Patient Data
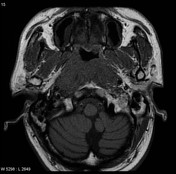

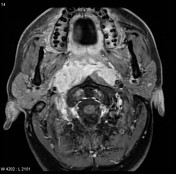

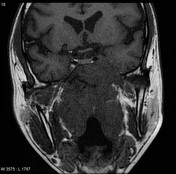
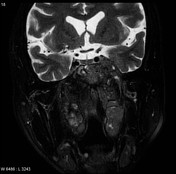



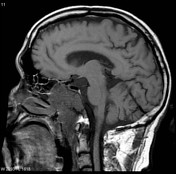
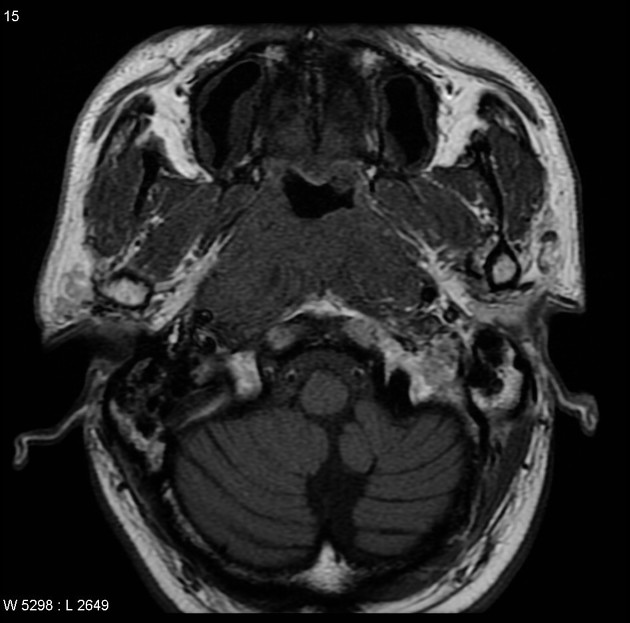
MRI through the nasopharynx and base of skull of an Asian patient including contrast-enhanced fat-suppressed sequences demonstrates a large nasopharyngeal mass invading the cavernous sinuses (especially on the left), clivus and pterygopalatine fossa. Large right-sided lymph nodes are present.
Case Discussion
Features are consistent with a nasopharyngeal carcinoma, which was confirmed on biopsy.
Histology
Both biopsies show similar features, with invasive poorly differentiated non-keratinizing squamous cell carcinoma involving fragments of soft tissue and bone. The tumor is positive for EBV by in situ hybridization for EBER.
EBV is highly associated with nasopharyngeal carcinoma.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.