Optic chiasm
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
At the time the article was created Craig Hacking had no recorded disclosures.
View Craig Hacking's current disclosuresAt the time the article was last revised Elmira Hassanzadeh had no financial relationships to ineligible companies to disclose.
View Elmira Hassanzadeh's current disclosures- optic chiasma
- chiasm
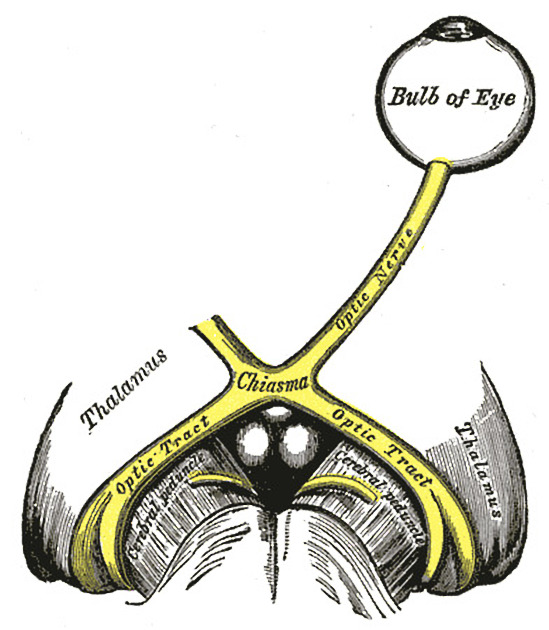
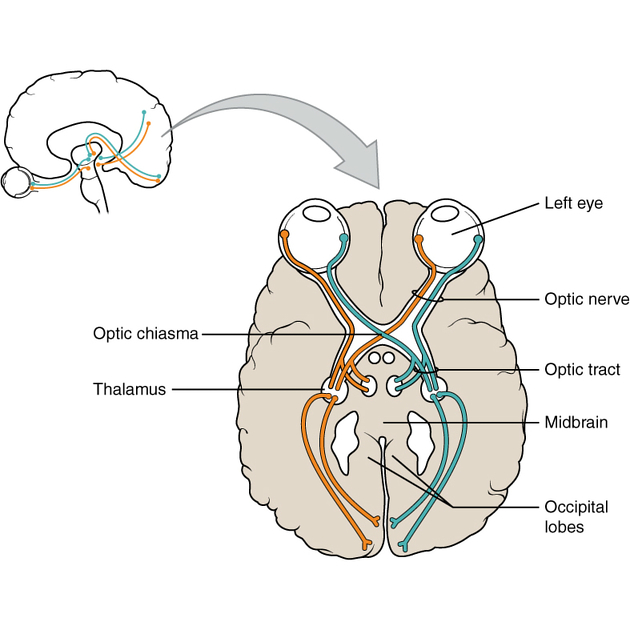
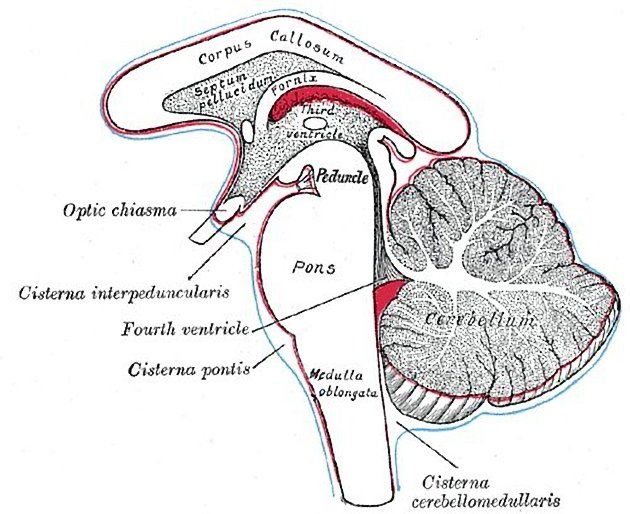
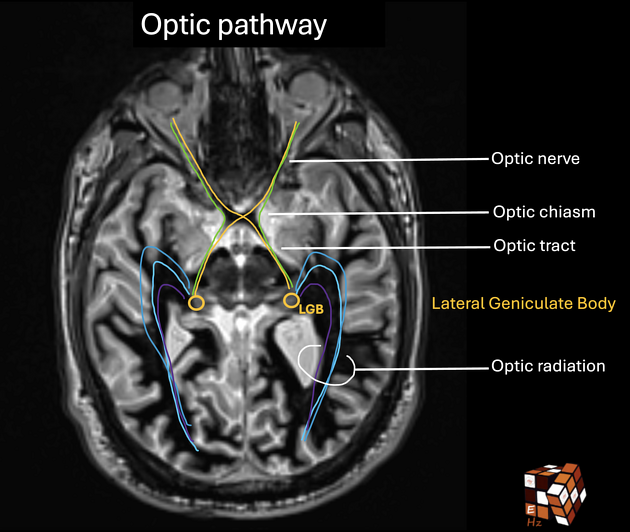
The optic chiasm or chiasma is the midline structure where the nasal (medial) fibres of the optic nerves decussate to continue posteriorly as the optic tracts. It lies in the chiasmatic cistern and along with the pituitary stalk, is completely encircled by the circle of Willis.
