Presentation
Sever left knee pain.
Patient Data
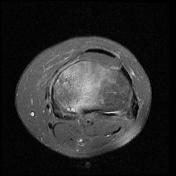



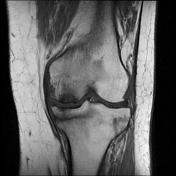

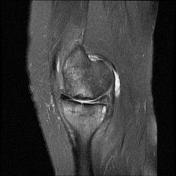

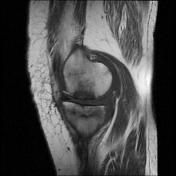

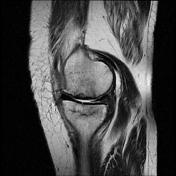

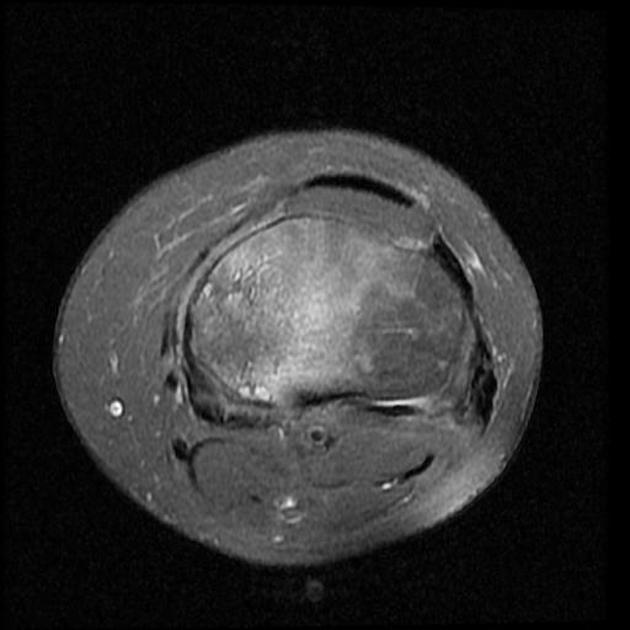
A pattern of bone marrow edema in the tibial plateau particularly medially associated with a horizontal fracture line consistent with an insufficiency fracture. Mild joint effusion. Osteochondral injury measuring about 12*5 mm at the middle weight-bearing of the medial femoral condyle.
Degenerative changes as cartilage thinning and fraying associated with subchondral bone marrow edematous changes at the medial femorotibial compartment. Marginal and patellofemoral osteophyte formation.
Chondromalacia patellae as cartilage loss associated with subchondral cystic changes at the mid to medial facet joints of the patella.
Horizontal tear at the body and posterior horn of the medial meniscus. ACL mucoid degeneration. A Baker cyst measuring about 6*22 mm at the posteromedial aspect of the knee joint.
Case Discussion
Subchondral insufficiency fracture is a type of stress fracture, which is the result of normal stresses on abnormal bone. This diagnosis was achieved based on clinical data and imaging appearances.
These fractures are usually not identified on conventional radiographs. Radionuclide bone scan, and especially MRI are the modalities of choice when assessing this condition.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.