Rim sign (osteonecrosis)
Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Gaillard F, Knipe H, Macori F, et al. Rim sign (osteonecrosis). Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 06 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-1987
Permalink:
rID:
1987
Article created:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was created Frank Gaillard had no recorded disclosures.
View Frank Gaillard's current disclosures
Last revised:
Disclosures:
At the time the article was last revised Henry Knipe had the following disclosures:
- Radiopaedia Events Pty Ltd, Speaker fees (past)
- Integral Diagnostics, Shareholder (ongoing)
- Micro-X Ltd, Shareholder (ongoing)
These were assessed during peer review and were determined to not be relevant to the changes that were made.
View Henry Knipe's current disclosures
Revisions:
8 times, by
7 contributors -
see full revision history and disclosures
Systems:
Sections:
Synonyms:
- Rim sign (AVN)
- Rim sign of AVN
- Rim sign (avascular necrosis)
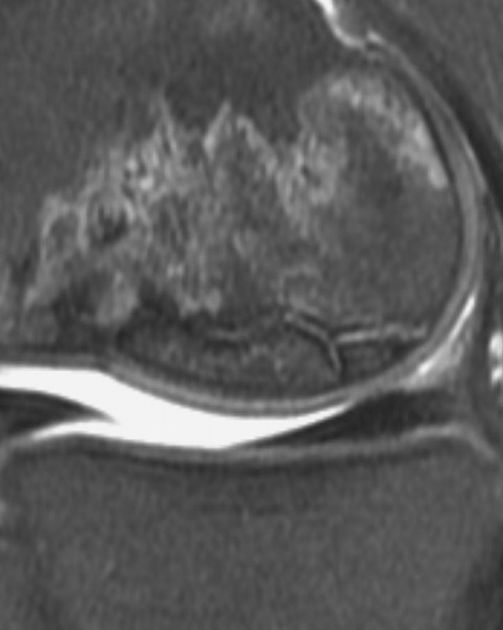
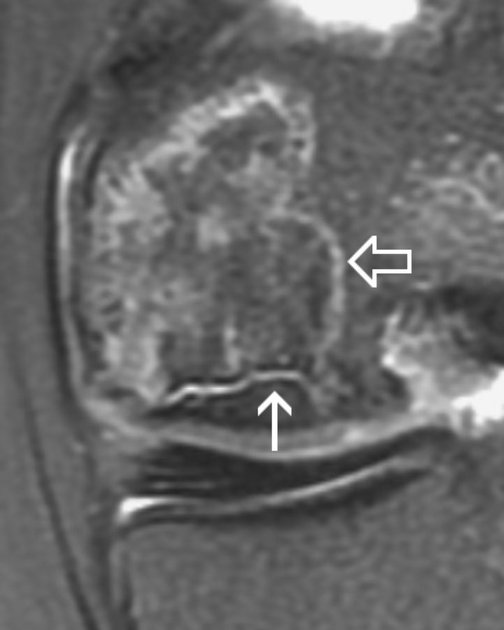
A rim sign can be seen in osteonecrosis and comprises a high T2 or intermediate T1 signal line sandwiched between two low signal lines, and represents fluid between the sclerotic borders of an osteochondral fragment, and implies instability (stage III).
This rim sign should not be confused with the double line sign of osteonecrosis.
Quiz questions
References
- 1. Donald Resnick, Mark J. Kransdorf. Bone and Joint Imaging. (2005) ISBN: 9780721602707 - Google Books
Incoming Links
Articles:
Cases:
- Subchondral insuffiency fracture of the acetabulum
- Osteochondritis dissecans - knee
- Osteonecrosis of the knee
- Osteochondritis dissecans of the knee - paediatric
- Osteochondritis dissecans - knee
- Avascular necrosis of humerus
- Avascular necrosis of bilateral femoral heads
- Osteochondritis dissecans
- Avascular necrosis of the knee
Multiple choice questions:




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.