Mucopolysaccharidoses (MPS) constitute a group of hereditary disorders, one of a number of lysosomal storage disorders, having in common an excessive accumulation of mucopolysaccharides secondary to deficiencies in specific enzymes (lysosomal hydrolases) responsible for degradation of mucopolysaccharides (also known as glycosaminoglycans) 5.
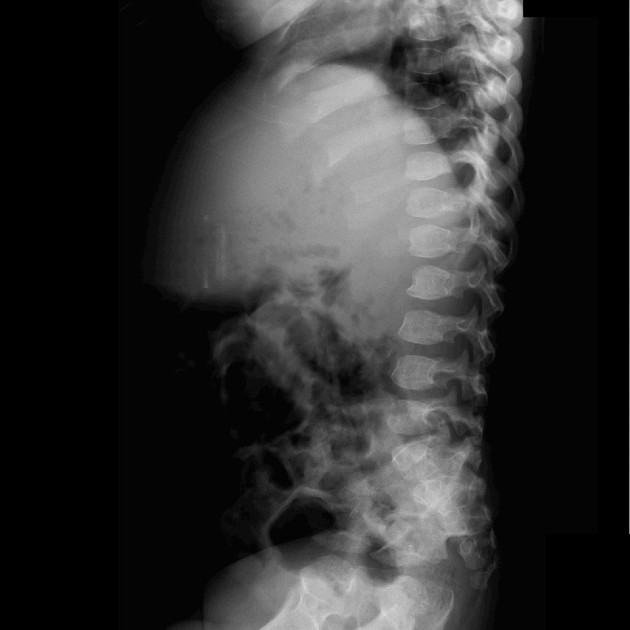
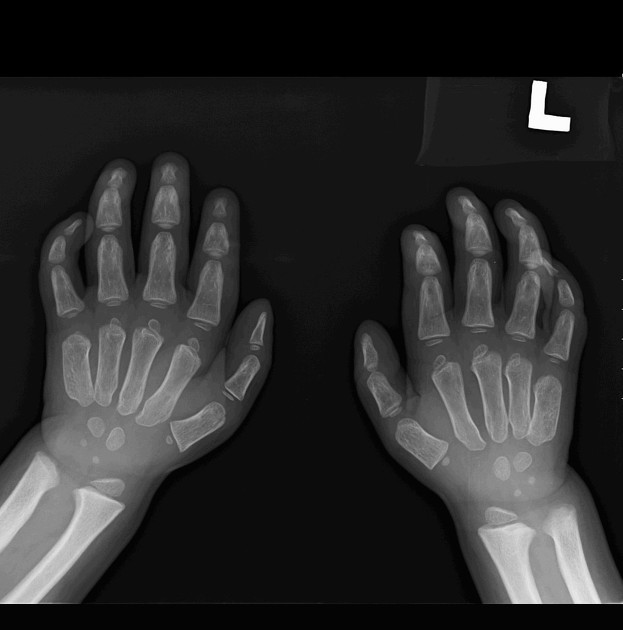
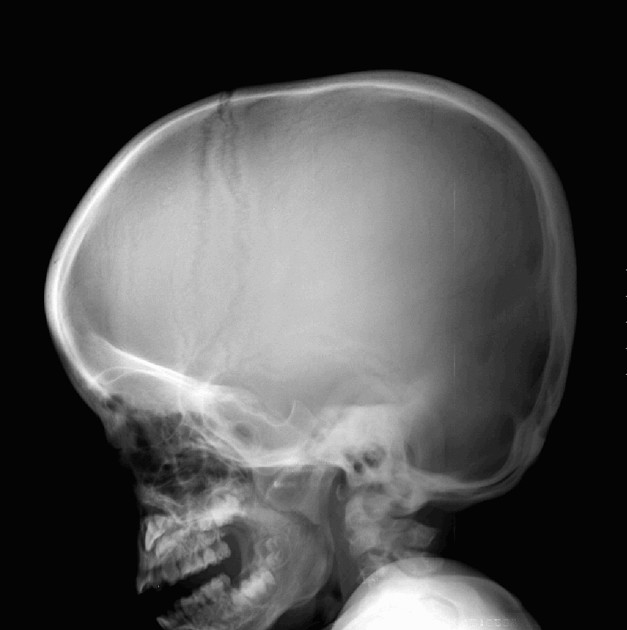
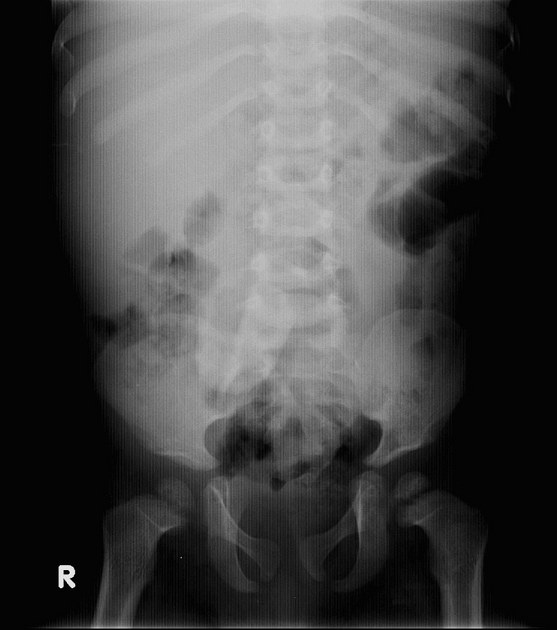
