Presentation
A middle aged lady presented with progressive generalized bone pain for 6 years and weakness for 2 years. At presentation she required support for walking.
Patient Data
Initial presentation




Frontal chest radiograph shows diffuse osteopenia. Frontal radiograph of the lumbar spine shows diffuse osteopenia with variable decrease in vertebral body heights. Frontal radiograph of the pelvis and proximal femurs demonstrates coarse trabeculations involving bilateral femoral necks with the presence of looser zones.
Magnified image of Lt...
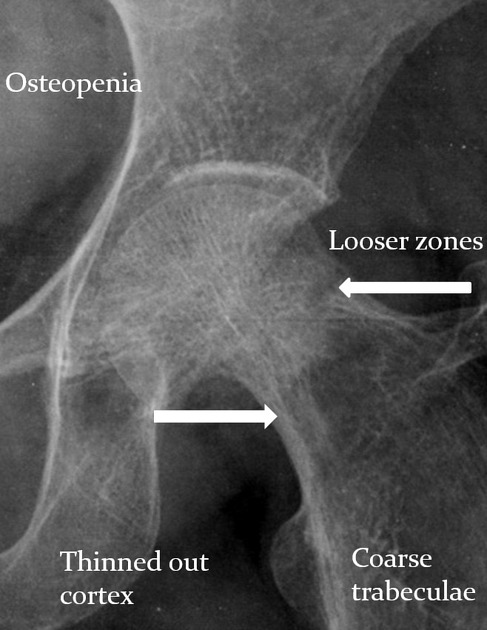
Magnified image of Lt femoral neck
Left femur neck with osteopenia, coarse trabeculations, thinning of cortex with presence of looser zone
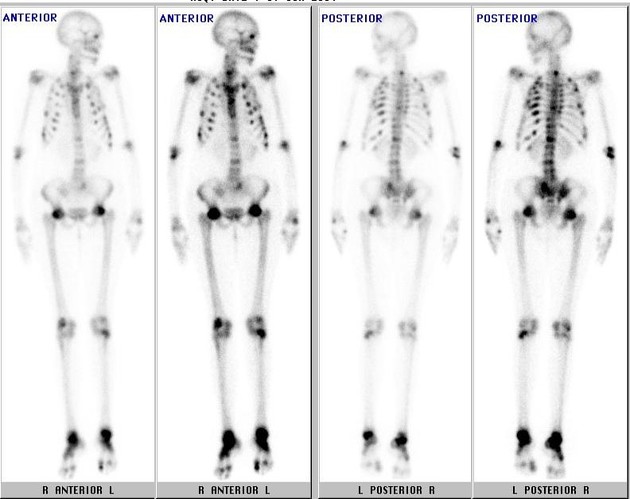
Bone scan demonstrating increased tracer uptake in multiple ribs and vertebral bodies suggestive of multiple fractures.
Increased uptake seen in multiple large joints.
She was also found to have hypophosphatemia. Her serum calcium level was normal.
Summary:
- middle-aged woman
- progressive bone pains with difficulty in walking
- on imaging, severe osteopenia with multiple fractures
- on blood investigations, hypophosphatemia
Provisional diagnosis:
- adult-onset hypophosphatemic osteomalacia
The patient went on to be evaluated to try and ascertain the underlying cause. Workup included vitamin D deficiency/resistance, renal tubular acidosis and malabsorption all of which were negative.
To be evaluated for a paraneoplastic cause and blood pool scintigraphy was done.
Blood pool scintigraphy

Blood pool scintigraphy demonstrating pooling of tracer in the region of right anterior skull base.
CT was done to look for any...

CT was done to look for any obvious anterior skull base abnormality
CT scan did not demonstrate any abnormality in the anterior skull base region.
In addition, nasal endoscopy also did not show any lesion.
The patient was started on phosphate, calcium and vitamin D supplementation and requested to follow up in the outpatient department.
Patient presented after 2...

Patient presented after 2 yr with inability to walk
Fractures involving bilateral femoral necks.
Post bilateral hip replacement

Patient underwent bilateral hip replacement.
She continued supplementation with phosphate and calcium.
Unfortunately, the patient was lost to follow up for 6 years. At presentation, she was now predominantly bed bound with significant bone pain and depressed mood.
She was found to be hypophosphatemic in spite of supplementation.
Blood pool scintigraphy was...

Blood pool scintigraphy was repeated
Compared to the previous 'blood pool scintigraphy' done 8 years ago, the present study demonstrated increased tracer pooling the region of anterior skull base.
MRI scan was done for further evaluation.

















MRI brain shows a well defined lobulated, solid-cystic mass in the left basifrontal region with extension into the olfactory groove. There is surrounding mass effect with midline shift to the right.
Specific findings:
- T2: Well defined lobulated solid cystic mass in the left basifrontal region with extension into the olfactory groove. Surrounding mass effect with midline shift to right.
- FLAIR: Cystic component did not show suppression on FLAIR.
- T1: T1W hyperintense foci within the mass suggestive of internal hemorrhage or fat.
- T1 C+: The solid component of the mass demonstrating intense enhancement with extension into the left upper nasal cavity.
- DWI/ADC: Negative for focal areas of hyperintensities to suggest diffusion restriction.
- SWI: Multiple foci of blooming suggestive of internal hemorrhage.
Case Discussion
At this stage the differentials considered were:
- hemangiopericytoma
- esthesioneuroblastoma
- phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor
The patient underwent left frontal craniotomy and total excision of the left anterior skull base mass.
Histopathology:
phosphaturic mesenchymal tumor, mixed connective tissue type
Discussion:
Oncogenic osteomalacia or tumor induced osteomalacia, is an acquired para-neoplastic syndrome.
Cases typically are diagnosed in 6th decade of life.
Tumors that can lead to this syndrome are classified histologically as:
- phosphaturic mesenchymal tumors with mixed connective tissue (70 -80%)
- osteoblastoma like tumors
- ossifying fibrous like tumors
- nonossifying fibrous like tumors
These tumors are often small in size and difficult to localize. The average time between the onset of symptoms and tumor localization is approximately 7 years.
These tumors often express somatostatin receptors. Therefore, scintigraphy using somatostatin analog can be used for tumor localization.
Cases can also have elevated serum Fibroblast Growth Factor 23 (FGF-23) levels which can be used for diagnosis or to assess disease progression.
FDG-PET scan is increasingly been used for tumor localization.
Treatment:
Tumor resection is the preferred treatment option. Post-surgery, FGF-23 levels fall off drastically. Serum phosphate and 1,25-dihydroxy vitamin D levels return to normal levels within days after tumor resection. Long-term skeletal changes reverse within months.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.