On this page:
Gross anatomy
Relations
The circle of Willis encircles the pituitary stalk and optic chiasma.
lateral: anterior perforated substance
anterior: optic nerves
posterior: optic tracts, tuber cinereum, pituitary stalk, mammillary bodies, posterior perforated substance
superior: supraoptic recess of the third ventricle, anterior commissure
superoposterior: hypothalamus
inferior: suprasellar cistern
The anterior-to-posterior location of the chiasm relative to the pituitary fossa is variable 4:
prefixed: tuberculum sellae (15%)
normal: diaphragma sellae (70%)
postfixed: dorsum sellae (15%)
Historically, it has been believed that the crossing fibres made an anterior bend into the prechiasmatic optic nerve; this is known as Wilbrand knee. However, this has been suggested to possibly be artifactual ref.
Blood supply
Small branches of the anterior cerebral artery and the superior hypophyseal artery supply the chiasm and intracranial portion of the optic nerves whereas the optic tracts are supplied by small branches of the anterior choroidal and posterior communicating arteries.
Related pathology
Lesions compressing the chiasm classically produce the visual field defect of bitemporal hemianopia, where there is loss of the temporal fields.
References
- 1. Keith L. Moore, Arthur F. Dalley, A. M. R. Agur. Clinically Oriented Anatomy. (2013) ISBN: 9781451119459 - Google Books
- 2. Last, R. J., McMinn, R. M. H.. Last's Anatomy, Regional and Applied. (1994) ISBN: 044304662X - Google Books
- 3. Paul Butler, Adam Mitchell, Jeremiah C. Healy. Applied Radiological Anatomy. (2012) ISBN: 9780521766661 - Google Books
- 4. Gulsen S, Dinc A, Unal M, Cantürk N, Altinors N. Characterization of the Anatomic Location of the Pituitary Stalk and Its Relationship to the Dorsum Sellae, Tuberculum Sellae and Chiasmatic Cistern. J Korean Neurosurg Soc. 2010;47(3):169-73. doi:10.3340/jkns.2010.47.3.169 - Pubmed
Incoming Links
- Adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma
- Diaphragma sellae
- Wilbrand knee (optic radiation)
- Medical abbreviations and acronyms (O)
- Lymphocytic hypophysitis
- Pituitary fossa
- Pituitary lymphoma
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Non-decussating retinal-fugal fibre syndrome
- Hypothalamus
- Optic nerve
- Pituitary stalk
- Marcus Gunn pupil
- Tuber cinereum
- Body of sphenoid
- Pituitary macroadenoma
- Pituitary MRI (an approach)
- Pituitary metastasis
- Pituitary stone
- Rathke cleft cyst
- Pituitary macroadenoma
- Tuberculum sellae meningioma
- Optic nerve glioma (pilocytic astrocytoma) - neurofibromatosis type 1
- Intracranial epidermoid cyst
- Bilateral cavernous segments internal carotid artery aneurysms
- Pituitary macroadenoma with apoplexy
- Normal MRI orbits
- Tuberculum sellae meningioma
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Anterior clinoid process meningioma
- Trigeminal schwannoma
- Optic neuritis
- Optic nerve and chiasm (Gray's illustration)
- Anophthalmia
- Pituitary xanthogranuloma
- Planum sphenoidale meningioma
- Pituitary apoplexy
- Hypothalamitis regression after steroid administration
- Neurofibromatosis type 1 - with optic pathway gliomas
- Optic pathway glioma
Related articles: Anatomy: Brain
-
brain
- grey matter
- white matter
-
cerebrum
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- frontal lobe
- parietal lobe
-
occipital lobe
- occipital pole
- lingual gyrus
- fusiform gyrus (Brodmann area 37)
- calcarine (visual) cortex
- cuneus
- temporal lobe
- basal forebrain
- limbic system
- insula
-
cerebral sulci and fissures (A-Z)
