Ovarian tumours are relatively common and account for ~6% of female malignancies. This article focuses on the general classification of ovarian tumours. For specific tumour features, please refer to the relevant subarticles.
Pathology
Subtypes
Primary ovarian tumours
Surface epithelial-stromal ovarian tumours (60-70%):
-
ovarian serous tumours
- ovarian serous cystadenoma: ~60% of serous tumours
- ovarian borderline serous cystadenoma: ~15% of serous tumours
- ovarian serous cystadenocarcinoma: ~25% of serous tumours; commonest malignant ovarian tumour
-
ovarian mucinous tumours: ~20% of all ovarian tumours 11
- ovarian mucinous cystadenoma: ~80% of mucinous tumours
- ovarian borderline mucinous cystadenoma: 10-15% of mucinous tumours
- ovarian mucinous cystadenocarcinoma: 5-10% of mucinous tumours
- ovarian endometrioid tumour: 8-15% of all ovarian tumours
- clear cell ovarian carcinoma: ~5% of ovarian cancer
- Brenner tumour: ~2.5% of ovarian epithelial neoplasms
- squamous cell carcinoma of the ovary
- ovarian cystadenofibroma* / ovarian adenofibroma: can be serous, mucinous, endometrioid, clear cell or mixed
- ovarian cystadenocarcinofibroma: extremely rare
- ovarian fibrosarcoma
- undifferentiated carcinoma of the ovary: ~4% of all ovarian tumours
* sometimes classified as a separate category rather than under epithelial 7
Germ cell ovarian tumours (~20%):
