Citation, DOI, disclosures and article data
Citation:
Goel A, Le L, Verikios N, et al. Pyopneumothorax. Reference article, Radiopaedia.org (Accessed on 29 Mar 2025) https://doi.org/10.53347/rID-29776
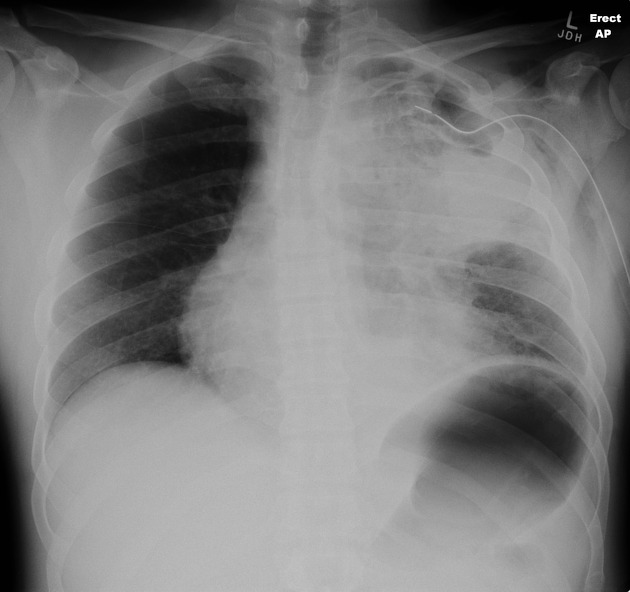
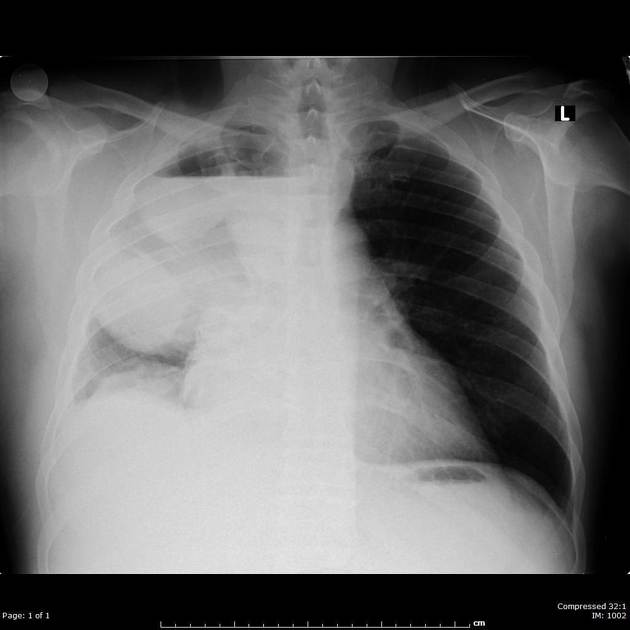
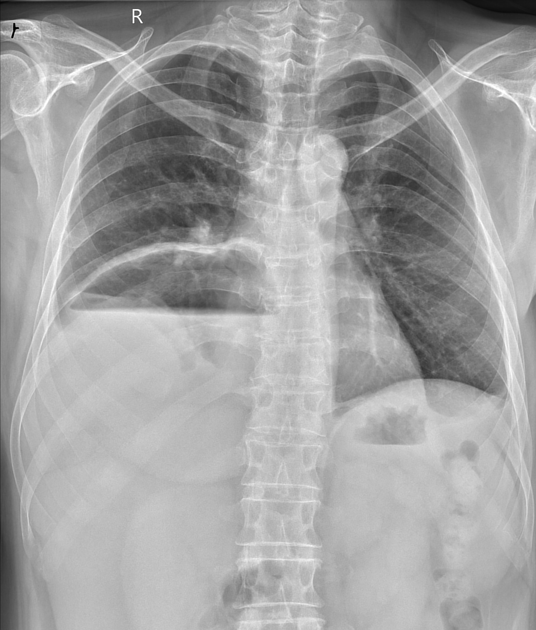
Pyopneumothorax, also known as infected hydropneumothorax or empyemic hydropneumothorax, is a pleural collection of pus and gas. It may be thought of a variant of a thoracic empyema with gas-containing components although the etiology may be different.
The patient usually presents with chest pain and fever. Cough and breathing difficulty may be present.
Etiology
As with a hydropneumothorax, it has a range of causes:
Many causative organisms have been implicated including Mycobacterium tuberculosis, anaerobes, bacteria and fungi.
Plain radiograph
A gas-fluid level is noted. It may be loculated. Loss of silhouette with the dome of diaphragm may be seen. It may be difficult to differentiate a pyopneumothorax from non-infected hydropneumothorax. Presence of thick pleural lining strongly favors the former.
