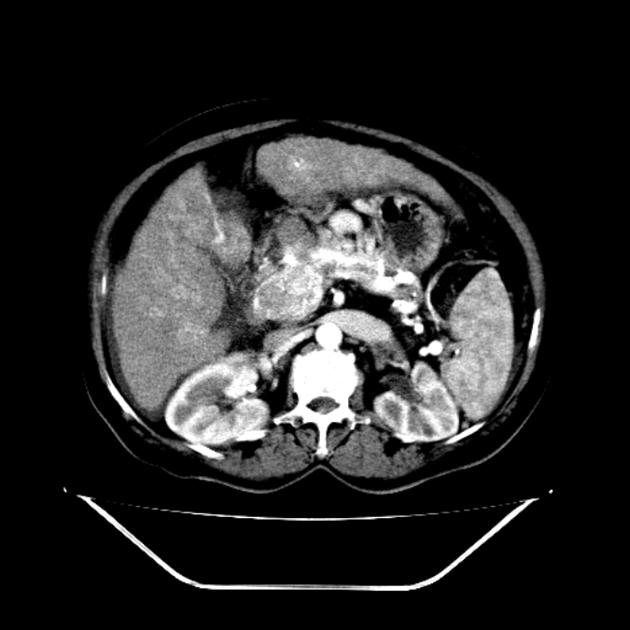
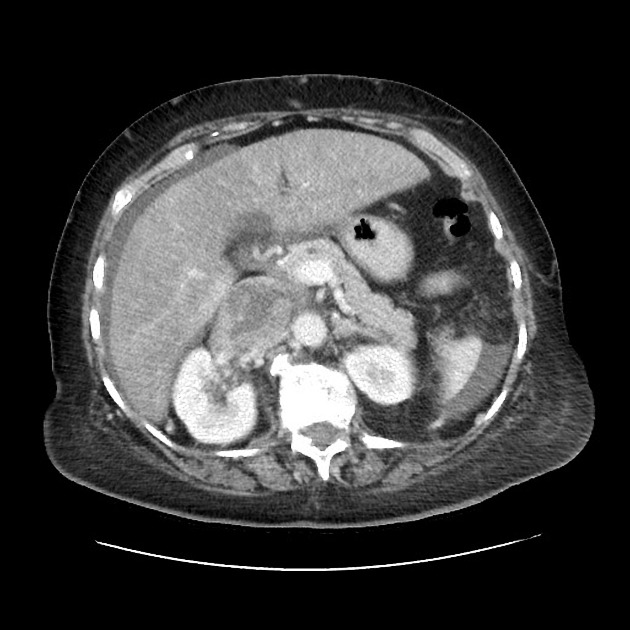
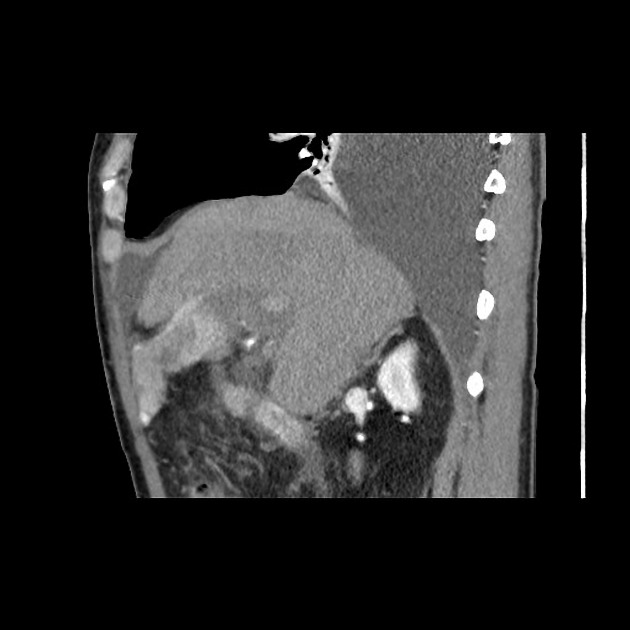
Tumor thrombus is defined as tumor extending into a vessel, typically a vein. It occurs in a wide variety of malignancies. It is vital to distinguish tumor thrombus from "bland" thrombus (free of neoplastic cells) in the setting of neoplasia, as this often impacts staging and treatment approach.
