Presentation
Bilateral painful focal foot swelling
Patient Data
Age: 55 years
Gender: Male
From the case:
Tophaceous gout


Show annotations
Download
Info

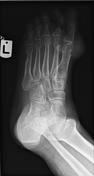
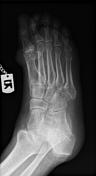
Several well-circumscribed punched-out bony erosions with sclerotic margins exist bilaterally, particularly in the vicinity of the first MTP joints.
Juxta-articular soft tissue densities and swelling are also visible.
Case Discussion
Findings of x-rays are characteristic of tophaceous gout.
The typical appearance of gout on x-ray evaluation is the presence of well-defined, punched-out erosions with sclerotic margins in a marginal and juxta-articular distribution with overhanging edges. Tophi are also pathognomonic features of gout.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.