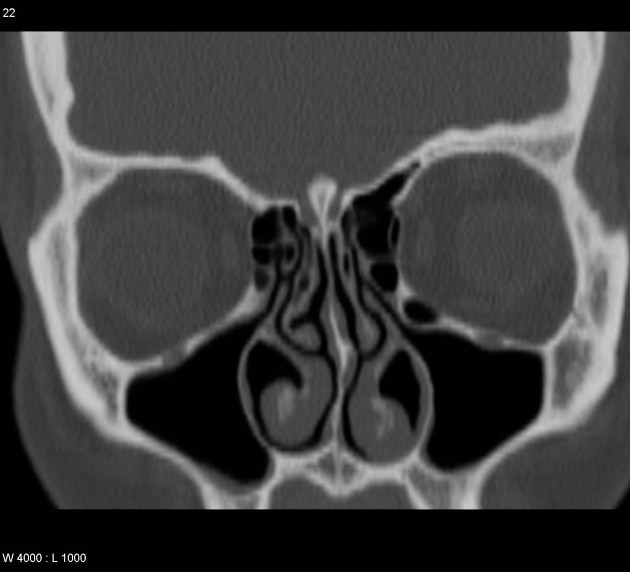
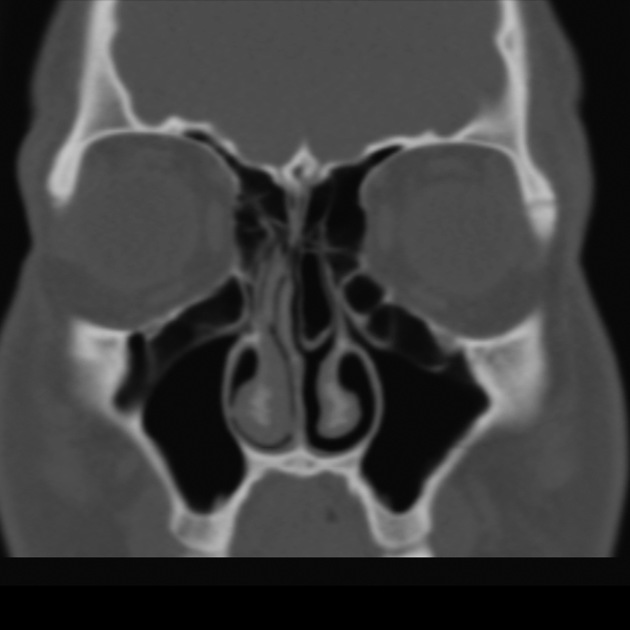
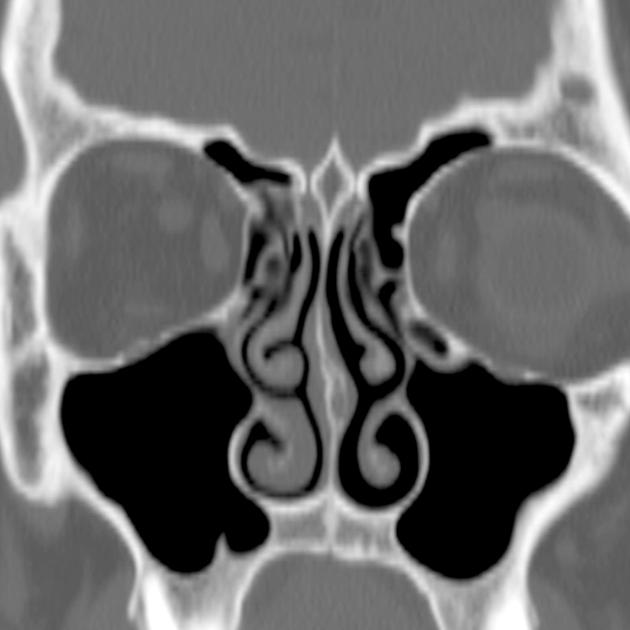
Haller cells, also known as infraorbital ethmoidal air cells, are ethmoid air cells located lateral to the maxillo-ethmoidal suture along the inferomedial orbital floor.
On this page:
Epidemiology
They are present in ~20% (range 2-45%) of patients, depending on their exact definition 1-3.
Clinical presentation
In most instances they are asymptomatic and (although some controversy exists 4,5) they are generally not thought to be associated with increased rates of sinusitis 3.
They may become clinically significant in a number of situations:
- become infected, with the potential for extension into the orbit
- may narrow the ipsilateral ostiomeatal complex (OMC) if large, thereby predisposing the ipsilateral maxillary antrum to obstruction 4
- may lead to inadvertent entry into the orbit if unrecognised at endoscopic surgery 4
History and etymology
They are named after Albrecht von Haller (1708-1777) 6, Swiss anatomist and physiologist; he was a qualified medical doctor but was unsuccessful in clinical practice.
