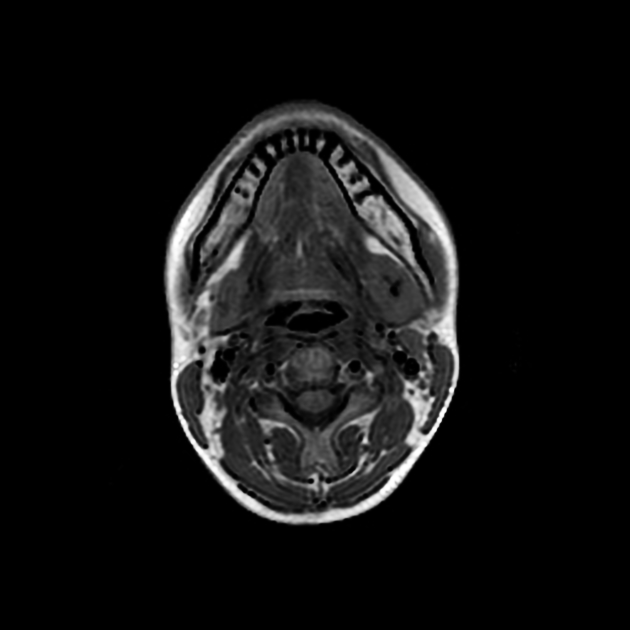
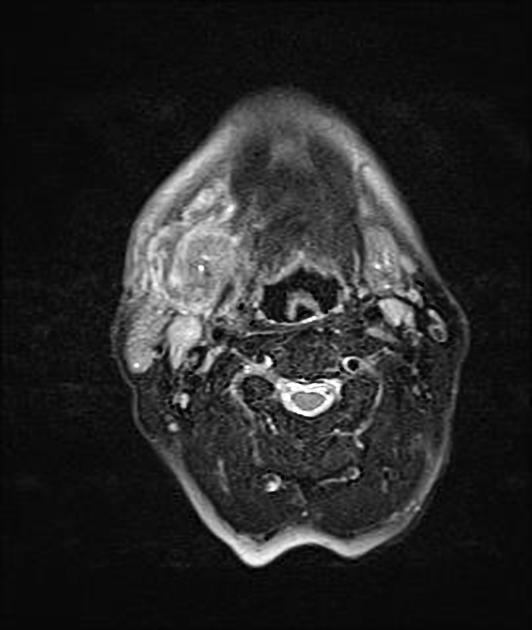
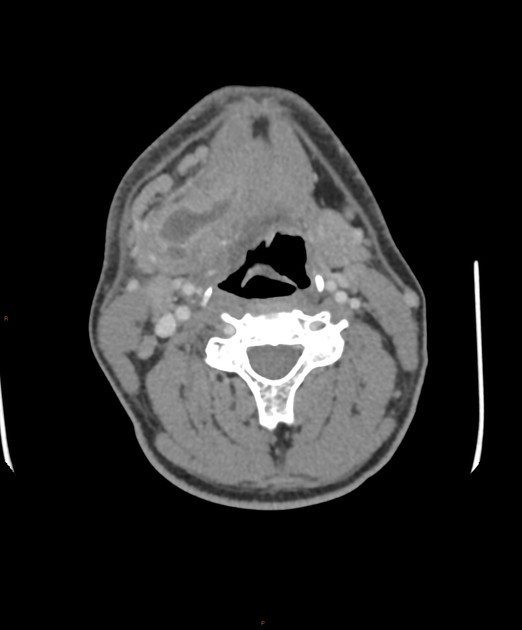
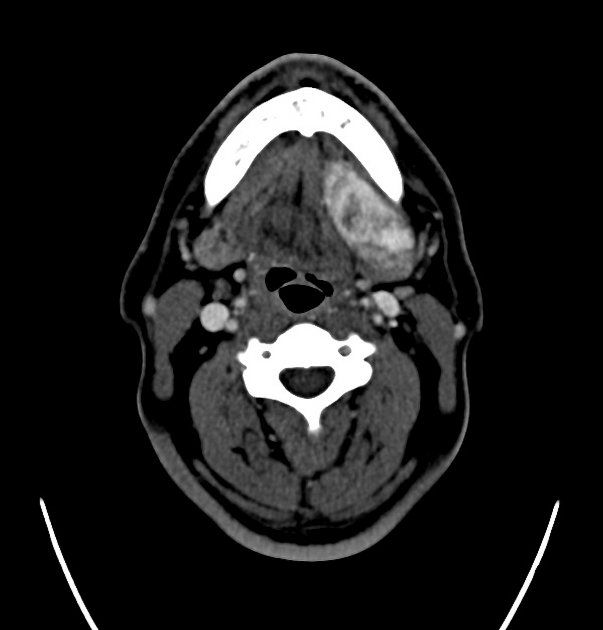
Submandibular gland enlargement refers to an increase in the volume of the submandibular gland, exceeding "normal" values of 7.4 ± 1.8 mL 1.
Pathology
Causes
Obstruction
submandibular duct stenosis (e.g. tumor, granulomatous disease)
Infection
acute sialadenitis: following sialolithiasis
-
acute suppurative sialadenitis (submandibular abscess)
from odontogenic infection
from hematogenous spread
-
acute viral sialadenitis
Inflammatory
-
chronic sialadenitis
IgG4-related disease: diffuse submandibular gland enlargement, with a homogeneous density 2
submandibular gland sarcoidosis 4 - rare
Neoplastic
All salivary gland tumors are to be considered
-
benign
-
malignant
myoepithelioma
adenocarcinoma
Miscellaneous
bulimia nervosa: painless diffuse swelling of major salivary glands 1
pneumosialodenitis of the submandibular gland: gas in the submandibular gland 7
compensatory hypertrophy in the setting of contralateral congenital absence or atrophy/disease 6




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.