Presentation
Patient with cognitive impairment.
Patient Data
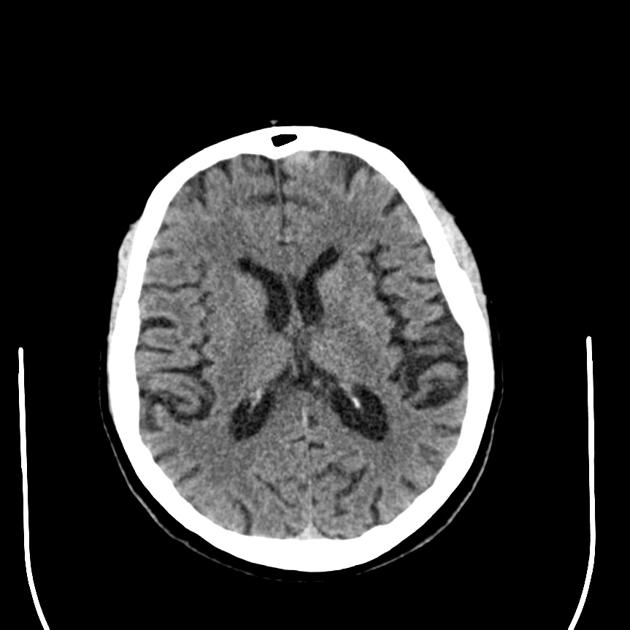
CT scan shows enlargement of cerebral sulci and loss of gyral volume associated with mild compensatory dilation of the ventricular system. This is perhaps most marked in the parietal regions. These are nonspecific findings that are sometimes found in the asymptomatic population in this age group.
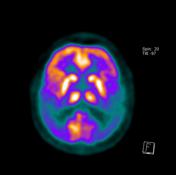

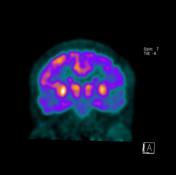

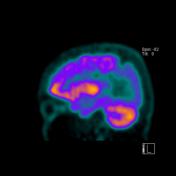

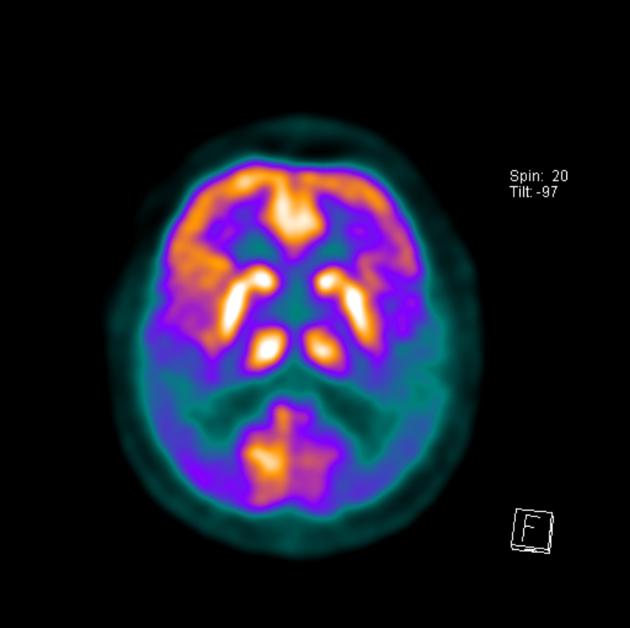
PET-CT uses radiolabeled glucose analog FDG to measure glucose metabolism, which indicates levels of neuro-synaptic activity. On these FDG PET images, it is seen decreased metabolism activity on the bilateral parietotemporal cortex.




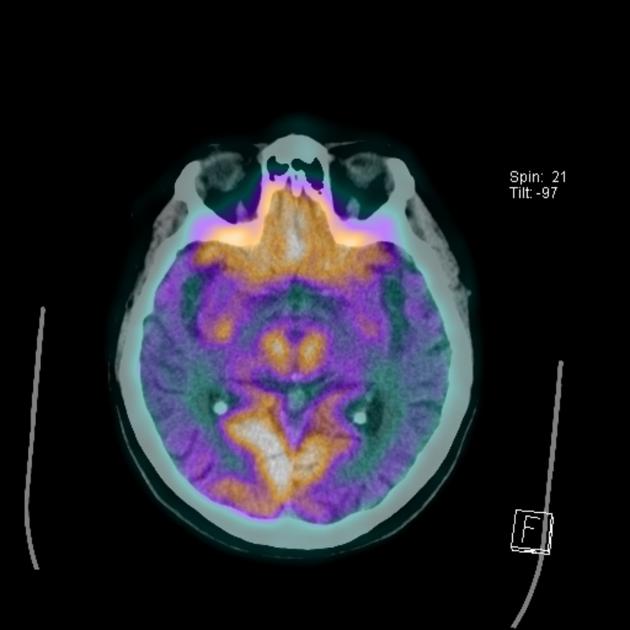
FDG PET-CT images show decreased metabolic activity in the bilateral parietotemporal cortex.
Case Discussion
This patient not only had cognition and memory impairment over the last 6 months but also had a family history of Alzheimer disease.
The severe hypometabolism noted in the temporal and parietal regions bilaterally is consistent with the pattern of Alzheimer disease.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.