The internal capsule (TA: capsula interna) is a deep subcortical structure that contains a concentration of afferent and efferent white matter projection fibres. Anatomically, this is an important area because of the high concentration of both motor and sensory projection fibres 1,2. Afferent fibres pass from cell bodies of the thalamus to the cortex, and efferent fibres pass from cell bodies of the cortex to the cerebral peduncle of the midbrain 2. Fibres from the internal capsule contribute to the corona radiata.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
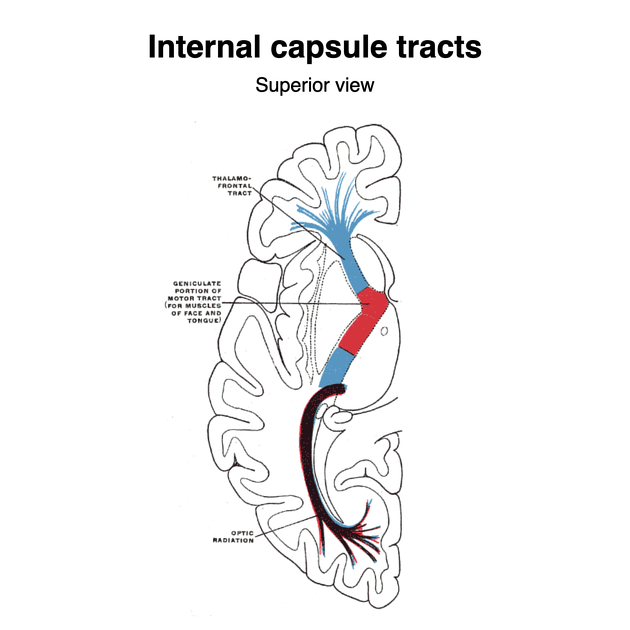
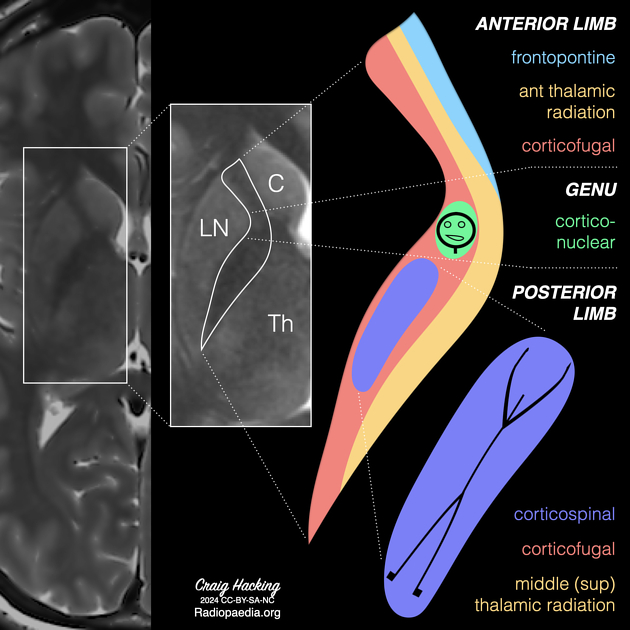
The internal capsule is made up of five parts. These are the anterior limb, genu, posterior limb, retrolentiform and sublentiform parts of the internal capsule 1,2:
-
anterior limb (anterior crus)
lies between the head of the caudate nucleus medially and the lentiform nucleus laterally
contains the anterior thalamic radiation and frontopontine fibres
-
genu
lies medial to the apex of the lentiform nucleus
contains corticonuclear fibres (previously called corticobulbar fibres)
-
posterior limb (posterior crus)
lies between the thalamus medially and the lentiform nucleus laterally
-
contains the
-
corticospinal fibres lying in the anterior two-thirds of the posterior limb
fibres from anterior to posterior: head, arm, hand, trunk, leg, perineum 2
middle (superior) thalamic radiation which contains somatosensory fibres from the ventral posterior thalamic nucleus
-
-
retrolentiform part
lies posterior to the lentiform nucleus
-
contains the
geniculocalcarine or optic radiation (posterior thalamic radiation) from the lateral geniculate nucleus
corticopontine fibres (parietopontine and occiptopontine fibres) 2
-
sublentiform part
lies inferior to the lentiform nucleus
contains the auditory radiations (inferior thalamic radiation) from the medial geniculate nucleus)and temporopontine fibres
Arterial supply
The blood supply of the internal capsule is variable but is commonly from small perforating branches of the middle cerebral artery and anterior cerebral artery. These include the lateral lenticulostriate arteries and the recurrent artery of Heubner respectively 3. In addition, the anterior choroidal artery from the internal carotid artery supplies the posterior limb and retrolentiform part of the internal capsule 3,4.
Radiographic features
CT
best appreciated on axial images at the level of the insular cortex
appears relatively hypodense to surrounding basal ganglia structures
MRI
in term neonates, internal capsule appears as higher T1-weighted and lower T2-weighted intensity when compared to basal ganglia and thalamus 6








 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.