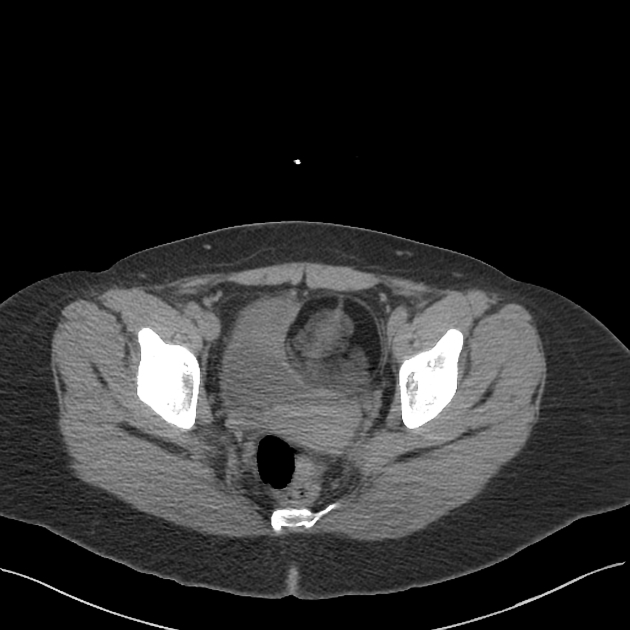
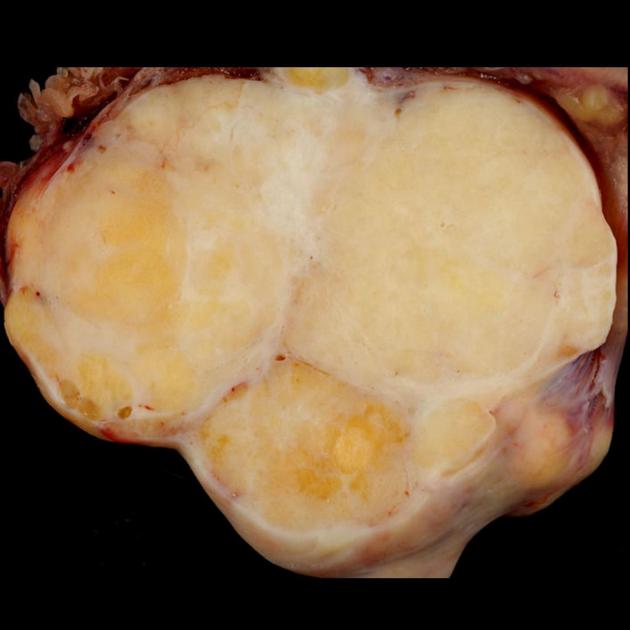
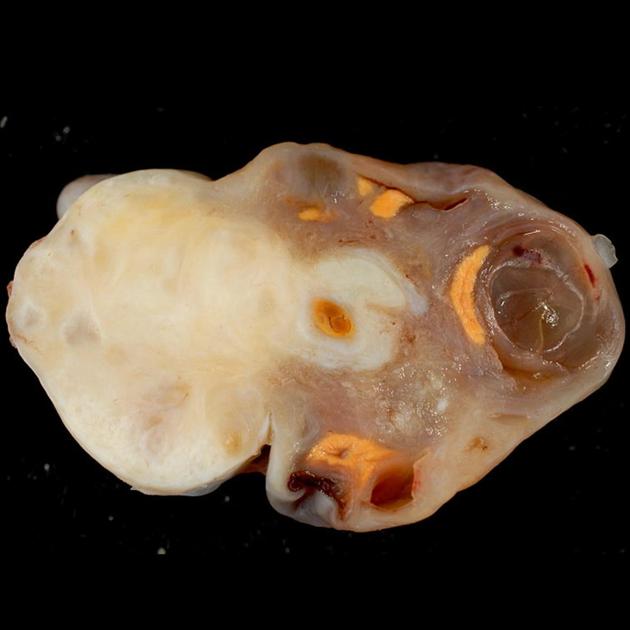
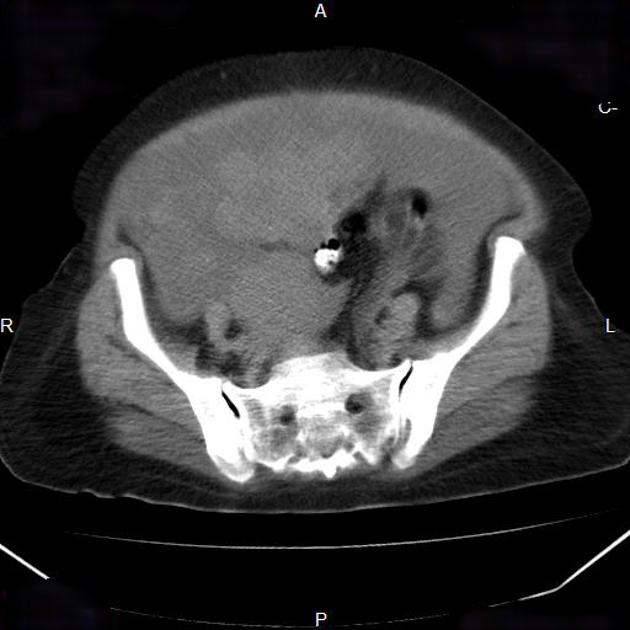
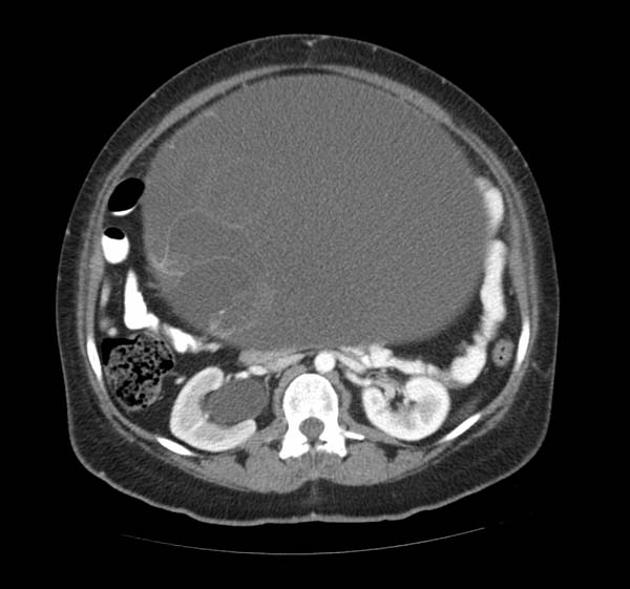
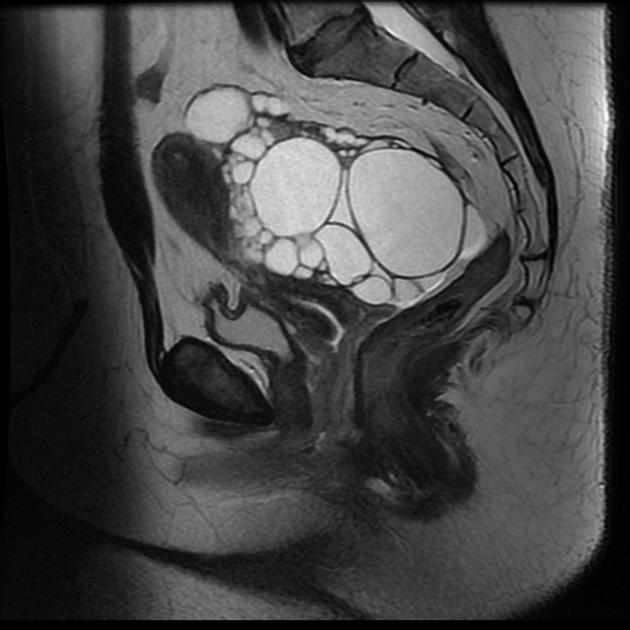
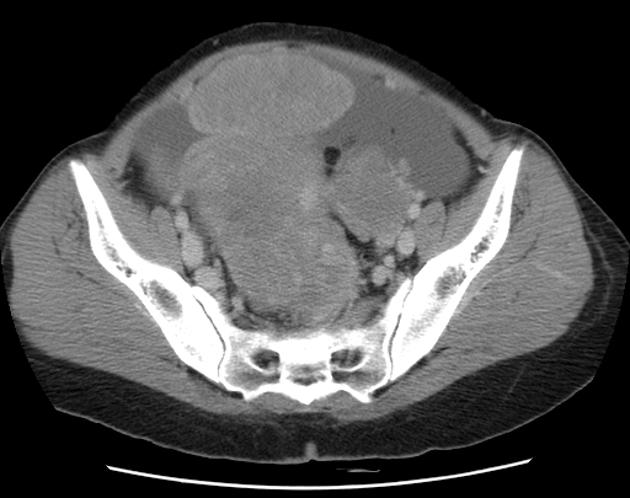
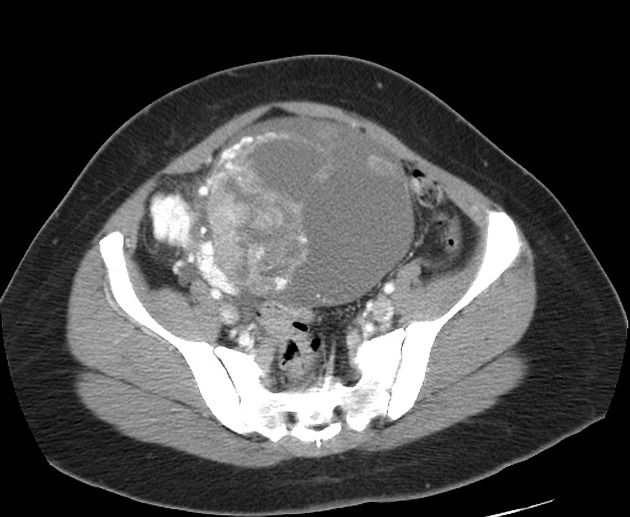
- ovarian teratoma: the commonest primary benign tumour of the ovary
- ovarian dysgerminoma
- ovarian yolk sac tumour: endodermal sinus tumour
- ovarian embryonal carcinoma
-
ovarian choriocarcinoma: <1% of ovarian tumours
- pure primary ovarian choriocarcinoma: extremely rare 2
- malignant mixed germ cell tumour of the ovary
Sex cord / stromal ovarian tumours (8-10%):
-
ovarian fibrothecoma: ~5% of ovarian tumours
- ovarian fibroma: ~4% of ovarian tumours
- ovarian thecoma: ~1% of ovarian tumours
- sclerosing stromal tumour of the ovary: rare 9
- ovarian Sertoli-Leydig cell tumour - ovarian androblastoma: ~0.5% of ovarian tumours
- granulosa cell tumour of the ovary: commonest malignant sex cord tumour
- small cell carcinoma of the ovary 15
Mixed
These are uncommon:
Other
- ovarian lymphoma
-
metastases to the ovary
- Krukenberg tumour
- other metastatic lesions to the ovary
Classification according to morphology
Predominantly cystic
- serous cystadenoma
- mucinous cystadenoma
- mature cystic teratoma
- serous cystadenocarcinoma