On this page:
Pathology
Tumor thrombus is usually composed of a soft tissue component and a thrombotic component.
Etiology
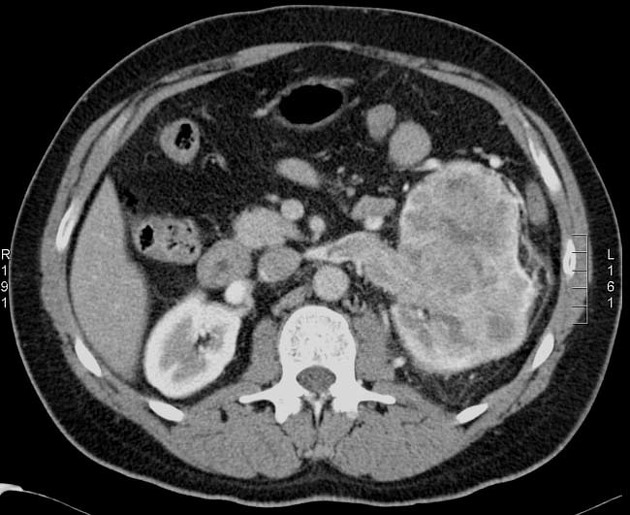
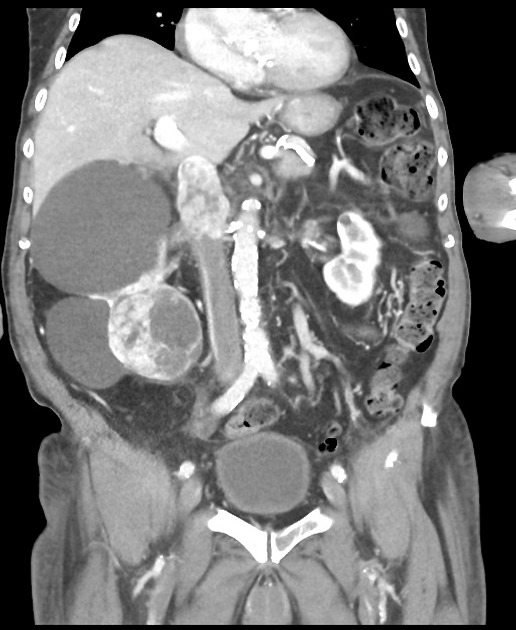
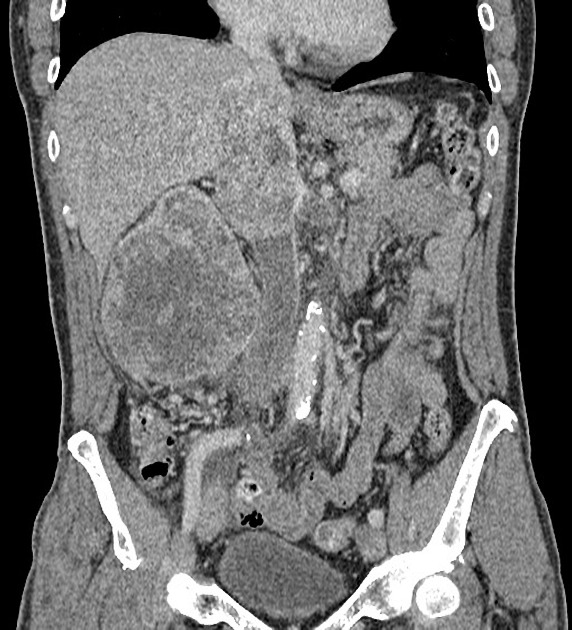
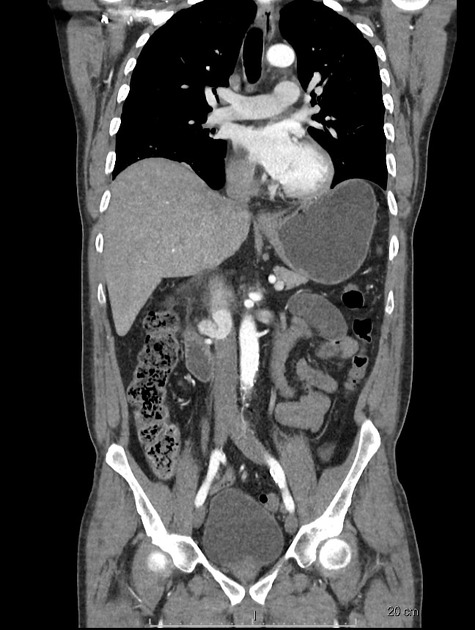
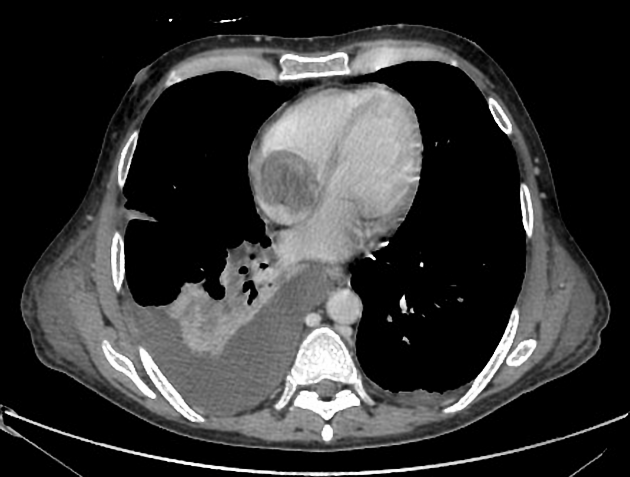
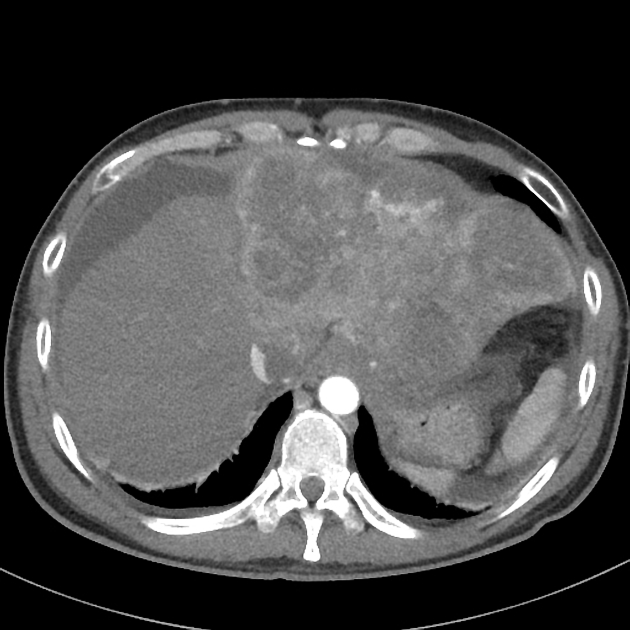
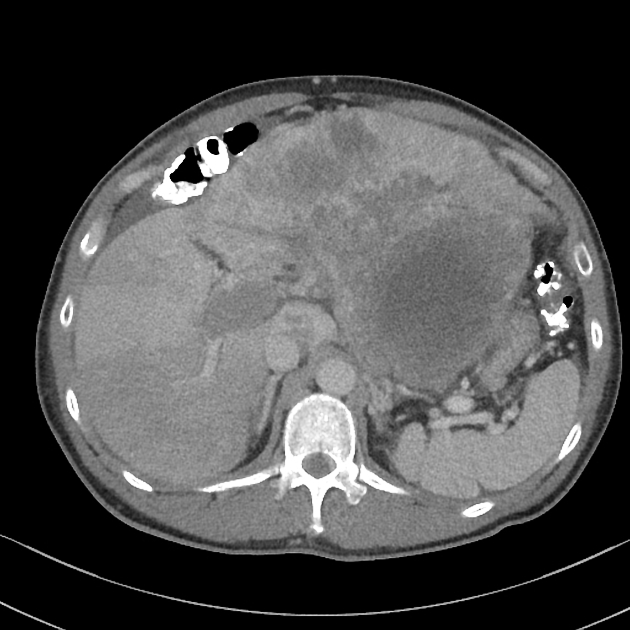
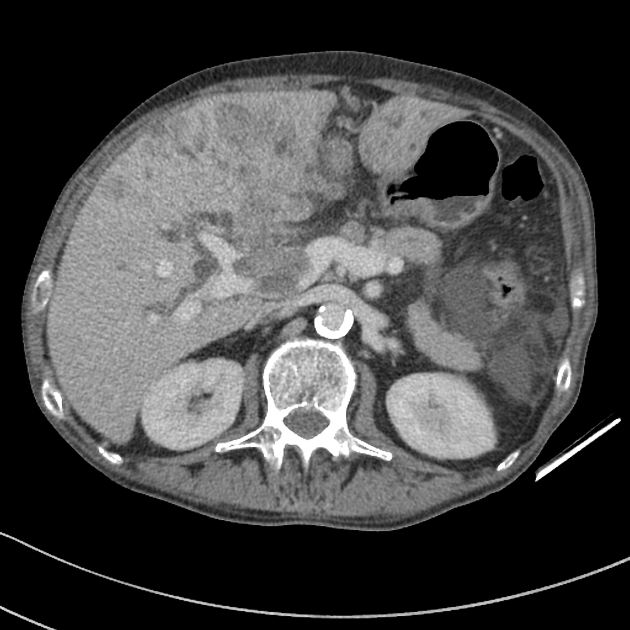
Tumor thrombus is perhaps most frequently associated with renal cell carcinoma, where tumor may invade the renal vein and grow caudally into the right atrium. However, this phenomenon is not isolated to renal cell carcinoma, and is recognized in 2,3:
