Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Weerakkody Y, Feger J, Furaiji H, et al. Hoffa fracture. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 29 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-16584
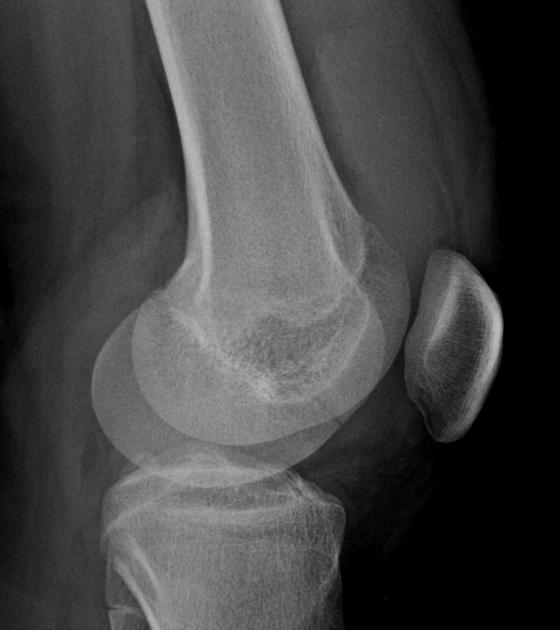
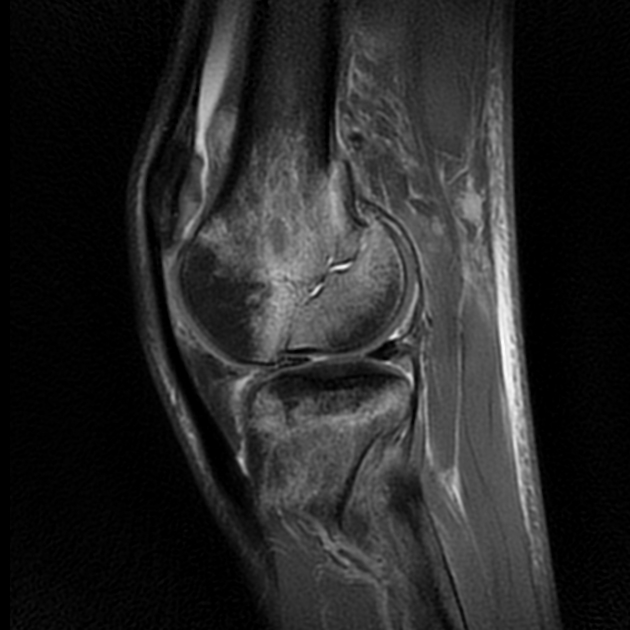
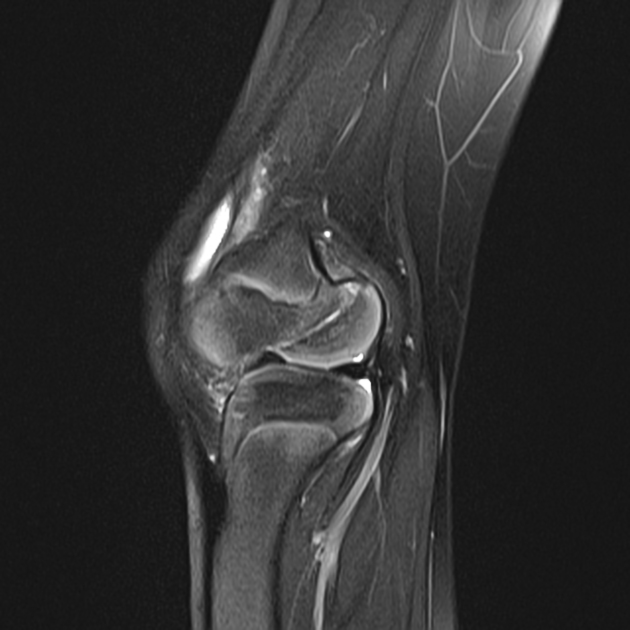
Hoffa fracture, also known as Busch-Hoffa fracture, is a type of distal condylar femoral fracture and is characterized by an associated fracture component in the coronal plane.
While they are rare in absolute numbers, they can account for approximately 40% of intercondylar fractures. They are typically seen in adults 4.
Hoffa fractures are intra-articular and characterized by a coronal plane fracture. They are typically seen after higher-energy trauma 4.
Location
Hoffa fragments are more commonly unicondylar and usually originate from the lateral femoral condyle. They can be occasionally bicondylar.
Plain radiograph
Initially, imaging evaluation of Hoffa fractures (as with other distal femoral fractures) is usually done with conventional radiographs. The fracture line is classically shown in the coronal plane and thus lateral views are essential to avoid overlooking a Hoffa fracture 8.
CT
Preoperative CT evaluation is considered to be useful particularly to assess fracture pattern 1.
Treatment and prognosis
At the time of writing, they are thought to be best treated by anatomical reduction and rigid fixation followed by early mobilization 2.
History and etymology
It is named after Albert Hoffa (1859-1907) who described it in 1888; he also described Hoffa fat pad 7.
-
1. Baker B, Escobedo E, Nork S, Henley M. Hoffa Fracture: A Common Association with High-Energy Supracondylar Fractures of the Distal Femur. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;178(4):994. doi:10.2214/ajr.178.4.1780994 - Pubmed
-
2. Gavaskar A, Tummala N, Krishnamurthy M. Operative Management of Hoffa Fractures--A Prospective Review of 18 Patients. Injury. 2011;42(12):1495-8. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.09.005 - Pubmed
-
3. Vaishya R, Singh A, Dar I, Singh A, Mittal V. Hoffa Fracture with Ipsilateral Patellar Dislocation Resulting from Household Trauma. Can J Surg. 2009;52(1):E3-4. PMC2637628 - Pubmed
-
4. Flanagin B, Cruz A, Medvecky M. Hoffa Fracture in a 14-Year-Old. Orthopedics. 2011;34(2):138. doi:10.3928/01477447-20101221-30 - Pubmed
-
5. Thakar C. The Hoffa Fracture--A Fracture Not to Miss. Emerg Med J. 2010;27(5):391-2. doi:10.1136/emj.2009.087213 - Pubmed
-
6. Allmann K, Altehoefer C, Wildanger G et al. Hoffa Fracture--A Radiologic Diagnostic Approach. J Belge Radiol. 1996;79(5):201-2. - Pubmed
-
7. Pires R, Giordano V, Fogagnolo F, Yoon R, Liporace F, Kfuri M. Algorithmic Treatment of Busch-Hoffa Distal Femur Fractures: A Technical Note Based on a Modified Letenneur Classification. Injury. 2018;49(8):1623-9. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2018.06.008 - Pubmed
-
8. Zhou Y, Pan Y, Wang Q, Hou Z, Chen W. Hoffa Fracture of the Femoral Condyle: Injury Mechanism, Classification, Diagnosis, and Treatment. Medicine (Baltimore). 2019;98(8):e14633. doi:10.1097/MD.0000000000014633 - Pubmed
Promoted articles (advertising)




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.