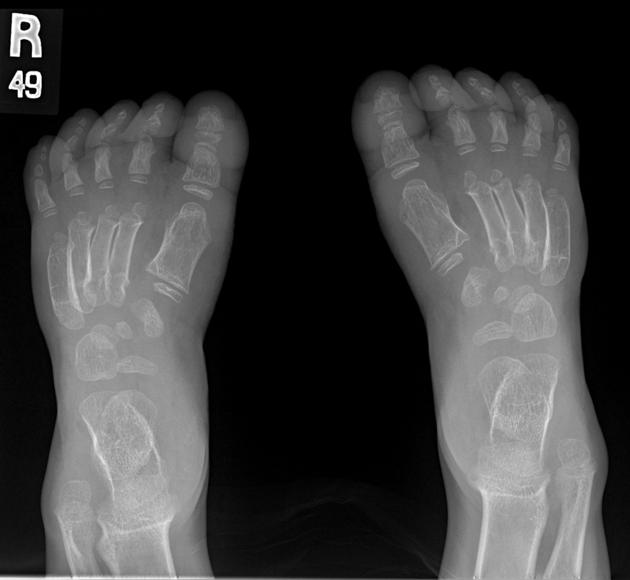
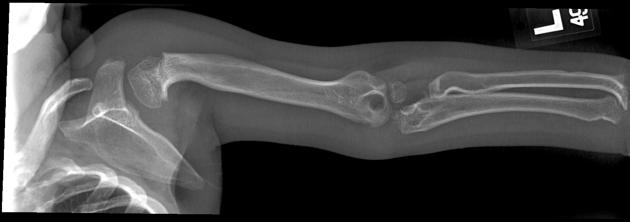
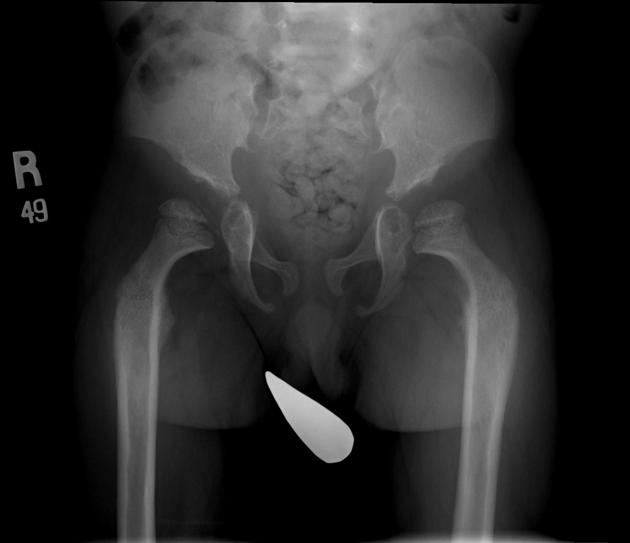
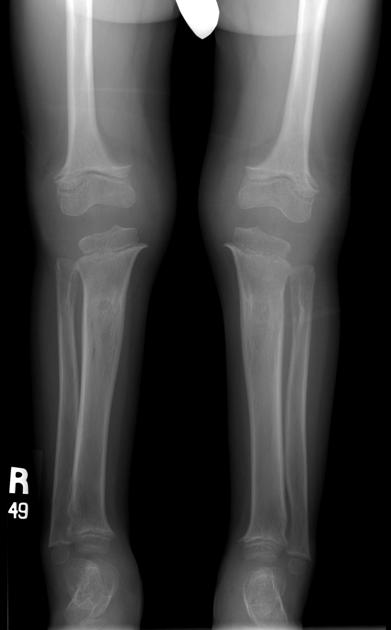
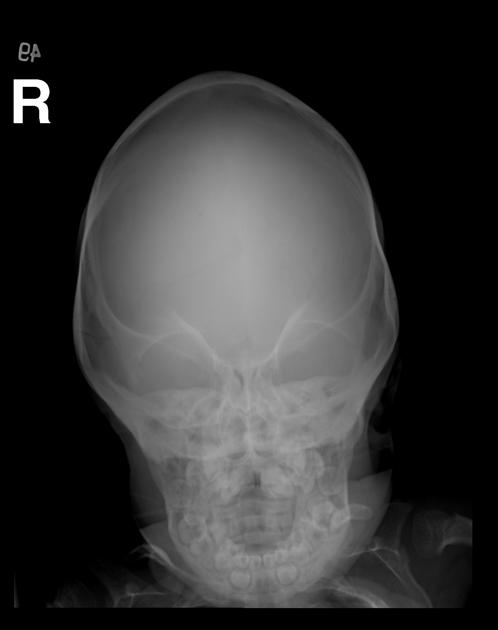
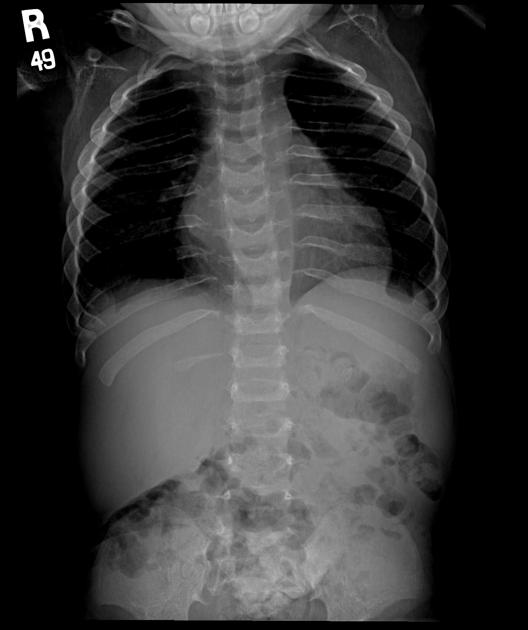
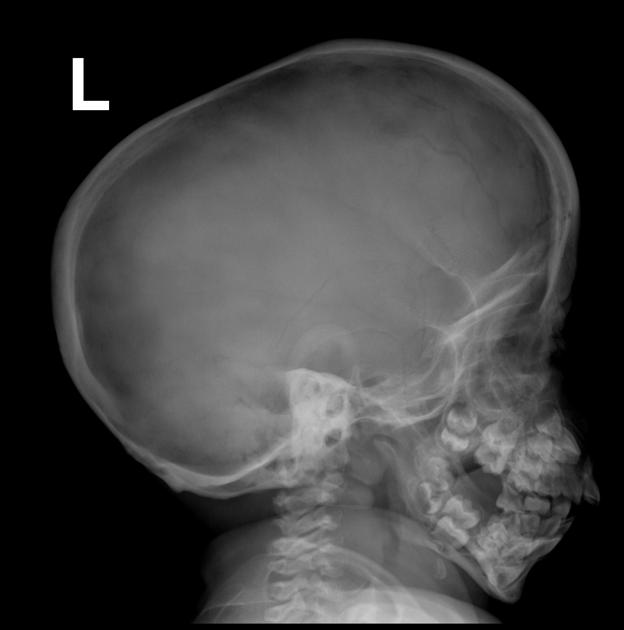
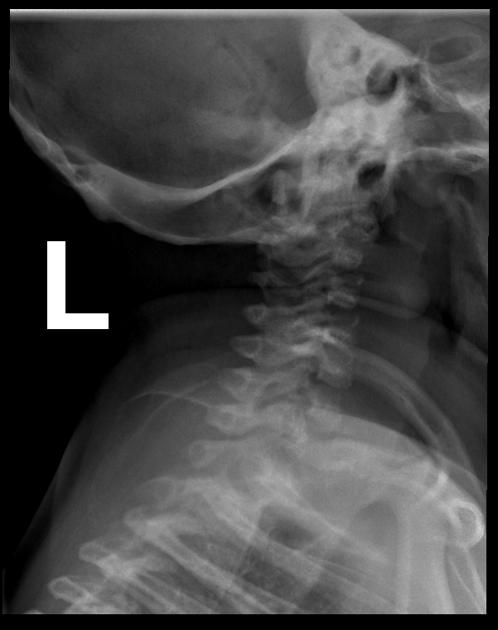
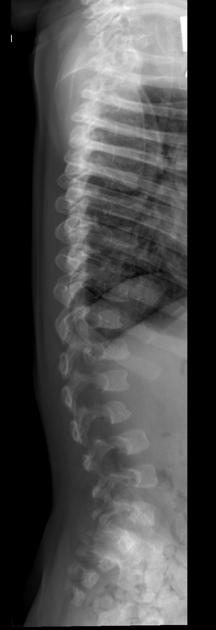
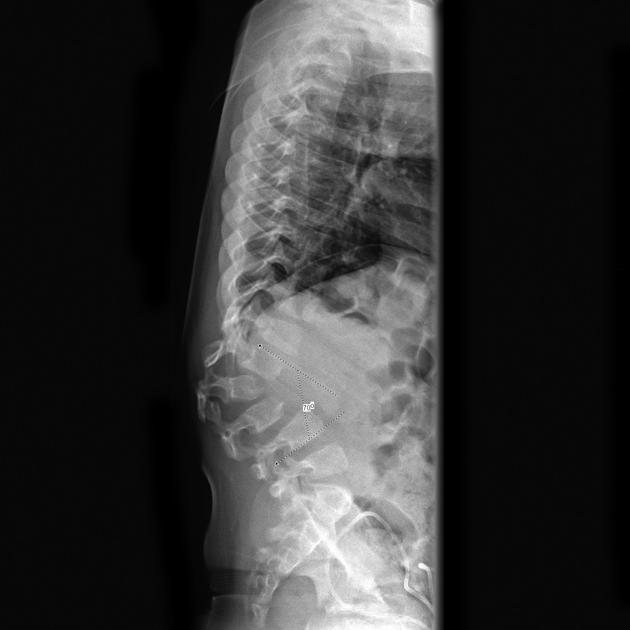
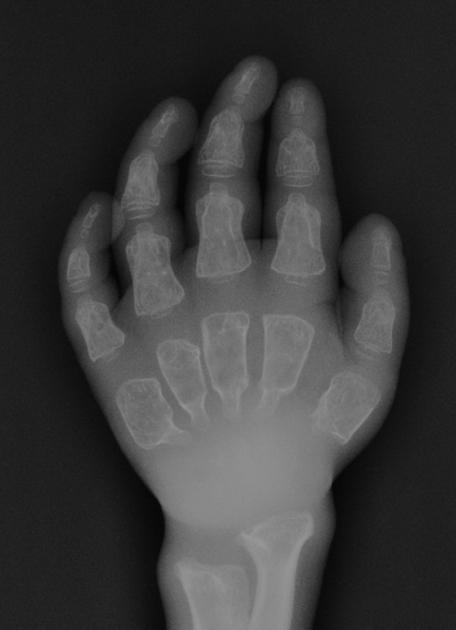
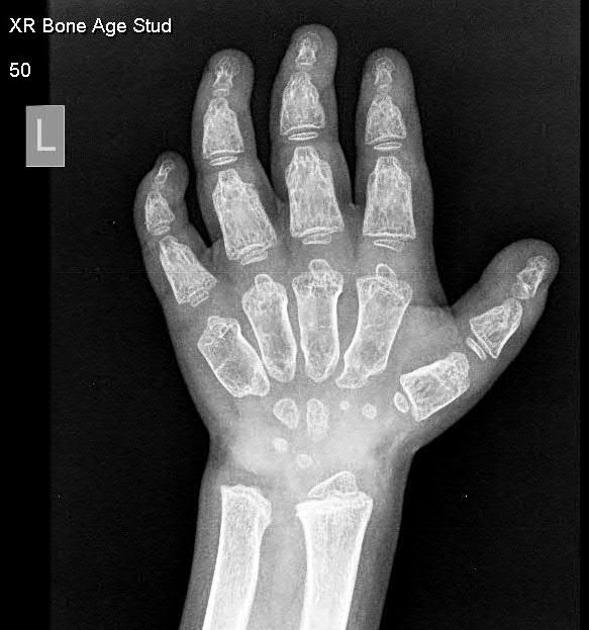