transitional cell carcinoma of renal pelvis (rarely) 4
Radiographic features
Ultrasound
Contrast-enhanced ultrasound is reported to be 100% sensitive and specific. The key feature of tumor thrombus is the presence of enhancement or color Doppler flow within the thrombus 3,5.
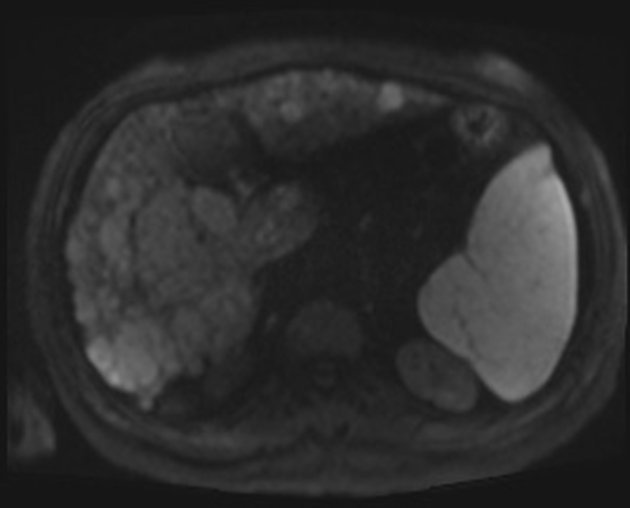
CT/MRI
Imaging features consistent with tumor thrombus on contrast-enhanced CT and MRI include:
presence of enhancement 3, the most specific sign
appearance of vessel expansion 3
diffusion restriction 3
Angiography
Streak and thread appearance of the tumor thrombus is characteristic in angiography due to parallel opacification of small vessels and arterial-venous shunting 3.
Nuclear medicine
FDG-PET
Increased activity associated with the presence of thrombus on CT 3
Treatment and Prognosis
In renal cell carcinoma, it may be possible to remove thrombus retrogradely at nephrectomy but the presence and nature of any tumor thrombus are important for determining the TNM stage.
In hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), surgical resection is rarely performed in the setting of tumor thrombus given poor underlying liver function and high rate of recurrence even after liver transplant. For that reason, it is considered an absolute contraindication to liver transplantation 3.






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.