Presentation
Two months of confusion.
Patient Data
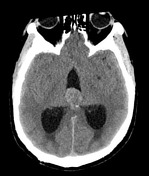

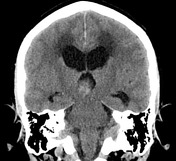

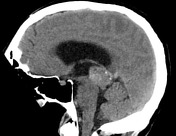

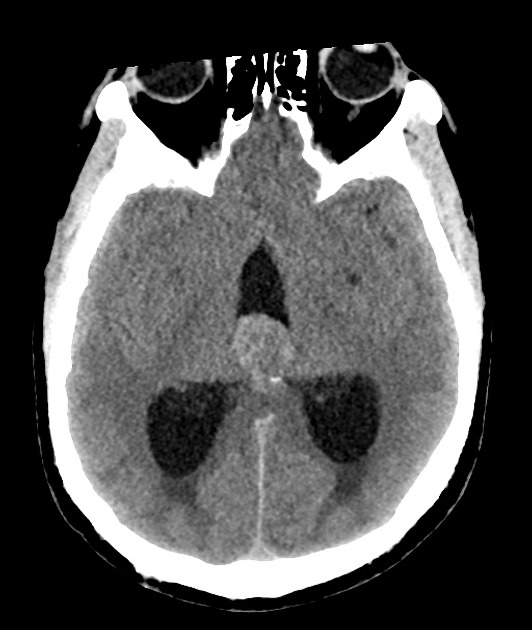
There is a large pineal region mass, which causes compression of the cerebral aqueduct resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus and transependymal edema. No acute intracranial hemorrhage. No transtentorial/tonsillar herniation or midline shift.
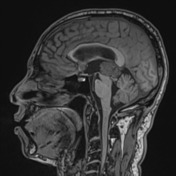

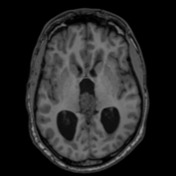

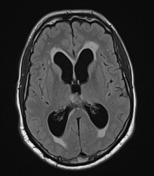

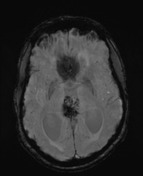



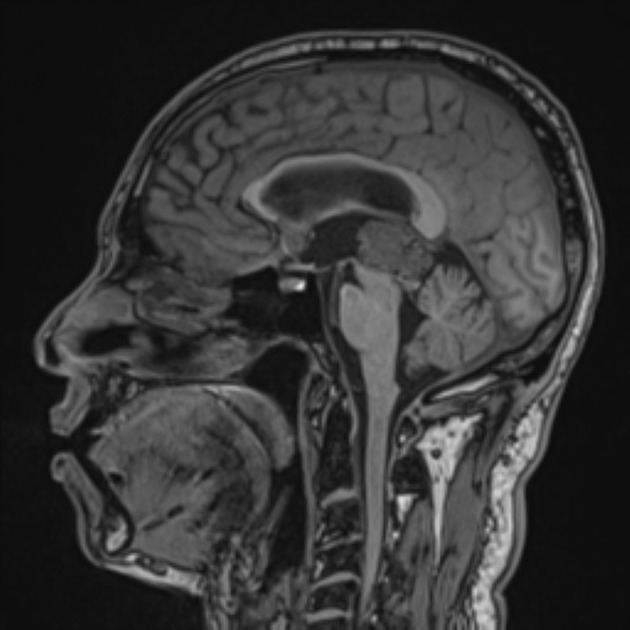
Large pineal region mass with heterogeneous T2 signal, mildly hyperintense on FLAIR and low T1 intensity. It is located inferior to the internal cerebral veins and cannot be separated from the tectal plate. No midbrain edema. Extensive susceptibility artifact consistent with blood product. It compresses the cerebral aqueduct resulting in obstructive hydrocephalus with transependymal edema. Anteriorly it protrudes into the third ventricle and posteriorly into the quadrigeminal cistern. Surrounding T2 flow voids. A normal pineal gland is not seen. No other intracranial lesion identified.
Post-contrast images not obtained due to early termination of the study.
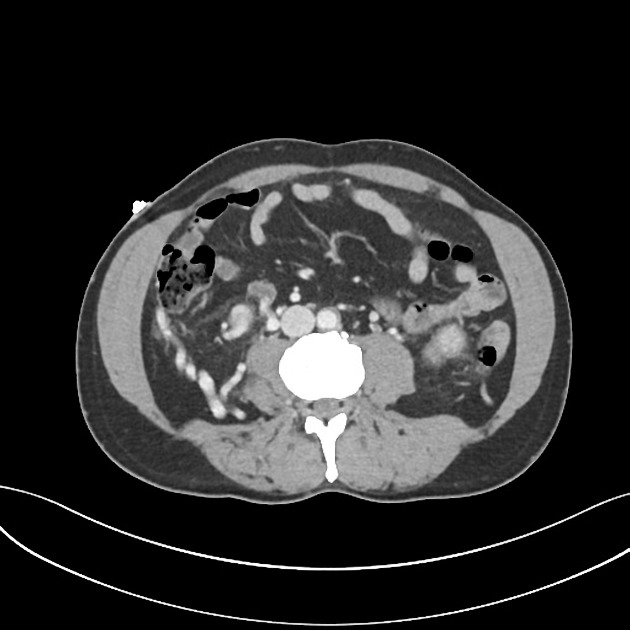
There are innumerable masses throughout the kidneys, adrenal glands, pancreas (body and tail) and right upper quadrant. These masses are expansile, demonstrate heterogeneous peripheral hyperenhancement with central areas of low density. Intramuscular nodule in the lateral left gluteus maximus. There are multiple homogeneously enhancing nodules involving the nerve roots - left S1, right S2, right L2, left T3 (extraforaminal).
Case Discussion
The patient underwent percutaneous biopsy of a buccal mass (not shown) with results consistent with metastatic clear cell renal cell carcinoma.
The imaging findings of hyperenhancing abdominopelvic masses and MRI characteristics (T2 flow voids, associated blood product) both in keeping with hypervascular metastases, of which RCC is a cause.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.