Presentation
Chest pain for 2 years
Patient Data

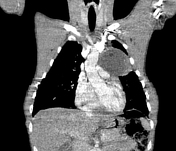

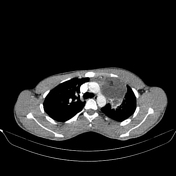

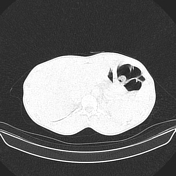

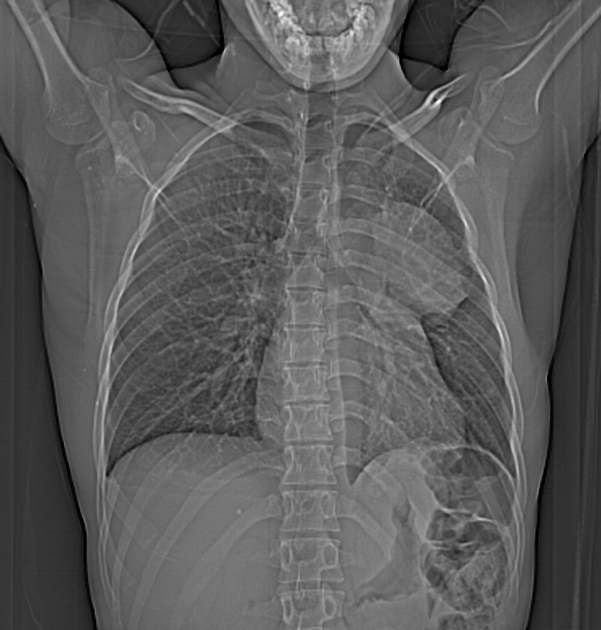
An anterior and middle mediastinal mass measuring 7.2 x 7.0 x 7.9 cm abutting and compressing the main and left pulmonary arteries. It also abuts the anterior chest wall and aortic arch and displaces the left main bronchus. The mass is partly cystic, with rim calcification and contains small areas of fat and soft tissue attenuation. The heart is normal in size. No pericardial effusion or intracardiac filling defects are seen. No lymphadenopathy. No bone destruction.
Areas of ground glass changes are noted in the left upper and lower lobes adjacent to the mass most likely due to compressive atelectasis. Otherwise normal.
Case Discussion
Mediastinal teratomas contain tissue derived from two or three embryological layers. On CT they usually appear cystic and may contain fat, soft tissue and calcification.
They usually present between 20 and 40 years of age and are typically large when they become symptomatic. The vast majority are located in the anterior mediastinum.
They may result in trichoptysis if they rupture into the tracheobronchial tree, a symptom which is rare but pathognomonic.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.