Presentation
Right flank pain and hematuria.
Patient Data


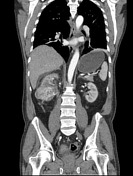

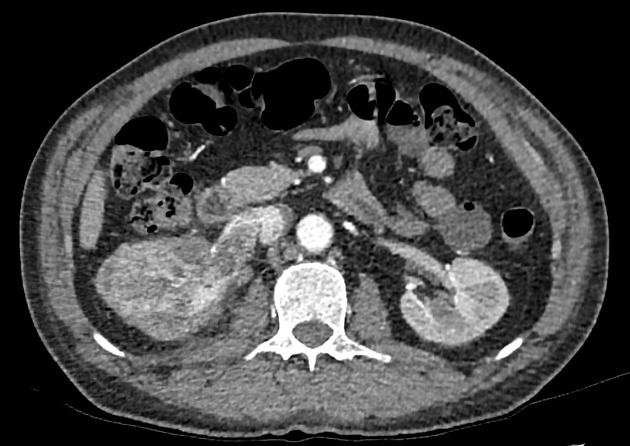
There is a 8 cm mass in the middle to lower pole of right kidney which avidly enhances with arterial phase contrast.
A tumor thrombus is seen invading and dilating the entire length of the right renal vein, but does not extend to the IVC.

Histo report post-radical nephrectomy
Confirmed clear cell renal cell carcinoma and tumor thrombus.
Case Discussion
The patient presented with macroscopic hematuria and right flank pain. These are two of the classic presentation triad of renal cell carcinoma, consisting of hematuria, flank pain and a palpable mass.
Correlated with the imaging findings, the patient was diagnosed with renal cell carcinoma. Radical nephrectomy was performed. Histopathology confirmed the diagnosis of renal cell carcinoma.
Tumor thrombus is classically associated with renal cell carcinoma. In some cases, it may be difficult to differentiate between a bland thrombus and a tumor thrombus in the renal vein on a non-contrast or venous phase CT, as both are seen as a filling defect in the renal vein. However, an arterial phase CT will show enhancement of a tumor thrombus due to neovascularization of the tumor, as in this case.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.