Presentation
Chronic abdominal pain. Symptoms of pancreatic exocrine deficiency ie malabsorption. Chronic alcoholic.
Patient Data

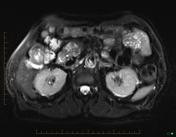
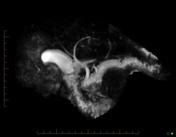

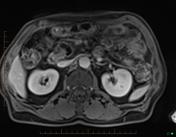

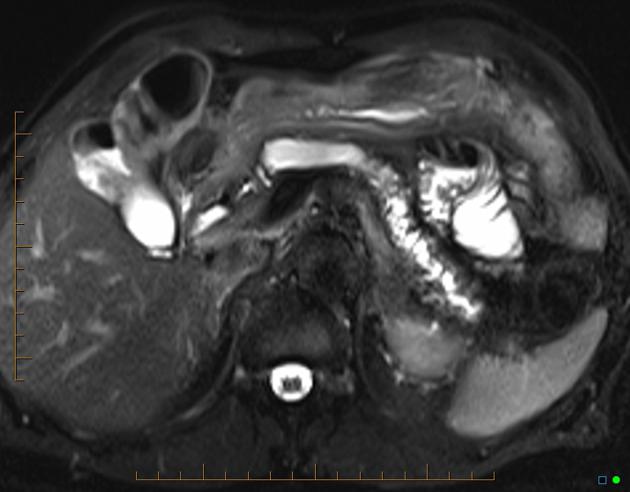
Gross dilatation of the pancreatic duct (and gland atrophy) with subtle filling defect in the duct at the head extending into the accessory duct draining the uncinate process - easily seen as calcification on CT but not that apparent on MRI. Calcification is actually calculi in the duct causing obstruction (thus failure of exocrine pancreatic function)
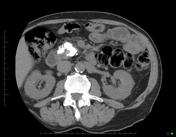
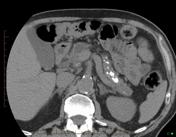
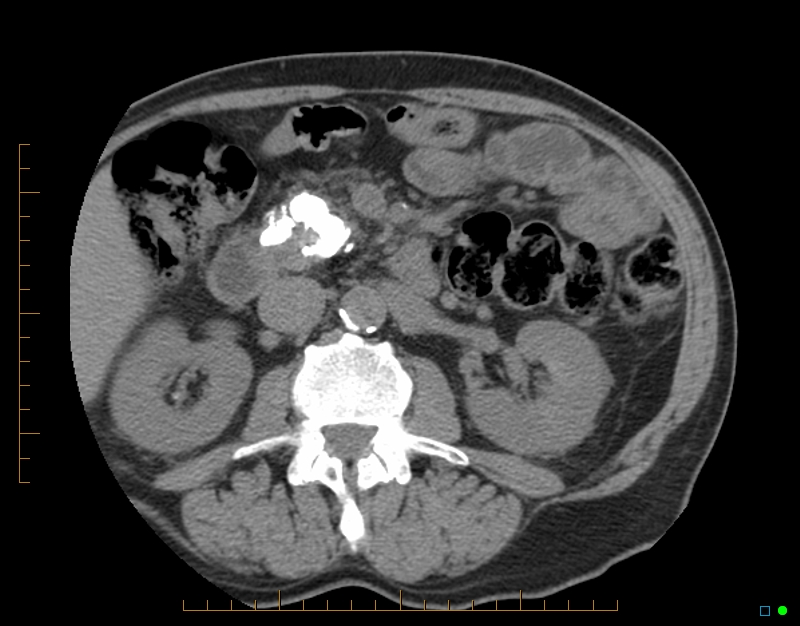
Non-contrast CT has been preformed to detect calcification, which are presence in abundance.
Case Discussion
Features typical of chronic pancreatitis with duct calculi on CT and MRI




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.