Presentation
Pulsatile tinnitus
Patient Data






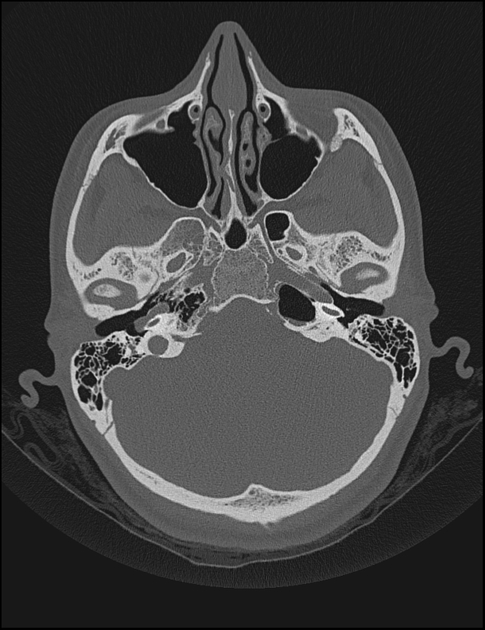
There is an aberrant right ICA, which enters the skull base through an enlarged inferior tympanic canaliculus just in front of the jugular bulb. Then courses anteriorly along the cochlear promontory in a typical fashion to join the petrous ICA. There is a relative narrowing as it turns forward in the tympanic canaliculus. The aberrant ICA bulges up into the hypotympanum and abuts /bulges the inferior eardrum outward. It also abuts the malleus insertion.
There is an associated aberrant stapedius artery which enlarges the anterior portion of the (tympanic) facial canal.

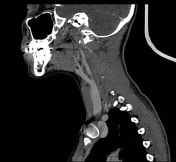


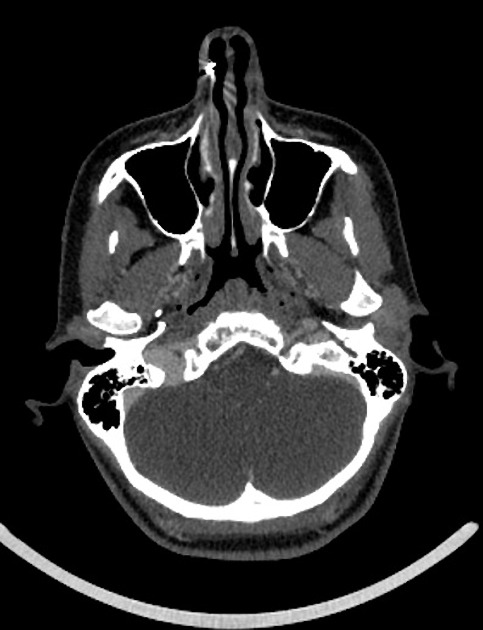
There is an aberrant right ICA, which enters the skull base through an enlarged inferior tympanic canaliculus just in front of the jugular bulb. Then courses anteriorly along the cochlear promontory in a typical fashion to join the petrous ICA. There is a relative narrowing as it turns forward in the tympanic canaliculus. The aberrant ICA bulges up into the hypotympanum and abuts /bulges the inferior eardrum outward. It also abuts the malleus insertion.
There is an associated aberrant stapedius artery which enlarges the anterior portion of the (tympanic) facial canal.
Case Discussion
Aberrant internal carotid arteries are a potential cause for pulsatile tinnitus. It forms due to a collateral pathway that occurs as a result of agenesis of the first embryonic segment of the ICA 1.
Although rare, misdiagnosis can result in severe morbidity and mortality, particularly during otologic procedures.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.