See also
- agger nasi cells: anteriormost ethmoidal cells
- Onodi cells: sphenoethmoidal cells
- supraorbital air cells
References
- 1. Yousem DM. Imaging of sinonasal inflammatory disease. Radiology. 1993;188 (2): 303-14. Radiology (abstract) [pubmed citation]
- 2. Laine FJ, Smoker WR. The ostiomeatal unit and endoscopic surgery: anatomy, variations, and imaging findings in inflammatory diseases. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 1992;159 (4): 849-57. AJR Am J Roentgenol (abstract) [pubmed citation]
- 3. Stallman JS, Lobo JN, Som PM. The incidence of concha bullosa and its relationship to nasal septal deviation and paranasal sinus disease. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 2004;25 (9): 1613-8. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol (full text) [pubmed citation]
- 4. Endoscopic paranasal sinus surgery. Dale H. Rice, Steven D. Schaefer; with illustrations by Lewis E. Calver, Scott Thorn Barrows, Eli Ensor. Philadelphia : Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, c2004. ISBN:0781740770 (find it at amazon.com)
- 5. Diseases of the Sinuses: Diagnosis and Management. David W. Kennedy, William E. Bolger, S. James Zinreich. B.C. Decker ISBN:1550090453 (find it at amazon.com)
- 6. Frixione E. Albrecht von Haller (1708-1777). (2006) Journal of neurology. 253 (2): 265-6. doi:10.1007/s00415-006-0998-x - Pubmed
- 7. O'Brien WT, Hamelin S, Weitzel EK. The Preoperative Sinus CT: Avoiding a "CLOSE" Call with Surgical Complications. (2016) Radiology. 281 (1): 10-21. doi:10.1148/radiol.2016152230 - Pubmed
- 8. Raina A, Guledgud M, Patil K. Infraorbital Ethmoid (Haller's) Cells: A Panoramic Radiographic Study. Dentomaxillofac Radiol. 2012;41(4):305-8. doi:10.1259/dmfr/22999207 - Pubmed
- 9. Shpilberg K, Daniel S, Doshi A, Lawson W, Som P. CT of Anatomic Variants of the Paranasal Sinuses and Nasal Cavity: Poor Correlation With Radiologically Significant Rhinosinusitis but Importance in Surgical Planning. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015;204(6):1255-60. doi:10.2214/ajr.14.13762 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
Related articles: Anatomy: Head and neck
- skeleton of the head and neck
-
cranial vault
- scalp (mnemonic)
- fontanelle
-
sutures
- calvarial
- facial
- frontozygomatic suture
- frontomaxillary suture
- frontolacrimal suture
- frontonasal suture
- temporozygomatic suture
- zygomaticomaxillary suture
- parietotemporal suture (parietomastoid suture)
- occipitotemporal suture (occipitomastoid suture)
- sphenofrontal suture
- sphenozygomatic suture
- spheno-occipital suture (not a true suture)
- lacrimomaxillary suture
- nasomaxillary suture
- internasal suture
- basal/internal
- skull landmarks
- frontal bone
- temporal bone
- parietal bone
- occipital bone
- skull base (foramina)
-
facial bones
- midline single bones
- paired bilateral bones
- cervical spine
- hyoid bone
- laryngeal cartilages
-
cranial vault
- muscles of the head and neck
- muscles of the tongue (mnemonic)
- muscles of mastication
-
facial muscles
- epicranius muscle
- circumorbital and palpebral muscles
- nasal muscles
-
buccolabial muscles
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- levator labii superioris alaeque nasalis muscle
- levator labii superioris muscle
- zygomaticus major muscle
- zygomaticus minor muscle
- levator anguli oris muscle
- malaris muscle
- risorius muscle
- depressors, retractors and evertors of the lower lip
- depressor labii inferioris muscle
- depressor anguli oris muscle
- mentalis muscle
- compound sphincter
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- incisivus labii superioris muscle
- incisivus labii inferioris muscle
-
orbicularis oris muscle
- muscle of mastication
- modiolus
- elevators, retractors and evertors of the upper lip
- muscles of the middle ear
- orbital muscles
- muscles of the soft palate
- pharyngeal muscles
- suprahyoid muscles
- infrahyoid muscles
- intrinsic muscles of the larynx
- muscles of the neck
- platysma muscle
- longus colli muscle
- longus capitis muscle
- scalenus anterior muscle
- scalenus medius muscle
- scalenus posterior muscle
- scalenus pleuralis muscle
- sternocleidomastoid muscle
-
suboccipital muscles
- rectus capitis posterior major muscle
- rectus capitis posterior minor muscle
- obliquus capitis superior muscle
- obliquus capitis inferior muscle
- accessory muscles of the neck
- deep cervical fascia
-
deep spaces of the neck
- anterior cervical space
- buccal space
- carotid space
- danger space
- deep cervical fascia
- infratemporal fossa
- masticator space
- parapharyngeal space
- stylomandibular tunnel
- parotid space
- pharyngeal (superficial) mucosal space
- perivertebral space
- posterior cervical space
- pterygopalatine fossa
- retropharyngeal space
- suprasternal space (of Burns)
- visceral space
- surgical triangles of the neck
- orbit
- ear
- paranasal sinuses
- upper respiratory tract
- viscera of the neck
- blood supply of the head and neck
-
arterial supply
-
common carotid artery
- carotid body
- carotid bifurcation
- subclavian artery
- variants
-
common carotid artery
- venous drainage
-
arterial supply
- innervation of the head and neck
-
cranial nerves
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
-
trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- trigeminal ganglion
- ophthalmic division
- maxillary division
- mandibular division
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- (spinal) accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- parasympathetic ganglia of the head and neck
- cervical sympathetic ganglia
- greater occipital nerve
- third occipital nerve
-
cervical plexus
- muscular branches
- longus capitis
- longus colli
- scalenes
- geniohyoid
- thyrohyoid
-
ansa cervicalis
- omohyoid (superior and inferior bellies separately)
- sternothyroid
- sternohyoid
- phrenic nerve
- contribution to the accessory nerve (CN XI)
- cutaneous branches
- muscular branches
- brachial plexus
- pharyngeal plexus
-
cranial nerves
- lymphatic drainage of the head and neck
- embryological development of the head and neck





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.