Presentation
Recurrent posterior ankle pain, has increased in the last few days. No trauma.
Patient Data

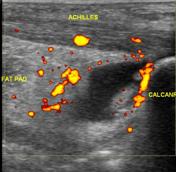
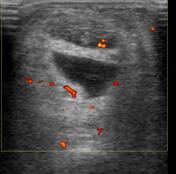
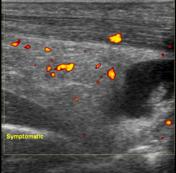

Ultrasound of the symptomatic side shows normal thickness and echopattern of the Achilles tendon. Fluid is noted deep to the tendon. Hypervascularity is noted in the fat pad and also in the tendon.
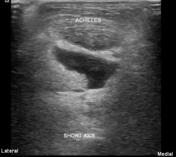
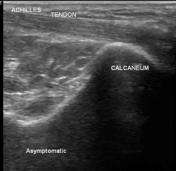
Ultrasound of the asymptomatic side shows normal Achilles tendon with no bursal fluid.
Case Discussion
Small amount of fluid is normally present in the retrocalcaneal or preachilles bursa. In this case, the amount of fluid is much more than normally seen, in addition to increased vascularity in the fat pad. The tendon itself is normal. However, there is increased vascularity which suggests early tendinosis.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.