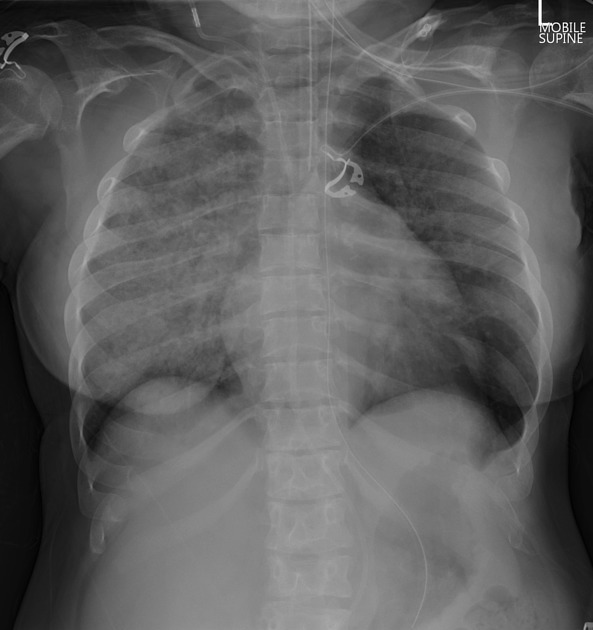
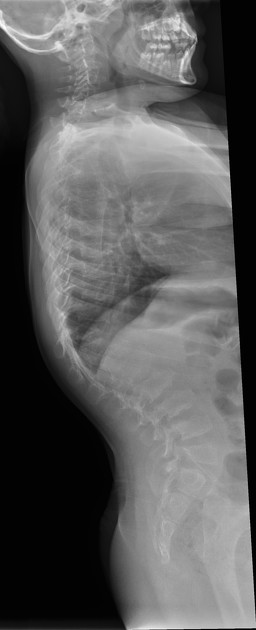
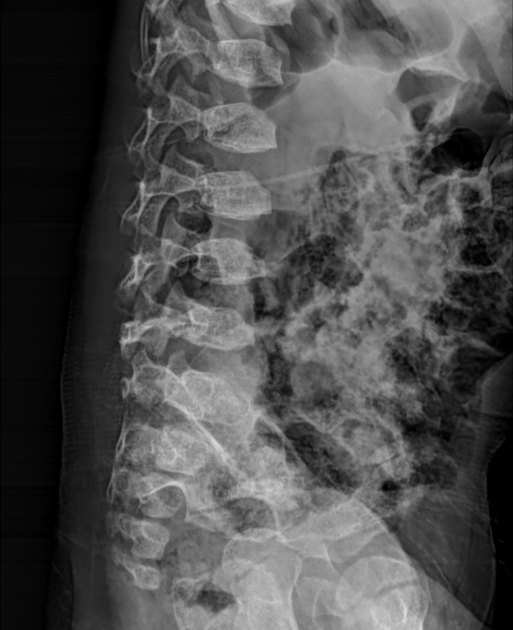
Several distinctive types of mucopolysaccharidoses have been described, each with distinctive clinical and radiologic features. Hurler (MPS-IH) and Morquio syndrome (MPS-IV) are perhaps most well known radiographically.
On this page:
Images:
Epidemiology
Mucopolysaccharidoses are rare with an overall estimated incidence of 1:25,000 5. Most are inherited as autosomal recessive traits, similar to most other enzyme deficiencies (MPS type II is the exception, inherited as an X-linked mutation) 5.
Diagnosis
The specific diagnosis of any of these conditions is made on the basis of the patient's age at onset, the level of neurologic stunting, the amount of corneal clouding, and other clinical features. With the exception of Morquio syndrome, all the mucopolysaccharidoses are marked by excessive urinary excretion of glycosaminoglycans; dermatan sulfate, keratan sulfate, chondroitin sulfate, hyaluronan and heparan sulfate 5.
Subtypes
- MPS I
- MPS IH: Hurler syndrome (most severe)
- MPS IS: Scheie syndrome (intermediate severity)
- MPS I H-S: Hurler-Scheie syndrome (least severe)
- MPS II: Hunter syndrome
- neuropathic (severe)
- non-neuropathic (mild)
- MPS III: Sanfilippo syndrome
- MPS IV: Morquio syndrome
- MPS VI: Maroteaux-Lamy syndrome
- MPS VII: Sly syndrome
- MPS IX: Natowicz syndrome





 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.