Pulmonary arterial hypertension from chronic thromboembolic disease
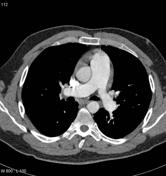

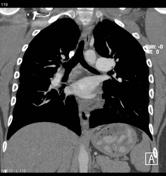

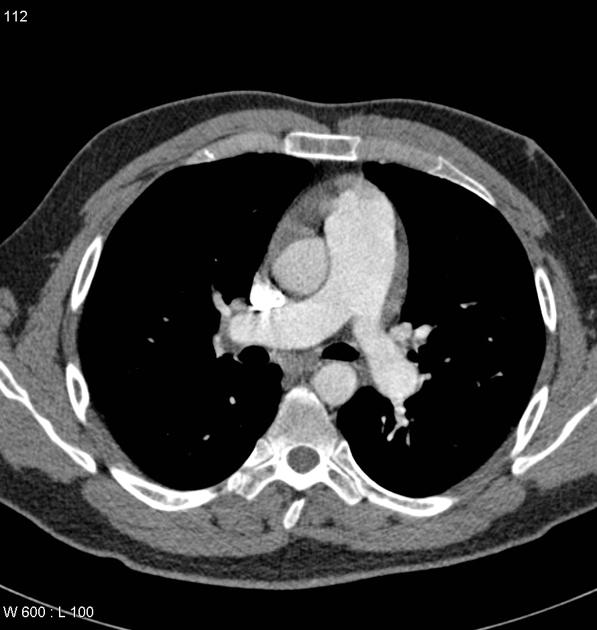
Chronic thromboembolic changes are noted involving both lower lobes (more marked in the right lower lobe with all the basal segments of the right lower lobe pulmonary artery being involved). A web is also noted in the superior segmental artery of the left lower lobe pulmonary artery.
Irregularity of the anterior wall of the proximal interlobar artery is identified which is likely to also represent evidence of eccentric laminated chronic thrombus along the vessel wall.
Evidence of bronchial collateral circulation is identified together with the patient's dilated main pulmonary trunk, which measures 3.4 cm in diameter. Small pericardial effusion is also identified, a finding commonly seen in patients with pulmonary arterial hypertension.
A small subpleural based nodule is noted in the lateral segment of the right middle lobe. This is associated with a focal area of pleural thickening. This appears less marked compared to the previous examination and may be a site of pulmonary infarction related to patient's known thromboembolic disease.




 Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.
Unable to process the form. Check for errors and try again.