Ultrasound
Fine internal echoes in the pleural collection strongly suggest infected fluid in appropriate clinical settings.
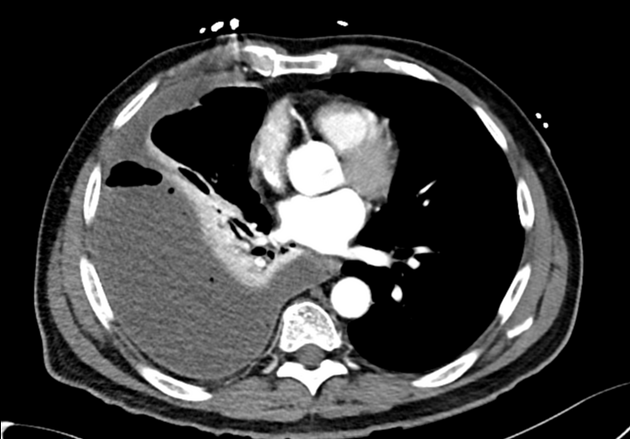
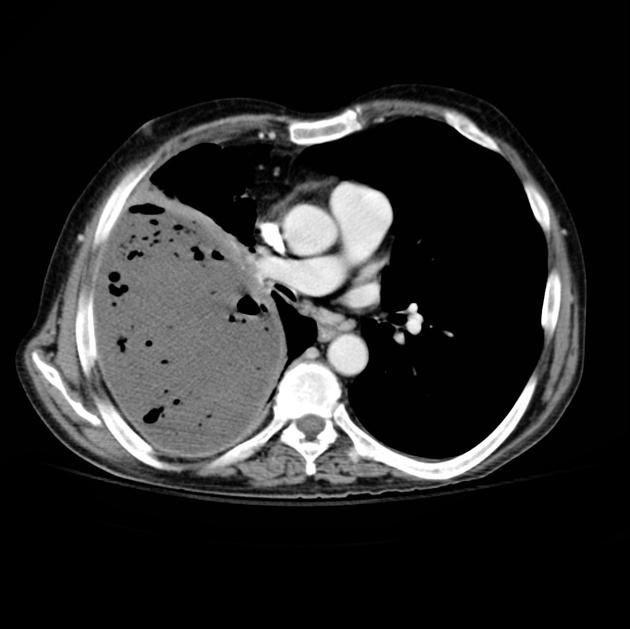
CT
CT will clearly depict the location of the collection as well as thickening of pleura and underlying disease process (if any).
Treatment and prognosis
Large collections require intercostal drainage with antibiotics.
On imaging consider
-
1. Farrow CS. Exercise in diagnostic radiology. Pyopneumothorax, secondary to distemper pneumonia. Can. Vet. J. 1981;22 (6): 182-3. Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
-
2. Lin FC, Chou CW, Chang SC. Differentiating pyopneumothorax and peripheral lung abscess: chest ultrasonography. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2004;327 (6): 330-5. Pubmed citation
-
3. Lin FC, Chou CW, Chang SC. Differentiating pyopneumothorax and peripheral lung abscess: chest ultrasonography. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2004;327 (6): 330-5. Pubmed citation
-
4. Verma SK, Mahajan V. Complete radiological clearance in bilateral loculated pyopneumothorax managed conservatively. Lung India. 2009;26 (2): 55-6. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.48901 - Free text at pubmed - Pubmed citation
-
5. Kartaloglu Z, Okutan O, Işitmangil T et-al. Pyo-pneumothorax in patients with active pulmonary tuberculosis: an analysis of 17 cases without intrapleural fibrinolytic treatment. Med Princ Pract. 2006;15 (1): 33-8. doi:10.1159/000089383 - Pubmed citation
-
6. Tyagi R, Barthwal M, Bhattacharya D, Katoch CD. Pyopneumothorax of rare cause. (2016) Lung India : official organ of Indian Chest Society. 33 (1): 79-81. doi:10.4103/0970-2113.173060 - Pubmed
-
7. Che Rahim MJ, Mohammad N, Wan Ghazali WS. Pyopneumothorax secondary to Streptococcus milleri infection. (2016) BMJ case reports. doi:10.1136/bcr-2016-217537 - Pubmed
-
8. Ourari B, Dhaoui S, El Gharbi L, Ben Amar J, Azzabi S, Ali Baccar M, Aouina H, Bouacha H. Tuberculosis pyopneumothorax: Retrospective study of 16 cases in Tunisia.
European Respiratory Journal 2013, 42 (Suppl 57) P4478. https://erj.ersjournals.com/content/42/Suppl_57/P4478
Promoted articles (advertising)






 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.