Hypothalamus
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Tariq Walizai had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Tariq Walizai's current disclosures- Hypothalami
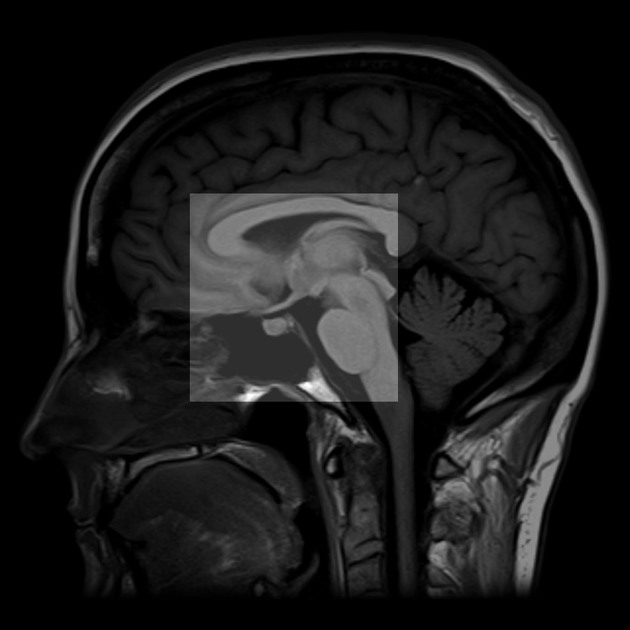
The hypothalamus (plural: hypothalami) is located, as the name would suggest, below the thalamus, and is intimately associated with both the limbic system and the pituitary gland.
Gross anatomy
Boundaries
Its boundaries are in some places poorly defined (outlined in blue in Figure 2):
anterior: lamina terminalis, with optic chiasm at its lower border and anterior commissure above
superior: an imaginary line drawn between the anterior and posterior commissures (AC-PC line)
posterior: an imaginary line sloping antero-inferiorly from the posterior commissure to the mammillary bodies
inferior (floor): infundibular stalk, tuber cinereum and mammillary bodies (from front to back)
Fibre tracts
postcommissural fornix: running posterior to the anterior commissure vertically down to end in the mamillary bodies
-
principal mammillary bundle: originates in the mamillary body and runs superiorly a short distance before dividing into
mammillothalamic tract (a.k.a. Vicq d'Azyr bundle): terminates in the anterior thalamic nucleus
mammillotegmental tract (smaller)
Nuclei
The hypothalamus is really a collection of nuclei arranged symmetrically around its floor and lateral walls and can be divided into medial and lateral areas.
Medial area
-
supraoptic (anterior)
supraoptic nucleus (medial part)
suprachiasmatic nucleus
medial preoptic nucleus
anterior nucleus
-
tuberal
dorsomedial nucleus
ventromedial nucleus
-
mammillary (posterior)
mammillary nuclei
posterior nucleus
Lateral area
-
supraoptic (anterior)
lateral preoptic nucleus
supraoptic nucleus (lateral part)
lateral nucleus (anterior part)
-
tuberal
lateral nucleus (tuberal part)
lateral tuberal nuclei
-
mammillary (posterior)
lateral nucleus (posterior part)
Arterial supply
tuberal: branches of PCOM and superior hypophyseal artery
posterior: branches of PCA
infundibulum: superior hypophyseal arteries from the ophthalmic segment of ICA (C6)
References
- 1. Saleem SN, Said AH, Lee DH. Lesions of the hypothalamus: MR imaging diagnostic features. Radiographics. 2007;27 (4): 1087-108. Radiographics (full text) - doi:10.1148/rg.274065123 - Pubmed citation
- 2. Kretschmann H, Weinrich W. Cranial Neuroimaging and Clinical Neuroanatomy. Thieme. (2004) ISBN:1588901459. Read it at Google Books - Find it at Amazon
Incoming Links
- Shapiro syndrome
- Stria terminalis
- Elevated prolactin (differential)
- Olfactory nerve
- Pituitary fossa
- Supraoptic nucleus
- Ependymal cells
- Deep brain stimulation
- Third ventricle
- Limbic system
- Congenital hypothyroidism
- Pilomyxoid astrocytoma
- Thalamus
- Tanycytes
- Hypothalamic hamartoma
- Suprasellar cistern lipoma
- Osteolipoma (intracranial)
- Langerhans cell histiocytosis (CNS manifestations)
- Central nervous system embryology
- Papez circuit
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.