Pyriform aperture stenosis refers to narrowing of the pyriform aperture and results from early fusion and hypertrophy of the medial nasal processes.
On this page:
Epidemiology
Pyriform aperture stenosis is a rare cause of airway obstruction, and its prevalence is unknown.
Pathology
Associations
alobar and semilobar forms of holoprosencephaly
facial hemangiomas
pituitary dysfunction
central megaincisor (in 75% of cases)
Radiographic features
CT
CT the imaging modality of choice. It is performed in planes angled along the hard palate with a multiplanar reformat thickness of 1-1.5 mm and should include the maxillary spines.
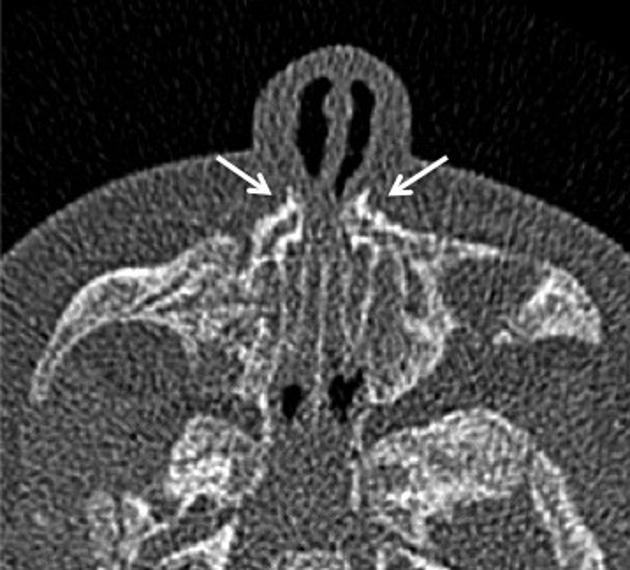
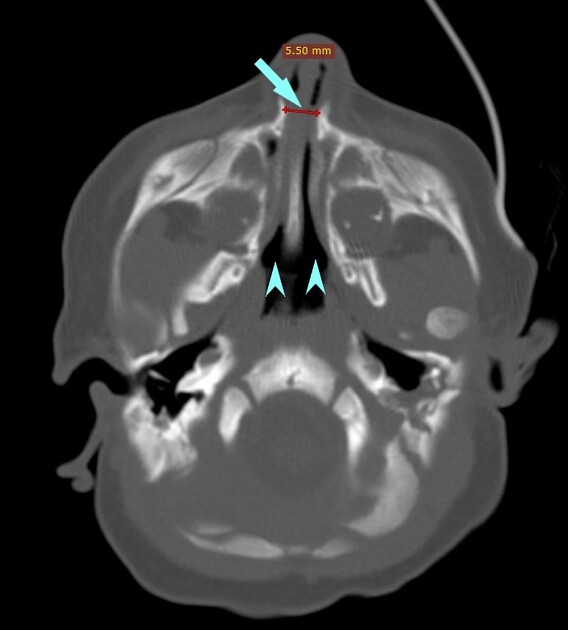
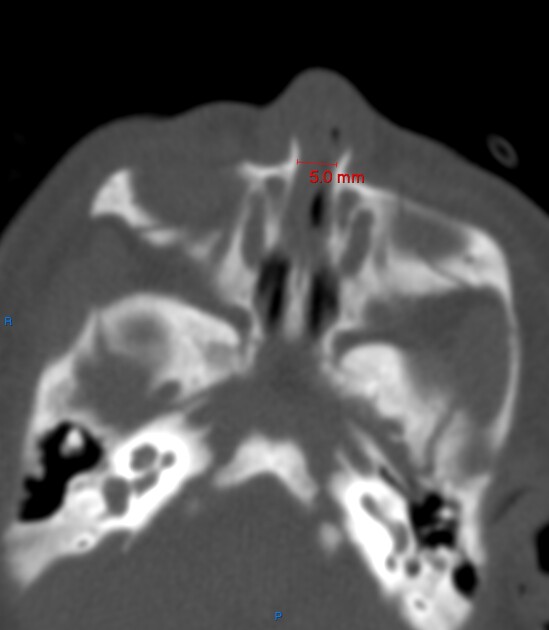
Imaging features of pyriform aperture stenosis include:
inward bowing and thickening of nasal processes of maxilla
narrowing of the pyriform aperture measuring less than 8 mm (normal is not <11 mm) 5
Treatment and prognosis
Treatment of mild cases of pyriform aperture stenosis includes administration of decongestants, which allows time for normal nasal growth. Severe cases may require surgical reconstruction with stent placement, sublabial resection of the anteromedial maxilla, or reconstruction of the anterior nasal passages.
Differential diagnosis
Possible consideration on axial CT images include




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.