Presentation
Abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting.
Patient Data
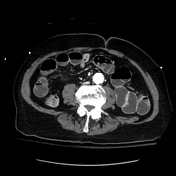

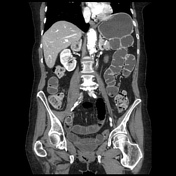

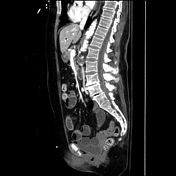


Gallbladder contraction, wall thickening, and a small amount of intraluminal gas. Pneumobilia. A thin fluid channel is seen between gallbladder and duodenum consistent with cholecystoduodenal fistula. Gallstone in distal ileum resulting in small bowel obstruction.
Bilateral adrenal myelolipomas. Atherosclerosis abdominal aorta with aneurysm.
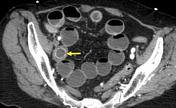

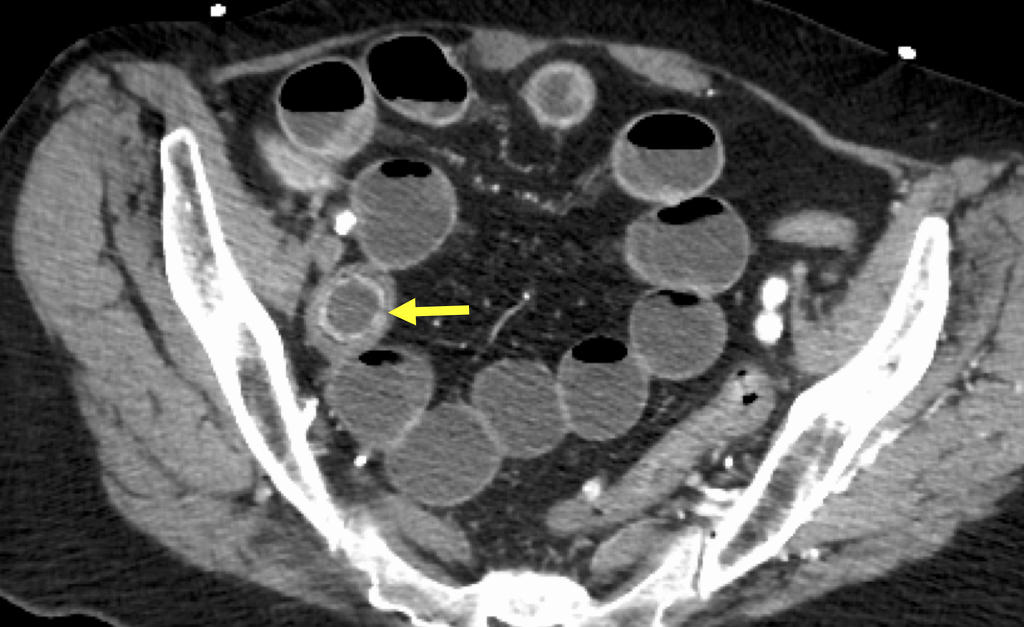
Axial arrow: intraluminal gallstone causing obstruction.
Coronal arrow: cholecytoduodenal fistula.
Case Discussion
Gallstone ileus occurs when a gallstone erodes through the gallbladder into the duodenum, resulting in small bowel obstruction. It is more common in elderly women. It results in Rigler triad i.e. pneumobilia, small bowel obstruction, and ectopic gallstone.
The gallstone can be difficult to see and often blends in with the bowel contents. Therefore, close examination of the gallbladder is required in every distal small bowel obstruction case. Don't be fooled if you are incorrectly given the history of cholecystectomy! The channel between the gallbladder and small bowel is called a cholecystenteric fistula.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.