- calcarine fissure
- callosal sulcus
- central (Rolandic) sulcus
- cingulate sulcus
- collateral sulcus
- inferior frontal sulcus
- inferior occipital sulcus
- inferior temporal sulcus
- interhemispheric fissure
- intraparietal sulcus
- lateral (Sylvian) sulcus
- lateral occipital sulcus
- marginal sulcus
- occipitotemporal sulcus
- olfactory sulcus
- paracentral sulcus
- paraolfactory sulcus
- parieto-occipital fissure
- posterior parolfactory sulcus
- precentral sulcus
- preoccipital notch
- postcentral sulcus
- rhinal sulcus
- rostral sulcus
- subparietal sulcus
- superior frontal sulcus
- superior occipital sulcus
- superior temporal sulcus
- cortical histology
- cerebral lobes and gyri
- white matter tracts
- deep grey matter
-
pituitary gland
- posterior pituitary and stalk (part of diencephalon)
- anterior pituitary
- inferior hypophyseal arterial circle
- diencephalon
-
cerebral hemisphere (telencephalon)
-
brainstem
- midbrain (mesencephalon)
- pons (part of metencephalon)
- medulla oblongata (myelencephalon)
- white matter
-
grey matter
- non-cranial nerve
-
cranial nerve nuclei
- oculomotor nucleus
- Edinger-Westphal nucleus
- trochlear nucleus
- motor nucleus of CN V
- mesencephalic nucleus of CN V
- main sensory nucleus of CN V
- spinal nucleus of CN V
- abducent nucleus
- facial nucleus
- superior salivatory nucleus
- cochlear nuclei
- vestibular nuclei
- inferior salivatory nucleus
- solitary tract nucleus
- ambiguus nucleus
- dorsal vagal motor nucleus
- hypoglossal nucleus
-
cerebellum (part of metencephalon)
- vermis
- cerebellar hemisphere
- cerebellar peduncles
- cranial meninges (meninx primitiva)
- CSF spaces
-
cranial nerves (mnemonic)
- olfactory nerve (CN I)
- optic nerve (CN II)
- oculomotor nerve (CN III)
- trochlear nerve (CN IV)
- trigeminal nerve (CN V) (mnemonic)
- abducens nerve (CN VI)
- facial nerve (CN VII) (segments mnemonic | branches mnemonic)
-
vestibulocochlear nerve (CN VIII)
- vestibular ganglion (Scarpa's ganglion)
- glossopharyngeal nerve (CN IX)
- vagus nerve (CN X)
- spinal accessory nerve (CN XI)
- hypoglossal nerve (CN XII)
- functional neuroanatomy
- CNS development
- cerebral vascular supply
- arteries
- vascular territories
-
circle of Willis
- internal carotid artery (ICA) (segments)
- vertebral artery
-
normal variants
- intracranial arterial fenestration
- internal carotid artery (ICA)
- anterior cerebral artery (ACA)
- middle cerebral artery (MCA)
- posterior cerebral artery (PCA)
- basilar artery
- persistent carotid-vertebrobasilar artery anastomoses (mnemonic)
- vertebral artery
- ophthalmic artery
-
cerebral venous system
-
dural venous sinuses
- basilar venous plexus
- cavernous sinus (mnemonic)
- clival diploic veins
- inferior petro-occipital vein
- inferior petrosal sinus
- inferior sagittal sinus
- intercavernous sinus
- internal carotid artery venous plexus of Rektorzik
- jugular bulb
- marginal sinus
- occipital sinus
- sigmoid sinus
- sphenoparietal sinus
- straight sinus
- superior petrosal sinus
- superior sagittal sinus
- torcula herophili
- transverse sinus
-
cerebral veins
-
superficial veins of the brain
- superior cerebral veins (superficial cerebral veins)
- inferior cerebral veins
- superficial middle cerebral vein
- superior anastomotic vein (of Trolard)
- inferior anastomotic vein (of Labbe)
-
superficial veins of the brain
-
deep veins of the brain
- great cerebral vein (of Galen)
- venous circle of Trolard
- normal variants
-
dural venous sinuses
- arteries
- glymphatic pathway






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.