- mucinous cystadenocarcinoma
Predominantly solid
- Brenner tumour
- thecoma
- fibroma
- endometroid granulosa cell tumours
- dysgerminoma
- endodermal sinus tumour (yolk sac tumour)
- metastatic
Serological tests
- CA-125 levels: elevated in most ovarian malignancies (~80% in general); some mucinous and germ cell tumours may not secrete this marker
- AFP levels: elevated particularly with immature ovarian teratomas (~50% of cases) and ovarian yolk sac tumours
- β HCG: in a small number of dysgerminomas
- human epididymis protein 4 (HE4): elevated in malignant ovarian diseases, being helpful to complement the Ca-125 in premenopausal women
Risk factors
General risk factors include
- nulliparity
- early menopause
- gonadal dysgenesis
- family history: contributes to 24% of cases of epithelial ovarian cancer14
- BRCA1/BRCA2 mutations: particularly for serous types
- Lynch syndrome-associated ovarian cancers most often have an endometrioid or serous type histology 14
- smoking: especially for mucinous adenocarcinoma
- previous history of breast, endometrial or colon cancer (Lynch II)
- certain ethnic groups
Protective factors
- oral contraceptives (OCP)
- breastfeeding (however this is controversial)
Risk assessment
Staging
The FIGO staging system is used for almost all of ovarian cancers: see ovarian cancer staging.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.