Pontine tegmental cap dysplasia (PTCD) is a rare congenital malformation of the brainstem and hindbrain with imaging hallmark of an ectopic dorsal transverse pontine fiber projecting from the tegmentum into the fourth ventricle.
On this page:
Epidemiology
PTCD is a rare congenital malformation with just over 20 reported cases in the literature 1. Actual prevalence may be underestimated due to failure to recognize the disease entity or misclassification.
Clinical presentation
Patients present with developmental delay, cerebellar and pyramidal abnormalities, and cranial nerve (V, VII, VIII and XII) dysfunction leading to neurosensorial hearing loss, swallowing impairment and oculomotor palsy 3,6.
Pathology
To date no specific mutations have been identified 1.
Radiographic features
CT
HRCT temporal bone may demonstrate duplicated internal auditory canal associated with VII/VIII nerve hypoplasia and aplasia 4
MRI
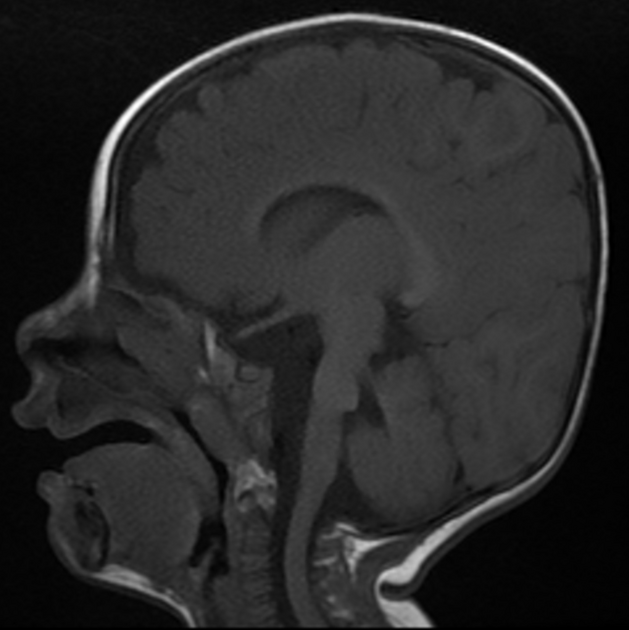
MRI is best imaging modality to characterize the structural abnormality 1,2,6:
-
ectopic dorsal transverse pontine fiber projecting from the tegmentum into the fourth ventricle
on diffusion tensor imaging (DTI) the ectopic fiber can be visualized as horizontally directed fiber (color-coded red) arising from the pontine tegmentum 2
hypoplasia and aplasia of the middle cerebellar peduncle
variable hypoplasia of the inferior cerebellar peduncle
lateralized course of the superior cerebellar peduncle resulting in "molar tooth" appearance of the midbrain
variable supratentorial abnormality which is non-specific to this condition (e.g. ventriculomegaly)
high resolution T2 weighted sequence is useful to detect cranial nerve abnormality such as V, VI, VII and VIII hypoplasia and aplasia 4-6
History and etymology
It was first described by Barth et al. in 2007 1.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.