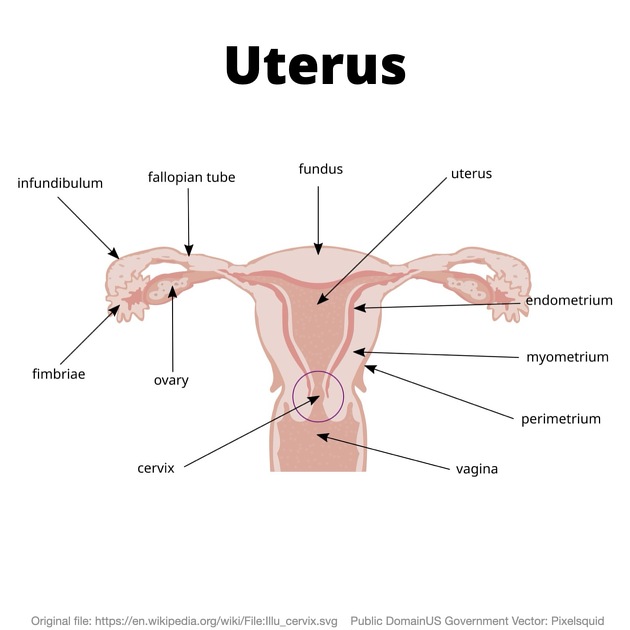
The myometrium is the muscular middle layer of the uterus. It comprises most of the thickness of the uterine wall and is situated between the inner endometrium and the outer serosa/perimetrium.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Though initially thought to be a homogenous structure histologically, MRI has enabled the division of the myometrium into two anatomically and functionally distinct layers - the junctional zone and the outer myometrium.
Junctional zone
The junctional zone is the interface between the endometrium and myometrium. It is responsible for normal trophoblastic invasion into the myometrium during placentation 1. This is important for vascular supply to the growing embryo through access to the spiral arteries of the myometrium 2.
Outer myometrium
The outer myometrium is composed mostly of smooth muscle fibers and connective tissue. It is anatomically separated into the fundal, body (upper) and isthmal (lower) segments 3.
The outer myometrium is largely responsible for the uterus' rhythmic, coordinated muscular contraction. The fundal and body segments contract during labor, while the isthmal segment relaxes to encourage the fetus through the cervix ref.
Blood supply
The arterial supply and venous drainage are the same for all sections of the uterine wall ref.
Uterine arteries (branches of the anterior division of internal iliac artery) and the ovarian artery (branch of the abdominal aorta) pass through the myometrium toward the endometrium, supplying both tissues along the way ref.
Venous drainage occurs via the uterine veins, which drain to the internal iliac veins ref.
Radiographic features
Ultrasound and MRI are the best imaging modalities to assess both the uterus proper and the myometrial layer. Both modalities are capable of assessing the most common myometrial pathologies, namely adenomyosis and leiomyoma ref.
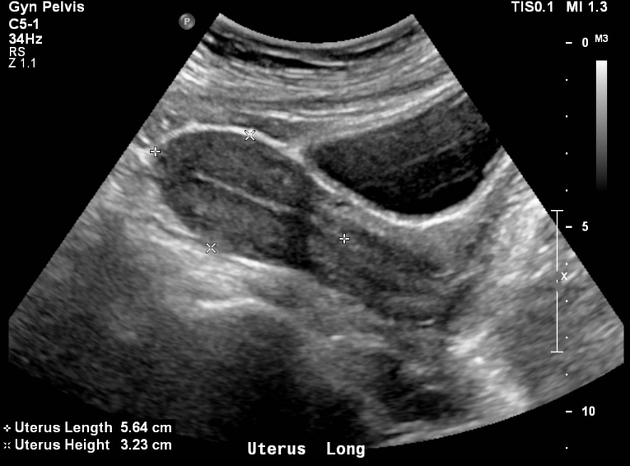
Ultrasound
The junctional zone appears as a hypoechogenic halo just deep to the myometrium that surrounds the relatively hyperechoic endometrium ref.
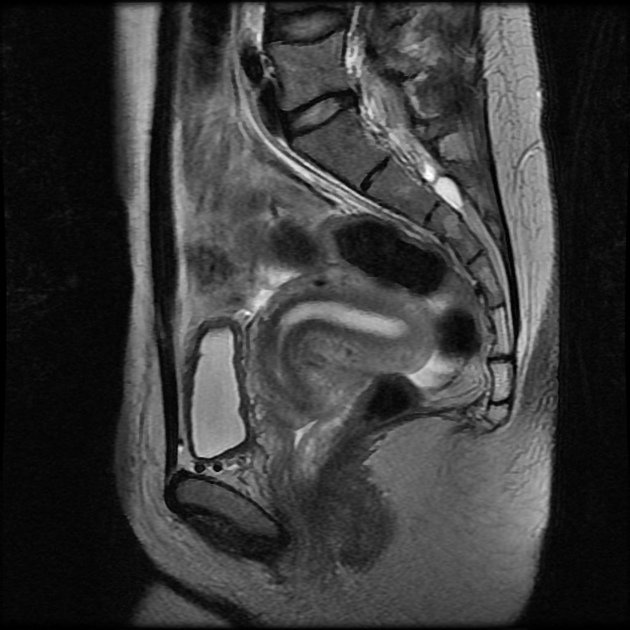
MRI
The junction zone is as a thin region of low signal on T2-weighted MRI just deep to the myometrium, reflecting its lower water content 1. The endometrium has a comparatively high T2-signal ref.
The outer myometrial zone is intermediate T2 signal that comprises the bulk of the thickness of the uterine wall.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.