Presentation
Patient with NF1, now progressive myelopathy.
Patient Data


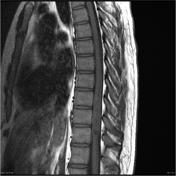

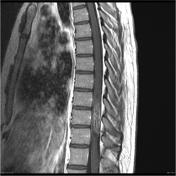

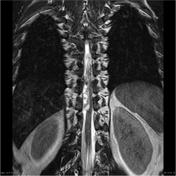

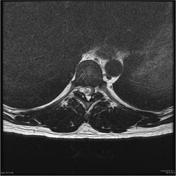

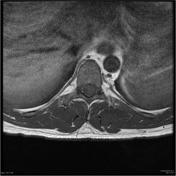

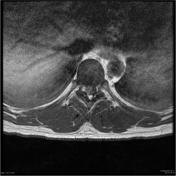

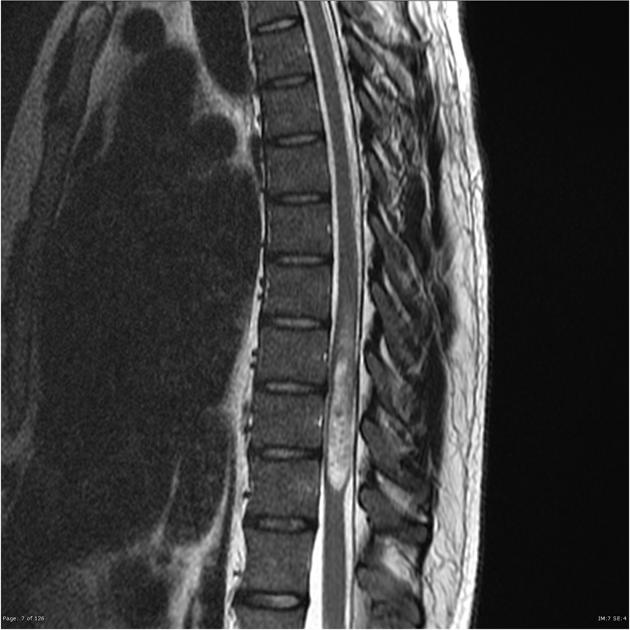
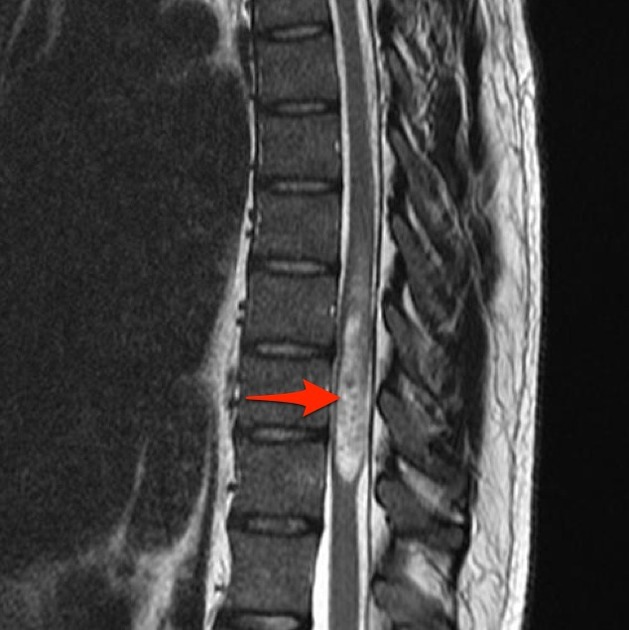
Intramedullary expansile eccentric and predominantly right sided solid/cystic mass present which demonstrates heterogenous enhancement and measures 10 x 9 x 42 mm (AP x RL x CC) and is centered on the T10 vertebral body and extends from the T9 to the T11 superior endplate (counting from above, from C1). T2 hyperintensity demonstrated within the cord superior to the mass. Some low T2 signal within but no discrete hemosiderin cap.Bone marrow signal is normal. Alignment is normal.
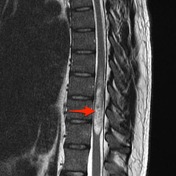
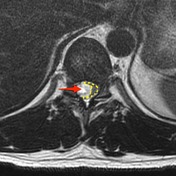
Large intramedullary tumor (red arrow) is located eccentrically on the right side of the cord. Normal cord tissue can be seen on the left side of the canal, distorted and displaced (yellow dotted line).
The patient went on to have a laminectomy and macroscopic excision of the tumor.
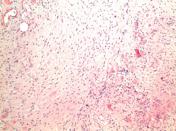
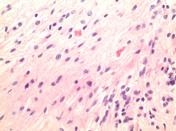
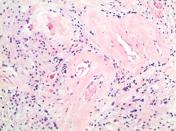
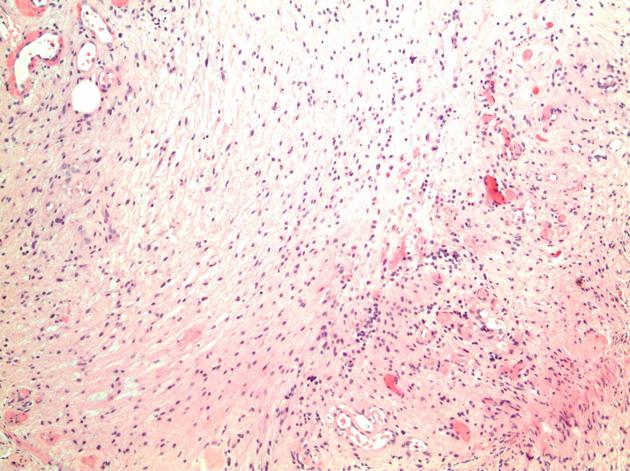
MICROSCOPIC DESCRIPTION: The tumor is a moderately hypercellular lesion consisting of a loose fascicular arrangement of piloid cells with coarse, strongly GFAP immunoreactive processes. These cells are admixed with a population of astrocytes with small round nuclei and a paucity of processes. Moderate numbers of Rosenthal fibers are noted. Small caliber thick-walled blood vessels are prominent in some areas of the lesion. No mitotic figures are identified and there is no vascular endothelial cell hyperplasia and no necrosis. No staining for IDH-1 or EMA is seen. The Ki-67 proliferative index is <1%.
FINAL DIAGNOSIS: Pilocytic astrocytoma (WHO Grade I)
Case Discussion
This case illustrates some of the features of a spinal cord pilocytic astrocytoma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.