Presentation
Presented with 3 days history of shortness of breath, hemoptysis and fever.
Patient Data
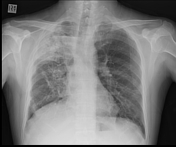
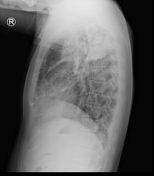
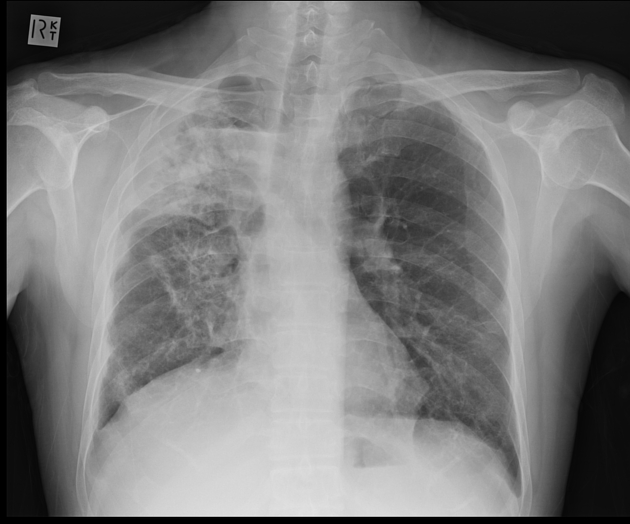
Right upper lobe consolidation with an air fluid level at the right apex. Airspace opacity at right apex. Mild volume loss in right lung field.
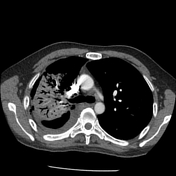

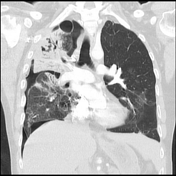



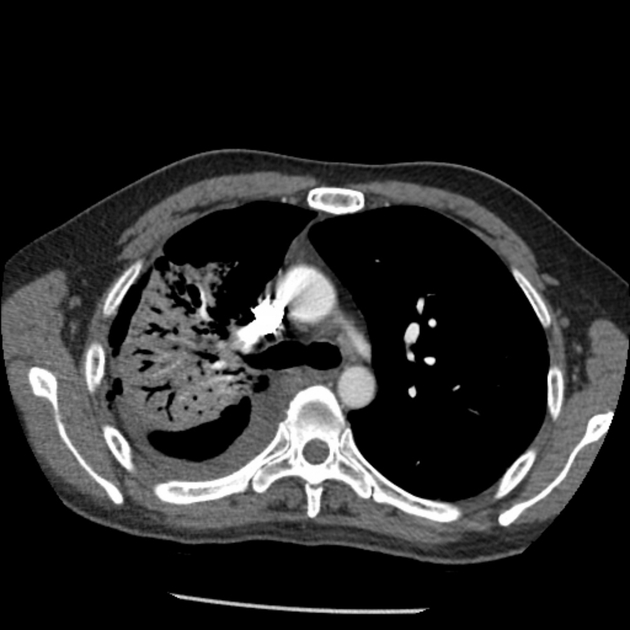
The right upper lobe shows confluent consolidation with evidence of cavitation within as well as bronchiectasis in right middle and upper lobe. Minor residual ground glass opacity and scarring. Patient has developed right sided hydropneumothorax.
Case Discussion
Patient had severe right upper lobe pneumonia and developed hypoxic respiratory failure requiring invasive ventilatory support in ICU. Subsequently patient developed hydropneumothorax requiring chest drain insertion. Sputum culture showed growth of Strep pyogenes.
Hydropneumothorax is defined as concurrent presence of pneumothorax and hydrothorax. It classically shows an air-fluid level on erect CXR. One of the main differential diagnosis to consider is pyopneumothorax, also commonly known as infected hydropneumothorax. The main differentiating features distinguishing pyopneumothorax from hydropneumothorax is he presence of thick pleural lining. Further imaging investigations can also be undertaken to differentiate the two conditions such as ultrasound and CT.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.