Presentation
Longstanding sensation of food "stuck in her chest" and halitosis.
Patient Data
Age: 35 years
Gender: Female
From the case:
Achalasia - with bird beak sign
Download
Info
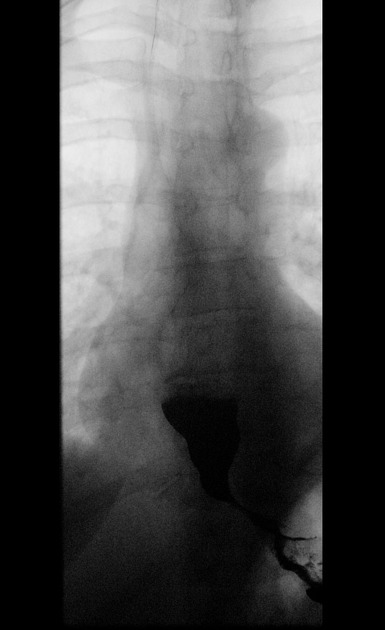
Rapid sequence fluoroscopic images from a barium esophagogram reveal a persistently dilated esophagus with an air-fluid level at the lower esophagus and classic "bird-beaking" at the gastroesophageal (GE) junction, despite normal primary peristaltic waves.
Case Discussion
Achalasia can be divided into primary and secondary (pseudoachalasia):
- primary achalasia is a smooth muscle motility disorder of the esophagus
- secondary achalasia is abnormal stricturing of the gastroesophageal junction, such as tumor compression or Chagas disease
Esophagogram is important in the evaluation of motility, reflux, and aspiration.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.